The class diagram for the shapefile reader and writer is shown in Shapefile Reader and Writer UML Diagram.
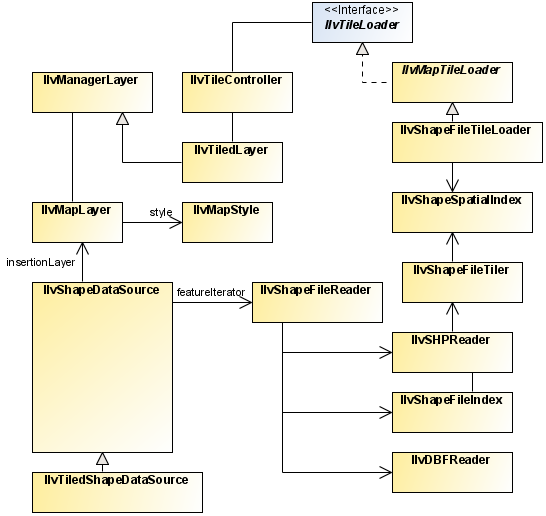
Shapefile Reader and Writer UML Diagram
These classes are based on the Shapefile Specifications listed in
the ESRI (Environmental Systems Research Institute) document:
ESRI Shapefile Technical Specifications -
An ESRI White Paper - July 1998.
The Shapefile format is the exchange format for
vector maps of the ESRI. This format supports polygons, arcs,
lines, and points. Each Shapefile contains one single theme,
meaning that all the objects in the file are of the same type
(either line, point, polygon, or another type of object). In the
Shapefile format, a theme is essentially described with four
different files:
- A shapefile (
.shp) contains the geometry of the objects. - A Dbase file (
.dbf) contains the attributes of the objects. - An index file (
.shx)contains the index and sizes of the objects of the .shpfile. - A spatial index file (
.idx) contains tiling information. This file is JViews Maps package specific, and is used to performload-on-demand on Shapefiles.
This format does not contain information concerning the coordinate
system used to reference the position of the graphic objects.
Objects in Shapefiles are often positioned within a geographic
coordinate system ( IlvGeographicCoordinateSystem), but this is
far from being the rule.
The Shapefile format comprises the following
classes:
The complete source code for an ESRI shapefile demonstration can be
found at <installdir> /jviews-maps810/samples/shape/index.html