Rogue Wave® JViews
Diagrammer provides special support for the layout of a disconnected graph.
If a graph is composed of several connected components or contains isolated
nodes (nodes without any links), it can be desirable to apply the
layout algorithm separately on each connected component and then
to position the connected components using a specialized layout
algorithm (usually, IlvGridLayout). The following figure shows
an example of a graph containing four connected components. By
enabling the layout of the connected components on the regular
layout instance (here, IlvTopologicalMeshLayout), the connected
components are automatically identified and laid out
individually. Finally, the four connected components are
positioned using a highly customizable placement algorithm ( IlvGridLayout).
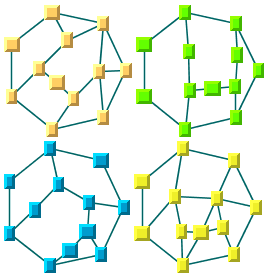
Automatic layout of connected components
in a disconnected graph
To indicate whether a subclass of
IlvGraphLayout
supports this feature, use the method in the class
IlvGraphLayout
:
boolean supportsLayoutOfConnectedComponents()
The default implementation returns
false
. A subclass can override this method in order to return
true
to indicate that this feature is supported.
In Rogue Wave JViews
Diagrammer you can enable the layout of the connected
components by using the method:
void setLayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled(boolean enable)
To obtain the current setting:
boolean isLayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled()
The default value is the value returned by
the following method:
boolean isLayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabledByDefault()
The default implementation of this method in
IlvGraphLayout
returns
false
. For some of the layout classes, it is appropriate that this
feature is enabled by default. Therefore IlvUniformLengthEdgesLayout overrides this
method to return
true
.
If enabled on a layout class that supports this feature, the
method
performLayout
of the class
IlvGraphLayout
cuts the attached graph model into connected components and lays
out each connected component separately.
How does the layout of connected components feature work when
this mechanism is enabled in the layout classes that support this
feature? Instead of directly calling the method layout to perform the layout on the entire
graph, the method performLayout first cuts the graph into
connected components.
Then, each connected component is laid out separately by a call of
the method
layout
. To do so, the attached graph is temporarily changed into
internally generated graphs corresponding to each of the connected
components of the original graph.
Finally, the layout instance returned by
the method:
IlvGraphLayout getLayoutOfConnectedComponents()
is used to position the connected
components. To specify the layout instance that places the
connected components, use the following method:
void setLayoutOfConnectedComponents(IlvGraphLayout layout)
If no layout instance is specified using this method, the method
getLayoutOfConnectedComponents
returns an instance of IlvGridLayout. Its layout region parameter
is set by default to the rectangle (
0
,
0
,
800
,
800
). Its “layout mode” parameter is set to TILE_TO_ROWS.
Note
The Tree, Hierarchical, and Circular layouts contain built-in
support for disconnected graphs. For the Tree and Hierarchical
layouts, the result can be different from the result of the
generic mechanism (the layout of connected components feature)
provided by the base class IlvGraphLayout. Depending on your
particular needs, you can use either the generic mechanism or
the built-in support.