JViews TGO allows you
to place labels in a network automatically to make them easier to
read. This placement overrides the default placement of labels in JViews TGO, namely:
- Below network elements
- At the center of gravity of groups
Label layout allows you to reduce overlap between labels and other
objects in the current view. Therefore, it is particularly useful
for positioning labels on links. Network
Links without Label Layout shows labels positioned by default. Network
Links with Label Layout shows the same links with customized
positioning of the labels through label layout.
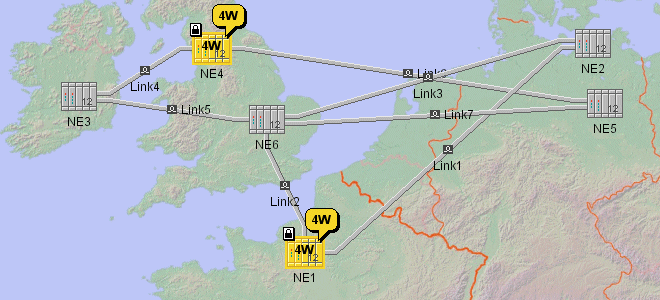
Network Links without Label Layout
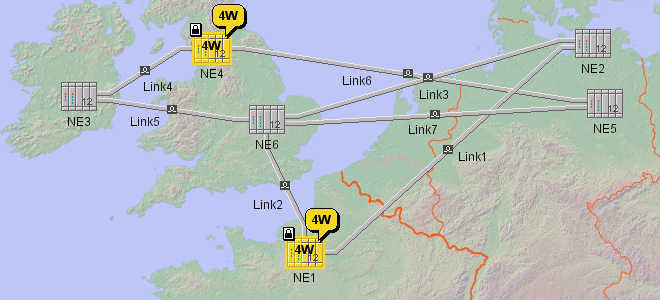
Network Links with Label Layout
Note
Label layout tries to find the best
position for your labels, but sometimes even this mechanism does
not achieve attractive results. To get the best results, leave
large spaces between network objects.
Label layout in JViews
TGO uses the label layout of Rogue Wave® JViews. See the Rogue
Wave JViews Diagrammer Using Graph
Layout Algorithms documentation for more details on label layout.
Using label layout
JViews TGO provides
the IltAnnealingLabelLayout class (a subclass
of IlvAnnealingLabelLayout) that moves the
labels of the nodes and the links so that they do not overlap. If
it is impossible to prevent some overlap, this class will
minimize the overlap between different labels.
The class IlpNetworkView provides the following
method for handling label layout:
void setLabelLayout (IltAnnealingLabelLayout layout);
This method sets the given layout for the specified view. This
method is also available from the class IlpNetwork, for convenience.
Unlike node layout and link layout, label layout is not performed
automatically when the content of the network changes. You need
to call
labelLayout.performLayout()
explicitly. There is a toolbar button for triggering label layout
computation. See the class IlpNetworkLabelLayoutButton.
Here is a typical example of how to use
label layout.
How to use label layout
IlpNetwork network = new IlpNetwork(); // fill the network with your elements IltAnnealingLabelLayout labelLayout = new IltAnnealingLabelLayout(); network.setLabelLayout(labelLayout); labelLayout.performLayout(); network.setLabelLayout(null);
In this example you:
- Create the label layout.
IltAnnealingLabelLayout labelLayout = new IltAnnealingLabelLayout();
- Attach this layout to the current network.
network.setLabelLayout(labelLayout);
- Perform the layout, placing the labels esthetically and where they will be easy to read.
labelLayout.performLayout();
- Optionally, detach the layout from the network and release the resources used by label layout. The positions of the labels are maintained.
network.setLabelLayout(null);
Defining the labels you want to position
Label layout positions only the labels of
links by default. You can choose to apply the layout to other
types of object through the following methods:
void setObjects (IltLabelLayoutConstants[] types) void setObjects (int index, IltLabelLayoutConstants type) IltLabelLayoutConstants[] getObjects() IltLabelLayoutConstants getObjects (int index)
or through the following convenience
methods:
setUsesOthers(boolean flag) setUsesLinks(boolean flag) setUsesNetworkElements(boolean flag) setUsesBTS(boolean flag) setUsesLinearGroups(boolean flag) setUsesPolyGroups(boolean flag) setUsesRectGroups(boolean flag)
How to apply label layout to network elements only
IltAnnealingLabelLayout labelLayout = new IltAnnealingLabelLayout(); labelLayout.setObjects(0, IltLabelLayoutConstants.NETWORK_ELEMENTS); network.setLabelLayout(labelLayout); network.performLabelLayout(); network.setLabelLayout(null);
The method
setObjects
indicates whether a certain type of object will have its label
placed by the label layout. In this example, only Network
Elements will have their labels placed by the label layout.
How to apply label layout to network elements only using CSS
Network {
labelLayout: true;
}
LabelLayout {
class: 'ilog.tgo.graphic.graphlayout.labellayout.IltAnnealingLabelLayout";
objects[0]: NETWORK_ELEMENTS;
}
The property
objects
indicates whether a certain type of object will have its label
placed by the label layout. In this example, only network
elements will have their labels placed by the label layout.
Defining obstacles
The label layout positions the labels of
the objects by taking into account the obstacles that are in the
network view. By default, all objects are considered as
obstacles, but you can configure this behavior in CSS or through
the API:
How to specify obstacles in the label layout using CSS
Network {
labelLayout: true;
}
LabelLayout {
class:
'ilog.tgo.graphic.graphlayout.labellayout.IltAnnealingLabelLayout';
obstacles[0]: NETWORK_ELEMENTS;
obstacles[1]: LINKS;
}
How to specify obstacles in the label layout using the API
void setObstacles (IltLabelLayoutConstants[] types) void setObstacles (int index, IltLabelLayoutConstants type) IltLabelLayoutConstants[] getObstacles() IltLabelLayoutConstants getObstacles (int index)
Constraints
The following constraints exist for label
layout:
- Label layout does not work in subnetworks.
- If you move an object on which you have performed label layout, the label position will not be maintained. You must perform label layout again on the object after the move.
- Label layout is not appropriate for dynamically changing networks.Label layout is designed for stable networks. If you modify your network frequently, you need to call the method performLayout whenever any object with a label changes. The Rogue Wave JViews algorithm for annealing label layout used in JViews TGO consumes a lot of resources. Therefore, it is not recommend to call the method
performLayout()often. Note also that the layout does not always find the same position for the labels. See the Rogue Wave JViews Diagrammer User’s Documentation for more information.
You can configure the label layout in a CSS file through the
labelLayout
property. For more information, see The LabelLayout rule.