- java.lang.Object
-
- ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout
-
- ilog.views.graphlayout.tree.IlvTreeLayout
-
public class IlvTreeLayout extends IlvGraphLayout
The main class for the Tree Layout algorithm.The Tree Layout algorithm places the nodes of a tree starting from the root of the tree to the leaves. If the graph has parts that are disconnected, it arranges each connected component as an individual tree. The Tree Layout algorithm is primarily designed for a forest of pure trees. In a tree, each node except the root has a parent node. All the nodes that have the same parent are called children with respect to the parent and siblings with respect to each other. The Tree Layout algorithm can also be used for non-trees (for example, cyclic graphs). In this case, the layout algorithm ignores those links that violate the tree structure and takes only the spanning tree of the graph into account.
The algorithm has several layout modes:
- The nodes can be arranged freely in a horizontal or vertical way. This is suitable for a graph with a large variation of node sizes.
- The nodes can be arranged in horizontal or vertical levels. This is suitable for a graph that contains nodes of approximately the same size.
- The nodes can be arranged radially on concentric circles or on ellipses around the root of the tree.
- The nodes can be arranged radially around parents like balloons.
Several alignment options are provided. In particular, the free layout mode allows the tip-over alignment, which means that subtrees are arranged serially rather than in parallel. If the subtrees starting at one node are normally arranged horizontally, the tip-over alignment arranges them vertically. The tree layout provides layout modes that automatically adapt the tip-over alignment to best fit the layout to a given aspect ratio.
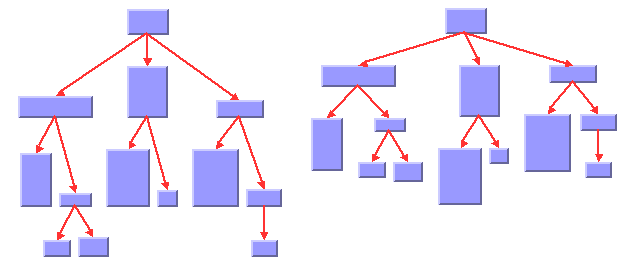
The following sample drawings are produced by the Tree Layout algorithm. The left drawing uses the level layout mode. The flow direction of the links is towards the bottom, and the nodes are south-justified (that is, they are aligned to the bottom) within each level. The right drawing is the same tree in free layout mode (which always uses north level alignment):
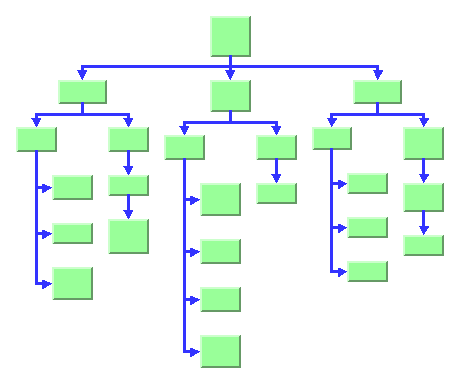
Here is another sample drawing in free layout mode with the tip-over alignment at some leaf nodes:
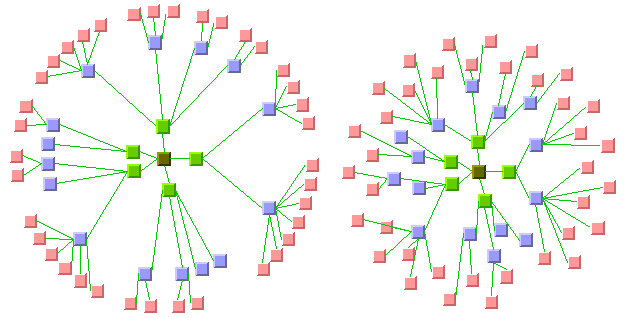
The following are two sample drawings in the two radial layout modes. The normal radial mode in the left drawing places the nodes of the same level on a circle around the root node. The alternating radial mode in the right drawing places the nodes of the same level alternating on two circles around the root node. This results in better usage of the space.
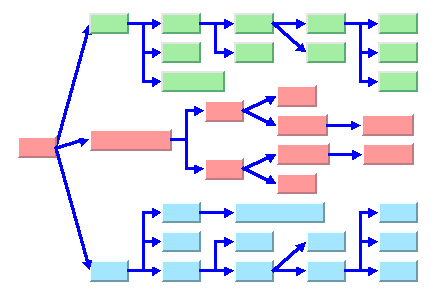
In nonradial layout modes, the Tree Layout algorithm supports different styles of links in the same drawing. The following sample drawing shows orthogonal and straight-line links. It also shows nodes that are aligned to the center (see the red nodes), to the east (green), and to the west (blue) of their children. The drawing was created by the free layout mode with the link flow direction to the right, and so north is to the left.
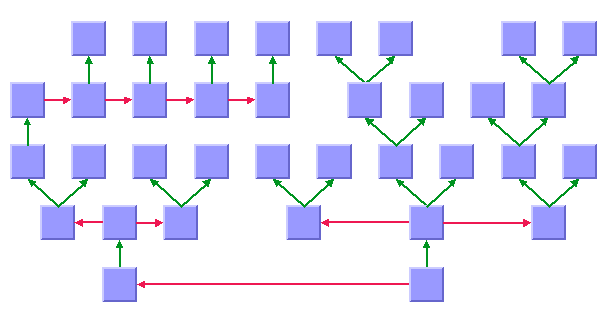
The Tree Layout algorithm supports node neighboring in all modes. The following sample drawing shows a tree layout with the flow direction towards the top. Some nodes are not placed as children but rather as neighbors at the same level as the corresponding parent node. The red links, which are perpendicular to the flow direction, are between nodes that were specified as neighbored.
See the corresponding chapter of the User's Manual for details on the algorithm, the types of graphs for which this algorithm can be used, the features and limitations, code samples, and so on.
Note the following points:
- If no root node is specified, the layout algorithm takes the direction of links into account to calculate a root node. Other than that, the direction of links does not affect the layout.
- The layout algorithm has an incremental mode that is designed to be stable when incremental changes are made. If nodes are added or removed after a layout, the next layout uses a heuristic to try to adjust the layout only minimally and to avoid major structural reorganization.
- In incremental mode, the initial position of the nodes (at the moment you start the layout) affects the resulting layout because the algorithm tries to preserve the relative order of the children on incremental changes.
CSS example:
SDM {
GraphLayout : true;
}
GraphLayout {
graphLayout : @#layout;
// optional settings for the graph layout renderer
}
Subobject#layout {
class : "ilog.views.graphlayout.tree.IlvTreeLayout";
allLevelsAlternating : "false";
allowedTime : "3";
aspectRatio : "3.0";
associateOffset : "3.0";
balloonAngleSpacing : "REGULAR";
balloonInnerChildrenAngle : "2";
balloonLeafChildrenAngle : "2";
balloonRadiusMode : "VARIABLE_RADIUS";
balloonRootChildrenAngle : "2";
balloonStartAngle : "2";
branchOffset : "3.0";
categorizingLinks : "false";
categorizingLinksWithoutLayout : "false";
connectorStyle : "CENTERED_PINS";
coordinatesMode : "MANAGER_COORDINATES";
firstCircleEvenlySpacing : "false";
flowDirection : "Left";
globalAlignment : "MIXED";
globalLinkStyle : "MIXED_STYLE";
incrementalMode : "false";
intergraphConnectivityMode : "false";
invisibleRootUsed : "false";
layoutMode : "FREE";
layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled : "false";
levelAlignment : "NORTH";
maxChildrenAngle : "2";
minBusyTime : "3";
nonTreeLinksStraight : "false";
numberOfAlternatingCircles : "2";
orthForkPercentage : "3.0";
overlapPercentage : "3.0";
parentChildAssociateOffset : "3.0";
parentChildOffset : "3.0";
position : "10,10";
recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed : "false";
recursiveLeafLayoutMode : "false";
respectNodeSizes : "false";
rootPosition : "false";
siblingOffset : "3.0";
tipOverBranchOffset : "3.0";
}
link.tag {
LinkStyle : "ORTHOGONAL_STYLE";
}
node.tag {
Alignment : "CENTER";
ChildAlignment : "UNSPECIFED";
EastSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
NorthSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
RootPreference : "2";
SouthSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
WestSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
}
CSS specification of per-node and per-link layout parameters:The following table lists the per-object rendering properties of the
GraphLayoutrenderer:PropertyTypeDefaultDescriptionGraphLayoutIlvGraphLayoutnullLets you define a different graph layout algorithm for each subgraph. If one is not specified, the same algorithm is applied recursively to all subgraphs.LayoutFixedStringfalseDeprecated, replaced by Fixed.FixedStringfalseLets you specify that the node or link must not be moved or reshaped by the layout algorithm.LayoutGroupStringnullLets you apply the algorithm to different groups of objects, one group after the other.LayoutIgnoredbooleanfalseIftrue, the object is ignored by the layout.The per-node and per-link layout parameters are specified in the style sheet through the CSS rules for nodes and links, not through the CSS rule for graph layout. For instance:
link.tag {
LinkStyle : "ORTHOGONAL_STYLE";
}
Note that the names of the node and link layout parameters use an initial capital, unlike the regular properties. See also the documentation of the class IlvGraphLayoutRenderer.
-
-
Property Summary
Properties Modifier and Type Property and Description intAlignment
Sets the alignment option of an individual node.booleanallLevelsAlternating
Sets whether at all levels, nodes are forced into alternating circular layers.longallowedTime
Sets the upper limit for the duration of the layout algorithm.doubleaspectRatio
Sets the aspect ratio for the layout.doubleassociateOffset
Sets the minimum offset between associates and the orthogonal link segment starting at the parent.intballoonAngleSpacing
Sets the current angle spacing for balloon layout mode.intballoonInnerChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children of inner nodes in balloon mode.intballoonLeafChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children of nodes that have only leaves as children in balloon mode.intballoonRadiusMode
Sets the current radius mode for balloon layout mode.intballoonRootChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children of the root node in balloon mode.intballoonStartAngle
Sets the start angle of the layout in balloon mode.doublebranchOffset
Sets the minimum offset between neighbor nodes that belong to different branches in the tree.booleancategorizingLinks
Sets whether the layout algorithm stores the categorization of links into forward, backward, and non-tree links.booleancategorizingLinksWithoutLayout
Sets whether the layout algorithm does not really perform a full layout.intChildAlignment
Sets the child alignment option of the node.java.lang.Stringclass
Default constructor.intconnectorStyle
Sets the style of the connectors.intcoordinatesMode
Sets the coordinates mode to be used during layout.doubleEastSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the east side of the subtree starting at the input node.booleanfirstCircleEvenlySpacing
Sets whether the nodes on the first circle must be evenly spaced in radial mode.intflowDirection
Sets the direction of the flow.intglobalAlignment
Sets the global alignment option.intglobalLinkStyle
Sets the global style of the shapes of links.booleanincrementalMode
Sets the incremental mode.booleanintergraphConnectivityMode
Sets whether the intergraph link connectivity is considered for the partitioning of the layout into subtrees.booleaninvisibleRootUsed
Sets whether an invisible root is used to combine components that are disconnected from each other.intlayoutMode
Sets the layout mode.booleanlayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled
Sets whether the generic connected component layout mechanism is enabled.intlevelAlignment
Sets the alignment within the levels.intLinkStyle
Sets the style of the shape of an individual link.intmaxChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children that are placed in radial mode.longminBusyTime
Sets the minimal time that the layout algorithm can be busy.booleannonTreeLinksStraight
Sets whether all non-tree links that don't have the no-reshape link style and that are not fixed and are not incident to fixed nodes are reshaped to be straight.doubleNorthSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the north side of the subtree starting at the input node.intnumberOfAlternatingCircles
Sets the number of alternating circles.doubleorthForkPercentage
Sets the percentage of the parent-child offset that determines the location where the orthogonal link routing places the bends in order to fork the routing towards the children.doubleoverlapPercentage
Sets the percentage for which a node is considered smaller in the flow direction.doubleparentChildAssociateOffset
Sets the minimum offset between the parent and the first associate.doubleparentChildOffset
Sets the minimum offset between a parent and its children.ilog.views.IlvPointposition
Sets the position of the layout.booleanrecursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed
Sets whether the layout instance of the ancestor graph is in principle allowed to treat this subgraph in a recursive layout.booleanrecursiveLeafLayoutMode
Sets whether the recursive layout of nested subgraphs in leaves of the tree is enabled.booleanrespectNodeSizes
Sets whether the algorithm must try to respect the size of the nodes.booleanrootPosition
Sets the meaning of the specified position.intRootPreference
Specifies the preference of the node to become root node.doublesiblingOffset
Sets the minimum offset between siblings, that is, between nodes that have the same parent in the tree structure.doubleSouthSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the south side of the subtree starting at the input node.doubletipOverBranchOffset
Sets the minimum offset in the flow direction between neighbor nodes that belong to different branches in the tree.doubleWestSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the west side of the subtree starting at the input node.
-
-
-
Property Detail
-
class
public java.lang.String class
Default constructor.
CSS example:class : "ilog.views.graphlayout.tree.IlvTreeLayout";
-
Alignment
public int Alignment
Sets the alignment option of an individual node. This alignment option is used only if the global alignment is set to#MIXED. Otherwise, all nodes have the alignment that is specified as the global alignment. This option has no effect in balloon layout mode.Valid values are:
-
#CENTER- the node is centered with respect to the centers of its child nodes. -
#BORDER_CENTER- the node is centered with respect to the border of its child nodes. -
#EAST- the node is aligned to the border of its easternmost child node. -
#WEST- the node is aligned to the border of its westernmost child node. -
#TIP_OVER_EAST- a parent is outside the border of the child nodes, and the child nodes are placed sequentially instead of in parallel on the east side of the parent. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes. -
#TIP_OVER_WEST- a parent is outside the border of the child nodes, and the child nodes are placed sequentially instead of in parallel on the west side of the parent. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes. -
#TIP_OVER_EAST_WEST- similar to#TIP_OVER_EASTor#TIP_OVER_WEST, but the child nodes are arranged on both sides of the link segment that starts at the parent node. The first child is placed on the east side. Further child nodes are placed on the east or west side, so that the space used on both sides is roughly the same, that is, the subtrees on the east side have roughly the same sum of heights as the subtrees on the west side. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes. -
#TIP_OVER_BOTH_SIDES- similar to#TIP_OVER_EASTor#TIP_OVER_WEST, but the child nodes are arranged in pairs on both sides of the link segment that starts at the parent node. Unlike the behavior with#TIP_OVER_EAST_WEST, the algorithm does not try to optimize the space used on both sides but always puts the odd-numbered child nodes to the west and the even-numbered child nodes to the east, and the pairs of child nodes, one on the east side and one on the west side, are aligned with one another. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes.
The default value is
#CENTER.
CSS example:Alignment : "CENTER";
Allowed values: CENTERBORDER_CENTEREASTWESTTIP_OVERTip over (east) TIP_OVER_WESTTip over (west) TIP_OVER_EAST_WESTTip over (east and west) TIP_OVER_BOTH_SIDES
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
- See Also:
globalAlignment
-
-
allLevelsAlternating
public boolean allLevelsAlternating
Sets whether at all levels, nodes are forced into alternating circular layers.This option has only an effect in layout mode
#ALTERNATING_RADIAL. Alternating placement means that the nodes of one level are placed alternating in several (normally 2) circular layers. Nonalternating placement means that the nodes of one level are placed in one circular layer. Normally, the layout analyses which levels must use the alternating placement in order to optimize space. If the alternating placement of a level does not improve the space usage, the nonalternating placement is used for the level even in alternating radial layout mode.This option allows to change this behavior: if the option is enabled, all levels use the alternating placement even if the alternating placement uses more space than the nonalternating placement. The option is ignored if the number of alternating circles is set to 0, because in that more, the number of alternating circles is automatically determined from the space usage.
The option is disabled by default.
CSS example:allLevelsAlternating : "false";
-
allowedTime
public long allowedTime
Sets the upper limit for the duration of the layout algorithm.When an iterative layout algorithm is used, the iterations can be stopped when this time is exceeded. Noniterative algorithms can also use this parameter as an upper limit for the computation time. The default value is normally
32000(32 seconds). Subclasses that support this feature can use a different default value depending on their particular behavior. Layout algorithms that are stopped in this way set the result code of the layout report either toIlvGraphLayoutReport#STOPPED_AND_VALIDor toIlvGraphLayoutReport#STOPPED_AND_INVALID.When the connected components of disconnected graphs are laid out separately (see
#supportsLayoutOfConnectedComponents()), the specified allowed time is considered as the total time for the layout of all the connected components plus the time for the connected components layout.Note that the layout algorithm may not obey exactly the allowed time specification.
Note for implementers of layout algorithms: the method
#performLayout(boolean, boolean, boolean)does NOT automatically stop the layout when the allowed time is exceeded. It is the sole responsibility of the implementation of the method#layout(boolean)to do this.A
RuntimeExceptionis thrown if the layout does not support this mechanism.
CSS example:allowedTime : "3";
-
aspectRatio
public double aspectRatio
Sets the aspect ratio for the layout. This is the ratiowidth / heightof the desired layout region.The effect of the aspect ratio depends on the layout mode:
- In layout modes
#RADIALand#ALTERNATING_RADIAL, the nodes are placed in circular layers if the aspect ratio is1. Otherwise, they are placed in elliptical layers. - In layout modes
#BALLOON, the nodes are placed in circular balloons if the aspect ratio is1. Otherwise, they are placed in elliptical ballons. - In layout modes
#TIP_OVER,#TIP_ROOTS_OVER,#TIP_LEAVES_OVER, and#TIP_ROOTS_AND_LEAVES_OVER, the nodes are placed as in in free mode, but local tip-over alignments are automatically added to better fit the layout to the aspect ratio. - The aspect ratio has no effect in other layout modes.
CSS example:aspectRatio : "3.0"; - In layout modes
-
associateOffset
public double associateOffset
Sets the minimum offset between associates and the orthogonal link segment starting at the parent. This offset is used if a parent has associate nodes. This method has no effect if the layout mode is radial or if no associates occur.If the flow direction is toward the top or bottom, the orthogonal link segment starting at the parent is vertical, and the associates are placed left or right of this link segment. Hence it is a horizontal offset. If the flow direction is toward the left or right, the orthogonal link segment starting at the parent is horizontal, and the associates are placed above or below this link segment. Hence it is a vertical offset.
If the Respect node sizes option is enabled, this is the minimum offset between node borders; otherwise, it is the minimum offset between node centers.
The default value is
30.
CSS example:associateOffset : "3.0";
-
balloonAngleSpacing
public int balloonAngleSpacing
Sets the current angle spacing for balloon layout mode. This setting has only an effect when the layout mode is#BALLOON. Valid values are:-
#REGULAR- the available angle range at a node is evenly split so that each subtrees balloon at the node can occupy the same angle. -
#FAST_PROPORTIONAL- the available angle range at a node is proportonally split so that larger subtrees balloons at the node can occupy larger angles. The algorithm uses a fast heuristic to calculate the angle ranges. This heuristic is not very precise. -
#PROPORTIONAL- the available angle range at a node is proportonally split so that larger subtrees balloons at the node can occupy larger angles. The algorithm uses a slower heuristic to calculate the angle ranges. This heuristic is more precise than the fast heuristic.
The default value is
#PROPORTIONAL.
CSS example:balloonAngleSpacing : "REGULAR";
Allowed values: REGULARFAST_PROPORTIONALProportional (fast) PROPORTIONALProportional (slow) - See Also:
layoutMode
-
-
balloonInnerChildrenAngle
public int balloonInnerChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children of inner nodes in balloon mode. This is the maximum angle between the two rays from the parent to its two outermost children. If the angle is 360 degree, outermost children do not really esist as the children cover the entire circle around the node. The angle must be between 1 and 360 degrees.The default value is 360.
This is an expert option. It has no effect in layout modes other than balloon.
CSS example:balloonInnerChildrenAngle : "2";
-
balloonLeafChildrenAngle
public int balloonLeafChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children of nodes that have only leaves as children in balloon mode. Basically, it is the maximum angle for the leaf balloons. This is the maximum angle between the two rays from the parent to its two outermost children. If the angle is 360 degree, outermost children do not really esist as the children cover the entire circle around the node. The angle must be between 1 and 360 degrees.The default value is 360.
This is an expert option. It has no effect in layout modes other than balloon.
CSS example:balloonLeafChildrenAngle : "2";
-
balloonRadiusMode
public int balloonRadiusMode
Sets the current radius mode for balloon layout mode. This setting has only an effect when the layout mode is#BALLOON. Valid values are:-
#VARIABLE_RADIUS- the radius of different child balloons at the same parent node can vary. -
#OPTIMIZED_VARIABLE_RADIUS- the radius of different child balloons at the same parent node can vary. An additional optimization heuristic reduces the radius. This has the advantage of smaller space requirements but looses symmetries in the diagram. -
#UNIFORM_LEAVES_RADIUS- the radiuses of all leaves that are children of the same node are uniform. The radius of balloons that contain more than one node can still vary. Use this mode if symmetries of the layout are important. -
#OPTIMIZED_UNIFORM_LEAVES_RADIUS- the radiuses of all leaves that are children of the same node are uniform. The radius of balloons that contain more than one node can still vary. An additional optimization heuristic reduces the radius. This has the advantage of smaller space requirements but looses symmetries in the diagram. -
#UNIFORM_RADIUS- the radiuses of all subtree balloons that are children of the same node are uniform. This mode requires the most area but also shows the most symmetries in the layout.
The default value is
#OPTIMIZED_UNIFORM_LEAVES_RADIUS.
CSS example:balloonRadiusMode : "VARIABLE_RADIUS";
Allowed values: VARIABLE_RADIUSVariable OPTIMIZED_VARIABLE_RADIUSVariable optimized UNIFORM_LEAVES_RADIUSUniform for leaves OPTIMIZED_UNIFORM_LEAVES_RADIUSUniform for leaves optimized UNIFORM_RADIUSUniform - See Also:
layoutMode
-
-
balloonRootChildrenAngle
public int balloonRootChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children of the root node in balloon mode. This is the maximum angle between the two rays from the parent to its two outermost children. If the angle is 360 degree, outermost children do not really esist as the children cover the entire circle around the root. The angle must be between 1 and 360 degrees.The default value is 360.
This is an expert option. It has no effect in layout modes other than balloon.
CSS example:balloonRootChildrenAngle : "2";
-
balloonStartAngle
public int balloonStartAngle
Sets the start angle of the layout in balloon mode. The angle must be between 0 and 360 degrees.The default value is 0.
The angle orientation is clockwise for flow direction left and top and counter clockwise for flow direction right and bottom. The start angle 0 is always towards the right.
This is an expert option. It has no effect in layout modes other than balloon.
CSS example:balloonStartAngle : "2";
-
branchOffset
public double branchOffset
Sets the minimum offset between neighbor nodes that belong to different branches in the tree. This is the offset between neighbor nodes that are not siblings. The offset is in the opposite direction of the link flow.If the flow direction is towards the top or bottom and the layout mode is not radial or balloon, this is a horizontal offset. If the flow direction is towards the left or right and the layout mode is not radial or balloon, this is a vertical offset. If the layout mode is radial, this is an offset tangential to the circles or ellipses.
If the layout mode is balloon, this is the minimal offset between nodes in all directions. The balloon mode does not distinguish between siblings and branches, hence the branch offset is used for all nodes.
If the respect node sizes option is enabled, this is the minimum offset between node borders; otherwise, it is the minimum offset between node centers.
The default value is
40.
CSS example:branchOffset : "3.0";
- See Also:
flowDirection
-
categorizingLinks
public boolean categorizingLinks
Sets whether the layout algorithm stores the categorization of links into forward, backward, and non-tree links. Iftrue, the next run of the layout algorithm makes the link categorization available through the methods#getCalcForwardTreeLinks(),#getCalcBackwardTreeLinks(), and#getCalcNonTreeLinks(). Iffalse, the link categorization is not made available. This saves memory and is faster. In this case, the methods#getCalcForwardTreeLinks(),#getCalcBackwardTreeLinks(), and#getCalcNonTreeLinks()will return empty enumerations.Note that only normal links can be categorized. Intergraph links are never categorized, even if
#setIntergraphConnectivityMode(boolean)is set totrue.The default value is
false.
CSS example:categorizingLinks : "false";
-
categorizingLinksWithoutLayout
public boolean categorizingLinksWithoutLayout
Sets whether the layout algorithm does not really perform a full layout. It only calculates a spanning tree but does not move nodes or links. If categorizing links is additionally enabled, it stores the calculated root nodes and the categorization of links into forward, backward, and non-tree links. Since intergraph links are never categorized, this works only in nonrecursive mode.Note that a run of the layout is necessary to make the categorization available. Otherwise, the methods
#getCalcForwardTreeLinks(),#getCalcBackwardTreeLinks(), and#getCalcNonTreeLinks()return empty enumerations if there was no run of the layout.The default value is
false.
CSS example:categorizingLinksWithoutLayout : "false";
- See Also:
categorizingLinks,recursiveLeafLayoutMode
-
ChildAlignment
public int ChildAlignment
Sets the child alignment option of the node. This child alignment option is used to specify exceptional alignments for the child that differ from the alignment specified at the parent for all child nodes. This method always overwrites the aligment specified using#setAlignment(Object, int)and#setGlobalAlignment(int)at the parent. Child alignments only take effect in free and level mode but not in radial or balloon mode, and only if the child node is not a root node of a tree.Valid values are:
-
#UNSPECIFIED- no exceptional alignment is specified for this child node. -
#EAST_NEIGHBOR- the child node is made a neighbor on the east side of its parent node. -
#WEST_NEIGHBOR- the child node is made a neighbor on the west side of its parent node. -
#TIP_OVER_ASSOCIATE_BOTH_SIDES- the child is laid out like an associate node of its parent node. Associate nodes occur alternating on the east and west sides of their parent node. -
#TIP_OVER_ASSOCIATE_EAST- the child is laid out like an associate node of its parent node. This associate nodes occurs on the east side of its parent node. -
#TIP_OVER_ASSOCIATE_WEST- the child is laid out like an associate node of its parent node. This associate nodes occurs on the west side of its parent node.
The default value is
#UNSPECIFIED.
CSS example:ChildAlignment : "UNSPECIFED";
Allowed values: UNSPECIFEDUnspecified EAST_NEIGHBORWEST_NEIGHBORTIP_OVER_ASSOCIATE_BOTH_SIDESTip over associate (east and west) TIP_OVER_ASSOCIATE_EASTTip over associate (east) TIP_OVER_ASSOCIATE_WESTTip over associate (west)
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
- See Also:
globalAlignment
-
-
connectorStyle
public int connectorStyle
Sets the style of the connectors.Valid values are:
-
#CENTERED_PINS- the link connector pins are placed in the center of the border of the node bounding box to which the link is attached. -
#CLIPPED_PINS- each link pointing to the center of the node is clipped at the bounding box of the node. This style affects straight links; it behaves like centered connector pins for orthogonal links. -
#EVENLY_SPACED_PINS- the link connector pins are evenly spaced along the border of the node bounding box. -
#AUTOMATIC_PINS- the connector style is selected depending on the link style.
The default value is
#AUTOMATIC_PINS.The connector style is ignored in the radial layout modes because clipped pins are always used in this case . The placement of connector pins also depends on the link clip interface and the connection box interface, in the following way:
- First, the bounding box of an end node is obtained. If a link
connection box interface was set via
IlvGraphLayout#setLinkConnectionBoxInterface(IlvLinkConnectionBoxInterface), the bounding box and offsets are delivered by that interface. Otherwise, the node bounding box delivered by the graph model (seeIlvGraphModel#boundingBox(Object)) is used. - Next, the initial connector pin of the link is placed at this bounding box in the manner specified by the connector style.
- Finally, if a link clip interface was set via
setLinkClipInterface
Note that when the graph attached to the layout is of type
IlvGrapher, the effect of the connector style depends on the type of the connectors installed at the node. We recommend using link connectors of typeIlvFreeLinkConnector. Other connector types may cause anIlvInappropriateLinkExceptionduring layout. You can use the methodIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinkConnectorsIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinks
CSS example:connectorStyle : "CENTERED_PINS";
Allowed values: CENTERED_PINSCLIPPED_PINSEVENLY_SPACED_PINSAUTOMATIC_PINS -
-
coordinatesMode
public int coordinatesMode
Sets the coordinates mode to be used during layout.Valid values are:
-
ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout#MANAGER_COORDINATES- The geometry of the graph is computed using the coordinate space of the manager (that is, the attachedIlvGrapher) without applying any transformation.This mode should be used if you visualize the graph at zoom level 1, or you do not visualize it at all, or the graph contains only fully zoomable objects. In all these cases there is no need to take the transformer into account during the layout.
Note that in this mode the dimensional parameters of the layout algorithms are considered as being specified in manager coordinates.
-
ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout#VIEW_COORDINATES- The geometry of the graph is computed in the coordinate space of the manager view. More exactly, all the coordinates are transformed using the current reference transformer.This mode should be used if you want the dimensional parameters of the layout algorithms to be considered as being specified in manager view coordinates.
-
ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout#INVERSE_VIEW_COORDINATES- The geometry of the graph is computed using the coordinate space of the manager view and then applying the inverse transformation. This mode is equivalent to the "manager coordinates" mode if the geometry of the graphic objects strictly obeys the transformer. (A small difference may exist because of the limited precision of the computations.)On the contrary, if some graphic objects are either nonzoomable (see
IlvGraphic#zoomable) or semizoomable (for example, links with a maximum line width), this mode gives different results than the manager coordinates mode. These results are optimal if the graph is visualized using the same transformer as the one taken into account during the layout.Note that in this mode the dimensional parameters of the layout algorithms are considered as being specified in manager coordinates.
The default value is
IlvGraphLayout#INVERSE_VIEW_COORDINATES.This option is useful only if the attached graph model is an
IlvGrapherAdapter(or a subclass). Otherwise, it has no effect. Note: the coordinates mode of the layout is used only while this layout is running. If layout is not running, operations on the grapher adapter use the coordinates mode that was set on the grapher adapter directly (seeIlvGrapherAdapter#setCoordinatesMode).
CSS example:coordinatesMode : "MANAGER_COORDINATES";
Allowed values: MANAGER_COORDINATESVIEW_COORDINATESINVERSE_VIEW_COORDINATES -
-
EastSubtreeBlockMargin
public double EastSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the east side of the subtree starting at the input node. If the value is set to a positive number, the subtree starting at this node is considered a rectangular block, and other nodes not belonging to this subtree are moved at least the specified margin away from this block. Specifying subtree block margins is useful if you plan to draw a rectangle around the subtree, since it ensures that unrelated nodes do not extend into the rectangle.The default value is -1, which means no margin.
CSS example:EastSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
firstCircleEvenlySpacing
public boolean firstCircleEvenlySpacing
Sets whether the nodes on the first circle must be evenly spaced in radial mode.By default, all nodes are placed as close as possible according to the offset parameters. In radial mode, this may cause the first circle to be only partially filled (that is, all nodes are placed close together at one part of the circle and there is a larger gap in another part of the circle).
To avoid this effect, you can enable the evenly spacing of the first circle. In this case, the children of the root node are placed such that their centers are approximately evenly spaced on the first circle, filling the entire circle. This may, however, cause the final result to waste much more space on the other circles.
It is disabled by default.
This is an expert option. It has no effect in layout modes other than radial. If there is east-west neighboring of the nodes in the first circle, these neighbors will not be equally spaced.
CSS example:firstCircleEvenlySpacing : "false";
-
flowDirection
public int flowDirection
Sets the direction of the flow. Valid values are:-
IlvDirection#Right- the root is on the left and the links flow to the right. -
IlvDirection#Left- the root is on the right and the links flow to the left. -
IlvDirection#Bottom- the root is at the top and the links flow to the bottom. -
IlvDirection#Top- the root is at the bottom and the links flow to the top.
Note that except for the radial layout modes, the compass direction
#SOUTHis identical to the flow direction.In the radial layout modes, all links flow radially from the center of the root outward. If connected component processing is disabled, the flow direction affects only the arrangement of disconnected trees in the radial modes.
The default value is
IlvDirection#Right.
CSS example:flowDirection : "Left";
Allowed values: LeftRightTopBottom -
-
globalAlignment
public int globalAlignment
Sets the global alignment option. This option has no effect in balloon layout mode. Valid values are:-
#CENTER- a parent is centered above its child nodes, taking the center of the child nodes into account. -
#BORDER_CENTER- a parent is centered above its child nodes, taking the border of the child nodes into account. This differs from the alignment#CENTERif the Respect node sizes option is enabled. -
#EAST- a parent is aligned to the border of its easternmost child node. -
#WEST- a parent is aligned to the border of its westernmost child node. -
#TIP_OVER_EAST- a parent is outside the border of the child nodes, and the child nodes are placed sequentially instead of in parallel. The child nodes are on the east side of the parent. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes. -
#TIP_OVER_WEST- a parent is outside the border of the child nodes, and the child nodes are placed sequentially instead of in parallel. The child nodes are on the west side of the parent. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes. -
#TIP_OVER_EAST_WEST- similar to#TIP_OVER_EASTor#TIP_OVER_WEST, but the child nodes are arranged on both sides of the link segment that starts at the parent node. The first child node is placed on the east side. Further child nodes are placed on the east or west side, so that the space used on both sides is roughly the same, that is, the subtrees on the east side have roughly the same sum of heights as the subtrees on the west side. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes. -
#TIP_OVER_BOTH_SIDES- similar to#TIP_OVER_EASTor#TIP_OVER_WEST, but the child nodes are arranged in pairs on both sides of the link segment that starts at the parent node. Unlike#TIP_OVER_EAST_WEST, this style does not try to optimize the space used on both sides but always puts the odd-numbered child nodes to the west and the even-numbered child nodes to the east. The pairs of child nodes, one on the east side and one on the west side, are aligned with one another. This alignment option is not possible in the radial or level layout modes. -
#MIXED- each node can have a different alignment option. The alignment of each individual node can be set by the method#setAlignment(Object, int)so that different alignments can occur in the same graph.
The default value is
#CENTER.
CSS example:globalAlignment : "MIXED";
Allowed values: MIXEDCENTERBORDER_CENTEREASTWESTTIP_OVERTip over (east) TIP_OVER_WESTTip over (west) TIP_OVER_EAST_WESTTip over (east and west) TIP_OVER_BOTH_SIDES -
-
globalLinkStyle
public int globalLinkStyle
Sets the global style of the shapes of links. Valid values are:-
#ORTHOGONAL_STYLE- all links have an orthogonal shape, that is, a shape consisting of a sequence of orthogonal line segments. This option is not available for the radial layout modes. -
#STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE- all links have a straight-line shape. -
#NO_RESHAPE_STYLE- no reshape is performed on any link. -
#MIXED_STYLE- each link can have a different link style. The style of each individual link can be set by the method#setLinkStyle(Object, int)so that different link shapes can occur in the same graph.
Unless the global link style is
#MIXED_STYLE, all links have the same shape style.The default value is
#STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE.Note that when the graph attached to the layout is of type
IlvGrapher, the effect of the link reshaping depends on the type of the links and the connectors installed at the node. For all link styles, we recommend using links of typeIlvPolylineLinkImage. For the orthogonal link style, we additionally recommend using link connectors of typeIlvFreeLinkConnector. Other link or connector types may cause anIlvInappropriateLinkExceptionduring layout. You can use the methodIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinkTypesIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinkConnectorsIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinks
CSS example:globalLinkStyle : "MIXED_STYLE";
Allowed values: MIXED_STYLEMixed links ORTHOGONAL_STYLEOrthogonal links STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLEStraight-line links NO_RESHAPE_STYLENo link reshape -
-
incrementalMode
public boolean incrementalMode
Sets the incremental mode.If the incremental mode is enabled, the algorithm tries to preserve the relative order of the children on incremental changes, unless a node comparator is specified. The logical order of children of nodes in the tree is calculated from their coordinates. In this case, the layout is stable when incremental changes are made. If nodes are added or removed after a layout, the next layout uses a heuristic to try to adjust the layout only minimally and to avoid major structural reorganization.
If the incremental mode is disabled, the algorithm calculates the logical order of children of nodes in the tree by using the order in which nodes are returned by
IlvGraphModel#getNodes().If a node comparator is specified, the algorithm calculate the logical order of children of nodes in the tree from the node comparator, independent from whether the incremental mode is enabled or disabled.
The incremental mode is enabled by default.
CSS example:incrementalMode : "false";
-
intergraphConnectivityMode
public boolean intergraphConnectivityMode
Sets whether the intergraph link connectivity is considered for the partitioning of the layout into subtrees. This affects nodes that represent subgraphs and that are only connected to other nodes by intergraph links (i.e. there are no normal intragraph links between the node and other nodes). If the option is disabled, these nodes are considered disconnected and are placed like disconnected nodes. If the option is enabled, the nodes are considered connected and arranged inside the tree structure (for instance as parent and child).Note that this option has no effect if the generic disconnected node placement is enabled (see
#setLayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled(boolean)).Even if this option is enabled, the Tree Layout algorithm does not route intergraph links. They should be routed by applying a Link Layout after the Tree Layout.
CSS example:intergraphConnectivityMode : "false";
-
invisibleRootUsed
public boolean invisibleRootUsed
Sets whether an invisible root is used to combine components that are disconnected from each other. The roots that are specified by#setRoot(Object)or#setRootPreference(Object, int)are the roots of each individual component. If an invisible root is used, all roots of each individual component are added as children to an invisible dummy node and the layout is performed on the resulting connected graph. By doing this, the components are arranged in the same global structure. In particular, this is useful for the radial layout modes to fit all components into the same global circular layer structure instead of generating an individual circular layer structure for each component.Note that the layout is no longer stable on incremental changes if an invisible root is used. The layout heuristic cannot preserve the relative order of the components in this case. This means that the order of the components may change in subsequent layouts, and hence the next layout may look very different from the previous layout.
The default value is
false.
CSS example:invisibleRootUsed : "false";
-
layoutMode
public int layoutMode
Sets the layout mode. Valid values are:-
#FREE- all links flow roughly in the flow direction. Nodes of different tree branches (that is, nodes with a different parent node) are not justified to each other; therefore, the level alignment parameter is ignored. Tip-over alignment is possible if specified as alignment. All link styles are possible. The aspect ratio is ignored. -
#LEVEL- all links flow roughly in the flow direction. Nodes are organized in levels and are justified to their borders or centered according to the level alignment parameter. Tip-over alignment is not possible, but all link styles are possible. The aspect ratio is ignored. -
#TIP_OVER- similar to the mode#FREE. However, in mode#TIP_OVER, the algorithm tries to optimize the layout to automatically fit best to the specified aspect ratio. Using a fast heuristic, it chooses the local alignment#TIP_OVER_EASTfor some nodes but keeps the alignment of all other nodes as specified. This heuristic is a fast compromise between the modes#TIP_LEAVES_OVER,#TIP_ROOTS_OVER, and#TIP_ROOTS_AND_LEAVES_OVER. -
#TIP_LEAVES_OVER- similar to the mode#TIP_OVER. The algorithm tries to optimize the layout to automatically fit best to the specified aspect ratio. This slow heuristic tries to tip over beginning with the leaves and then chooses the best layout. It checks the alignment mode#TIP_OVER_EAST, but not#TIP_OVER_BOTH_SIDESor other variants. It keeps the alignment of all nodes close to the root as specified. -
#TIP_ROOTS_OVER- similar to the mode#TIP_OVER. The algorithm tries to optimize the layout to automatically fit best to the specified aspect ratio. This slow heuristic tries to tip over beginning with the roots and then chooses the best layout. It checks the alignment mode#TIP_OVER_EAST, but not#TIP_OVER_BOTH_SIDESor other variants. It keeps the alignment of all nodes close to the leaves as specified. -
#TIP_ROOTS_AND_LEAVES_OVER- similar to the mode#TIP_OVER. The algorithm tries to optimize the layout to automatically fit best to the specified aspect ratio. This slow heuristic tries to tip over beginning with the roots and with the leaves, and then chooses the best layout. It checks the alignment mode#TIP_OVER_EAST, but not#TIP_OVER_BOTH_SIDESor other variants. It keeps the alignment of all nodes in the middle between roots and leaves as specified. -
#RADIAL- the root node is in the center, the links flow radially away from the center, and the nodes are placed in circular layers around the root node according to the level alignment. Tip-over alignment and orthogonal link styles are not possible. Clipped connector pins are used as the connector style. If an aspect ratio is specified, the layers are ellipses around the center. -
#ALTERNATING_RADIAL- this is the same as mode#RADIAL, with the exception that children of the same node are placed alternating in different circular layers when this results in a smaller radius and better usage of the space. Tip-over alignment and orthogonal link styles are not possible. Clipped connector pins are used as the connector style. If an aspect ratio is specified, the layers are ellipses around the center. -
#BALLOON- the root node is in the center and the subtrees are arranged as balloon circles around the root. It is very similar to the mode#RADIAL, however each subtree froms its own balloon recursively. If an aspect ratio is specified, the balloons are ellipses instead of circles. Tip-over alignment and orthogonal link styles are not possible. Clipped connector pins are used as the connector style. The recursive leaf layout mode is not supported in combination with the balloon mode.
The default value is
#FREE.Note that the tip-over layout modes work best if the node sizes are respected during layout.
CSS example:layoutMode : "FREE";
Allowed values: FREELEVELBALLOONRADIALALTERNATING_RADIALTIP_OVERAuto Tip Over (fast) TIP_ROOTS_OVERAuto Tip Over (Roots) TIP_LEAVES_OVERAuto Tip Over (Leaves) TIP_ROOTS_AND_LEAVES_OVERAuto Tip Over (Roots and Leaves) -
-
layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled
public boolean layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled
Sets whether the generic connected component layout mechanism is enabled. If enabled on a layout class that supports this mechanism (see#supportsLayoutOfConnectedComponents()), the method#performLayout(boolean, boolean, boolean)cuts the attached graph model into connected components and lays out each connected component separately. Then the connected components are placed using the layout instance returned by the method#getLayoutOfConnectedComponents().Notice that the connected component layout is not used if the graph is connected.
A
RuntimeExceptionis thrown if the layout does not support this mechanism.The default value is the value returned by the method
#isLayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabledByDefault().
CSS example:layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled : "false";
-
levelAlignment
public int levelAlignment
Sets the alignment within the levels. Valid values are:-
#CENTER -
#NORTH -
#SOUTH
This feature sets the alignment of the nodes within each level. It can be used in layout modes
#LEVEL,#RADIAL, and#ALTERNATING_RADIAL. It has an effect only if the respect node sizes option is enabled.If the nodes are center-justified, all nodes of the same level are placed with their centers along a line. Otherwise, all nodes of the same level are placed with the specified border justified to a line. For instance, if the link flow direction is to the right, the alignment
#NORTHmeans that the nodes are justified to the left and the alignment#SOUTHmeans that the nodes are justified to the right.In the radial layout modes, the alignment
#NORTHmeans that the nodes are aligned along a circle with the border that is closer to the root, and the alignment#SOUTHmeans that the nodes are aligned along a circle with the border that is farther away from the root.The default value is
#CENTER.
CSS example:levelAlignment : "NORTH";
Allowed values: NORTHNorth justified SOUTHSouth justified CENTERCenter justified -
-
LinkStyle
public int LinkStyle
Sets the style of the shape of an individual link. This link style is used only if the global link style is set to#MIXED_STYLEand the link is part of the spanning tree. If the global link style is not#MIXED_STYLE, all links of the spanning tree have the style that is specified as the global link style. Links that are not part of the spanning tree have the link style#NO_RESHAPE_STYLE.Valid values are:
-
#ORTHOGONAL_STYLE- the link has an orthogonal shape, that is, a shape consisting of a sequence of orthogonal line segments. This option is not available for the radial layout modes. -
#STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE- the link has a straight-line shape. -
#NO_RESHAPE_STYLE- no reshape is performed on the link.
The default value is
#STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE.When the graph attached to the layout is of type
IlvGrapher, the effect of the link reshaping depends on the type of the links and the connectors installed at the node. For all link styles, you are recommended to use links of typeIlvPolylineLinkImage. For the orthogonal link style, you are additionally recommended to use link connectors of typeIlvFreeLinkConnector. Other link or connector types may cause anIlvInappropriateLinkExceptionduring layout. You can use the methodIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinkTypesIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinkConnectorsIlvGraphLayoutUtil.EnsureAppropriateLinks
CSS example:LinkStyle : "ORTHOGONAL_STYLE";
Allowed values: ORTHOGONAL_STYLEOrthogonal links STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLEStraight-line links NO_RESHAPE_STYLENo link reshape
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
- See Also:
globalLinkStyle
-
-
maxChildrenAngle
public int maxChildrenAngle
Sets the maximum angle for children that are placed in radial mode. This is the maximum angle between the two rays from the parent to its two outermost children. The angle must be between 0 and 360 degrees. The angle 0 means that the angle is unspecified,The default value is 0.
In radial mode, children of a single node may cover nearly completely one circular layer. This sometime appears to be unbalanced, in particular because the links from the node to its outermost children are likely to cross other nodes. To avoid this effect, a maximum angle can be specified so that the children are placed more in the same direction and are not spread too widely around the parent. This angular restriction is applied to all children except the children of the root node. As a side effect, specifying a small maximum children angle enlarges the radius of the circles.
It is recommended choosing a value between
30and180degrees for good results. The algorithm uses a heuristic that has precision deviations below30degrees and above180degrees. If an aspect ratio is specified, the layout algorithm uses ellipses instead of circles. In this case, precision deviations may occur as well.This is an expert option. It has no effect in layout modes other than radial.
CSS example:maxChildrenAngle : "2";
-
minBusyTime
public long minBusyTime
Sets the minimal time that the layout algorithm can be busy. This is the time between two calls of#layoutStepPerformed()when the method#callLayoutStepPerformedIfNeeded()is used.The objective is to avoid the overhead of
#layoutStepPerformed()becoming too high if the method is called too often. Internal routines of layout algorithms usually call#callLayoutStepPerformedIfNeeded(), which calls#layoutStepPerformed()if the time since the last call was at least the minimal busy time.The default value is 50 (milliseconds).
CSS example:minBusyTime : "3";
-
nonTreeLinksStraight
public boolean nonTreeLinksStraight
Sets whether all non-tree links that don't have the no-reshape link style and that are not fixed and are not incident to fixed nodes are reshaped to be straight. Otherwise, the non-tree links are not changed at all.This option is disabled by default. When disabled, the tree layout only routes the links of the spanning tree, but no other link. When enabled, the tree layout iterates over the links obtained by
#getCalcNonTreeLinks()and makes them straight.It obeys the link clip interface and the link connection box interface when making the non-tree links straight. The tree layout can only obey the link style and the connector style of the tree links but not of the non-tree links. In particular, it is not able to route non-tree links orthogonally. Only tree-links can be routed orthogonally. Usually it is recommended to apply an additional link layout to the non-tree links if there are any. However, if the non-tree links should just be straight, this option comes in handy since an additional link layout can be omitted in this case.
CSS example:nonTreeLinksStraight : "false";
-
NorthSubtreeBlockMargin
public double NorthSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the north side of the subtree starting at the input node. If the value is set to a positive number, the subtree starting at this node is considered a rectangular block, and other nodes not belonging to this subtree are moved at least the specified margin away from this block. Specifying subtree block margins is useful if you plan to draw a rectangle around this subtree, since it ensures that unrelated nodes do not extend into the rectangle.The default value is -1, means no margin.
CSS example:NorthSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
numberOfAlternatingCircles
public int numberOfAlternatingCircles
Sets the number of alternating circles.This option has only an effect in layout mode
#ALTERNATING_RADIAL. Alternating placement means that the nodes of one level are placed alternating in several circular layers. By default, it uses 2 circular layers for the alternating placement. Nonalternating placement means that the nodes of one level are placed in one circular layer.This option allows to define how many alternating layers are maximally used. You cannot have more layers than nodes in the level, hence it is only the maximum number of layers. Furthermore, the layout analyses which levels must use the alternating placement in order to optimize space, unless the option
#isAllLevelsAlternatingreturns true.If you set the number to a positive value and
#isAllLevelsAlternatingreturns true, each level has exactly that many circular layers, unless the level has not sufficient nodes. If you set the number to a positive value and#isAllLevelsAlternatingreturns false, each level has either exactly that many circular layers or one circular layer, depending on which version uses the space better. If you set the number to 0, a heuristic tries to determine for each level how many circular layers are needed in order to optimize the space. In this case, different levels can have different number of circular layers, and the value of#isAllLevelsAlternatingis ignored.Note that the layout may have link crossings if a huge number of alternating circles per level is used.
The default value is 2.
CSS example:numberOfAlternatingCircles : "2";
-
orthForkPercentage
public double orthForkPercentage
Sets the percentage of the parent-child offset that determines the location where the orthogonal link routing places the bends in order to fork the routing towards the children. This has an effect only if the orthogonal link style is chosen.The default value is
45%.This is an expert option. In all normal cases, it is not necessary to change the option. It is recommended choosing an orthogonal fork percentage that is always larger than the overlap percentage to obtain a good layout.
CSS example:orthForkPercentage : "3.0";
-
overlapPercentage
public double overlapPercentage
Sets the percentage for which a node is considered smaller in the flow direction. This allows nodes to be placed closer together. However, in layout modes#FREE,#TIP_OVER,#TIP_ROOTS_OVER,#TIP_LEAVES_OVER, and#TIP_ROOTS_AND_LEAVES_OVER, outgoing links of a node may, in rare cases, cross the neighbor leaf nodes if the overlap percentage is high. To avoid this, set the parameter to0%.The default value is
30%, which is a good compromise for many graphs between wasting space and the risk of having links cross nodes.This is an expert option. In all normal cases, it is not necessary to change the option. It is recommended choosing an orthogonal fork percentage that is always larger than the overlap percentage to obtain a good layout.
This option has no effect if the respect node sizes option is disabled.
CSS example:overlapPercentage : "3.0";
-
parentChildAssociateOffset
public double parentChildAssociateOffset
Sets the minimum offset between the parent and the first associate. This offset is used if a parent has associate nodes. This method has no effect if the layout mode is radial or if no associates occur.If the flow direction is toward the top or bottom, the orthogonal link segment starting at the parent is vertical, and the associates are placed left or right of this link segment. In this case, it is a vertical offset between parent and child. If the flow direction is toward the left or right, the orthogonal link segment starting at the parent is horizontal, and the associates are placed above or below this link segment. In this case, it is a horizontal offset between parent and child.
If the Respect node sizes option is enabled, this is the minimum offset between node borders; otherwise, it is the minimum offset between node centers.
The default value is
30.
CSS example:parentChildAssociateOffset : "3.0";
-
parentChildOffset
public double parentChildOffset
Sets the minimum offset between a parent and its children.If the flow direction is towards the top or bottom and the layout mode is not radial or balloon, this is a vertical offset. If the flow direction is towards the left or right and the layout mode is not radial or balloon, this is a horizontal offset. If the layout mode is radial or balloon, this is an offset radial to the circle or ellipses. In balloon mode, it corresponds to the minimal radius of the balloon.
If the respect node sizes option is enabled, this is the minimum offset between node borders; otherwise, it is the minimum offset between node centers.
The default value is
40.
CSS example:parentChildOffset : "3.0";
-
position
public ilog.views.IlvPoint position
Sets the position of the layout. This can be used if connected component processing is disabled, or if the graph is fully connected. It has no effect otherwise.The meaning of the position depends on the flag
#isRootPosition(). If the flag istrue, it specifies the position of the first root node. This is useful in incremental mode. If the flag isfalse, it specifies the position of the top-left border of the layout.If no position is specified, the layout algorithm keeps the position of the first root node unchanged.
CSS example:position : "10,10";
- See Also:
rootPosition
-
recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed
public boolean recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed
Sets whether the layout instance of the ancestor graph is in principle allowed to treat this subgraph in a recursive layout. Whether the layout of the ancestor graph can handle the subgraph attached to this layout instance depends on the parameter settings of the ancestor layout. The layout instance of the ancestor graph must also be a tree layout and must have the recursive leaf layout mode enabled, otherwise the ancestor layout does not try to handle this subgraph.This option is enabled by default.
CSS example:recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed : "false";
-
recursiveLeafLayoutMode
public boolean recursiveLeafLayoutMode
Sets whether the recursive layout of nested subgraphs in leaves of the tree is enabled. Normally, the tree layout can only handle flat graphs. The recursive leaf layout mode is a mode so that the tree layout handles nested graphs. This works if the leaves of the tree are subgraphs, but not if the inner nodes of the tree are subgraphs. If this option is enabled, the Tree Layout algorithm routes intergraph links that are part of the spanning tree after flattening the leaf subgraphs. It does not route all intergraph links.The layout is suited if the nodes and links have no labels that need to be placed around the nodes and links. (Labels in the center of nodes don't cause a problem). The layout may produce suboptimal results if the nodes or links of subgraphs have very long labels that must be placed by a label layout. Since the label layout can only run after the tree layout, it will influence the bounding boxes of the subgraphs after they are already placed, which is the cause for the suboptimal result.
CSS example:recursiveLeafLayoutMode : "false";
-
respectNodeSizes
public boolean respectNodeSizes
Sets whether the algorithm must try to respect the size of the nodes. If the argument istrue, the spacing parameters are interpreted as the minimum distance between the node borders. If the argument isfalse, the spacing parameters are interpreted as the minimum distance between the node centers.If respecting node sizes is disabled, the level alignment option has no effect.
This is an expert option. The default is
true. It makes sense to switch this option off only if all nodes already have approximately the same size and the spacing parameters are larger than the largest node. If the option is switched off, large nodes may otherwise overlap. In particular, it is recommended keeping the option enabled if orthogonal links are used.
CSS example:respectNodeSizes : "false";
-
rootPosition
public boolean rootPosition
Sets the meaning of the specified position. The specified position is the one that can be obtained from#getPosition(). If passedtruethe specified position means the position of the root node. Otherwise, it means the position of the top-left border of the layout. This can be used if connected component processing is disabled, or if the graph is fully connected. It has no effect otherwise.
CSS example:rootPosition : "false";
- See Also:
position
-
RootPreference
public int RootPreference
Specifies the preference of the node to become root node. The higher the preference, the more likely the node will be selected as root node.If a negative value is passed as input, the preference of the node is unspecified. In this case, the algorithm calculates a preference so that for directed trees the canonical root nodes with degree 0 have the highest preference.
CSS example:RootPreference : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
siblingOffset
public double siblingOffset
Sets the minimum offset between siblings, that is, between nodes that have the same parent in the tree structure.If the flow direction is towards the top or bottom and the layout mode is not radial, this is a horizontal offset. If the flow direction is towards the left or right and the layout mode is not radial, this is a vertical offset. If the layout mode is radial, this is an offset tangential to the circles or ellipses.
This offset has no effect in balloon layout mode. Use the branch offset to control the spacing between all nodes in balloon layout mode.
If the respect node sizes option is enabled, this is the minimum offset between node borders; otherwise, it is the minimum offset between node centers.
The default value is
40.
CSS example:siblingOffset : "3.0";
-
SouthSubtreeBlockMargin
public double SouthSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the south side of the subtree starting at the input node. If the value is set to a positive number, the subtree starting at this node is considered a rectangular block, and other nodes not belonging to this subtree are moved at least the specified margin away from this block. Specifying subtree block margins is useful if you plan to draw a rectangle around this subtree, since it ensures that unrelated nodes do not reach into the rectangle.The default value is -1, which means no margin.
CSS example:SouthSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
tipOverBranchOffset
public double tipOverBranchOffset
Sets the minimum offset in the flow direction between neighbor nodes that belong to different branches in the tree. This offset is used to separate the branches if their common parent node has tip-over alignment. It has no effect if the layout mode is radial or if no tip-over alignment occurs.If the flow direction is towards the top or bottom, this is a vertical offset. If the flow direction is towards the left or right, this is a horizontal offset.
If the respect node sizes option is enabled, this is the minimum offset between node borders; otherwise, it is the minimum offset between node centers.
The default value is
40.
CSS example:tipOverBranchOffset : "3.0";
- See Also:
flowDirection
-
WestSubtreeBlockMargin
public double WestSubtreeBlockMargin
Sets the margin on the west side of the subtree starting at the input node. If the value is set to a positive number, the subtree starting at this node is considered a rectangular block, and other nodes not belonging to this subtree are moved at least the specified margin away from this block. Specifying subtree block margins is useful if you plan to draw a rectangle around this subtree, since it ensures that unrelated nodes do not extend into this rectangle.The default value is -1, means no margin.
CSS example:WestSubtreeBlockMargin : "3.0";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
-