
The purpose of the Dynamic data model is to avoid the overhead of the SRGraphData class when it is not needed. In the Dynamic model, the data values of a group— and only values— are stored in a contiguous buffer or array. A hi-low history, a similar array of CScale objects, is created only if explicitly requested. The Dynamic data buffer is encapsulated by the SRGraphDynamicData class.
The dynamic data storage class, SRGraphDynamicData, stores the data values for a group sequentially in a special array. Instead of declaring the storage as a simple array of doubles, it is declared as an array of SRGDataBuffer objects. SRGDataBuffer is defined as an union of 1, 2, 4, and 8-byte data types. In this manner, data of a variety of types can be stored.
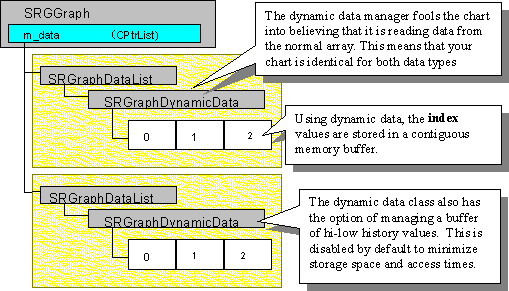
Figure 119 shows the data structure for Dynamic data storage.

Data in the buffer are accessed by two zero-based index members: an input index and an output index. These indices help speed sequential access to the data values and maintain compatibility with the Standard model.
For efficiency, the memory buffer can be set to grow in steps, allocating a fixed amount of memory when an index is accessed out of the range of existing values.
The buffer can also be set to cycle. When an index reaches the end limit, the index is reset to the start of the buffer.
In previous versions of Objective Chart, the Dynamic data model required the use of a special chart object of the SRDynamicGraph class, which is derived from SRGraph. The standard SRGraph class now handles Dynamic data, so SRDynamicGraph is no longer required.
SRGraphDynamicData is derived from SRGraphData. Overridden virtual functions in these classes fool the chart components into believing they are dealing with a list of discrete data items. Standard data selection requests are translated into buffer index offsets. Because of this translation, Dynamic data are accessed in the same manner as Standard data, apart from the initial setup.
In summary, the Dynamic data model has these features:
Data values are stored in a buffer of SRGDataBuffer objects managed by the SRGraphDynamicData class.
Dynamic data stores only data values. It does not store individual styles, annotations, or null flags. An annotation, style, and null flag are stored only in the SRGraphDynamicData object itself. Any request for annotations, style settings, or null status from an indexed data value always returns the annotation, style setting, or null flag from this object.
Dynamic data can not be individually styled.
Options for axis labels and feedback are limited. Annotations must be generated programmatically in an override of SRGraphDynamicData::GetAnnotation().
Data values in the Dynamic model can not be individually flagged as null or invalid.
To save space and minimize access times, SRGraphDynamicData does not maintain a hi-low history for the data values in the array by default. If hi-low histories are desired, an array of CScale objects can be generated by calling SetHiLoFunction(TRUE).
To set up a Dynamic data buffer, an SRGraphDynamicData object must be explicitly created and configured with its initial size and growth parameters. The actual memory buffer is created and resized automatically. Therefore, the Dynamic data storage seems, at least partially, internal to Objective Chart.
Because of its contiguous nature, the Dynamic data model provides faster sequential access than the Standard model. A stream of data may be placed quickly into the buffer for use in real-time data logging and charting operations.
Conversely, using the relatively fixed memory buffer would make inserting to (or deleting values from) the middle of the array very slow. In addition, it would require detailed knowledge of the data structure. Data rolling is particularly inefficient, although it is supported.
To initialize a chart using the Dynamic data storage model:
Create an SRGraph or SRDynamicGraph object somewhere in your application.
Create an SRGraphDynamicData object and set its initial size and growth parameters.
Add the prepared SRGraphDynamicData object to the SRGraphDataList object of the selected group.
Once configured, the Dynamic data buffer can be accessed with the same GetValue() and SetValue() functions that are used in the Standard model, except overloaded functions are provided for a variety of data types. In addition, SRGraphDynamicData has functions that can be used for more direct, sequential access.
SRGraph m_Graph;
SRGraphDynamicData* pD=new SRGraphDynamicData;
// Allocate the memory
pD->SetBufferSize(15000);
// Decide whether to allow the buffer to grow
// or remain cyclic
// pD->SetGrowSize(4096);
pD->SetCyclic(TRUE);
pD->SetNull(FALSE);
pD->GetStyle()->SetObjectStyle(CX_OBJECT_LINE);
SRGraphDataList* pDL=m_Graph.GetGroup(0);
pDL->SetDynamic(); // important
// Add the data object (buffer) to the list
pDL->AddTail(pD);
// You can add more than one but the second, third
// and so-on will never be seen
// Assign data values to the buffer
double x;
for(int i=0; i<15000; i++)
{
//standard access
m_Graph.SetValue( i,0, sin(RADIANS(i)) );
|
or
// faster, direct, sequential access
// via SRGraphDynamicData
pD->SetValue( sin(RADIANS(i)) );
}
|
Changes have been made to SRGraph, SRDynamicGraph, SRGDynamicDataManager, and SRGraphDynamicData to make Dynamic data easier to use. Dynamic data no longer requires explicit setup of the data buffer for each group as described above. SRGDynamicDataManager::NewGroup() will create and initialize an SRGraphDynamicData object with reasonable defaults.
To switch an existing chart from Standard to Dynamic storage models, simply change the chart object from SRGraph to SRDynamicGraph— or create an SRGDynamicDataManager and select it into the SRGraph using SRGraph::SetDataManager(). Then, in most cases, the data can be initialized using the same code as the Standard data model.
Using SetDataManager() to select an SRGDynamicDataManager is the preferred method because it allows the use of a custom SRGDynamicDataManager. Developers will commonly override SRGDynamicDataManager::NewGroup() to customize the initialization of the SRGraphDynamicData-based object. For example, SRGraphDynamicData::GetAnnotation() is commonly overridden to supply strings (for axis labels, etc.) based on the current index.
Also, SRGraphDynamicData no longer assumes that the entire data buffer is filled with data. It maintains a "high water mark", m_nMaxValid, indicating the highest index (+1) which has been initialized with a call to SetValue(). m_nMaxValid— accessed by GetHighestValidIndex()— determines the number of data values in the group. GetNull() returns TRUE for uninitialized indices greater than or equal to m_nMaxValid. With these changes, the chart can be dynamically displayed as data are acquired filling up the data buffer.
Copyright © Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Rogue Wave name and logo, and Stingray, are registered trademarks of Rogue Wave Software. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Provide feedback to Rogue Wave about its documentation.