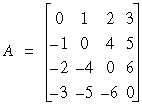

LAPACK.h++ contains two mechanisms for extracting and operating on a submatrix of a matrix. These mechanisms are based on whether the original matrix is a general rectangular matrix, or some other type.
Subscripting allows you to access submatrices of a general rectangular matrix. The submatrix is a view of the original matrix's data. A complete description of subscripting and the subscripting index classes RWRange, RWSlice, and RWToEnd can be found in the Math.h++ User's Guide and Reference. A mechanism for matrices other than general rectangular matrices is described next.
In general, it is not possible to access arbitrary submatrices with matrix shapes other than general. However, the special case of accessing the upper-left corner of a matrix, called the leading submatrix, occurs so frequently that LAPACK.h++ includes a member function for this purpose. The leadingSubmatrix() function is implemented for all matrix types except general rectangular, RWGenMat, which has the more general subscripting feature. For example, if A is the skew symmetric matrix:
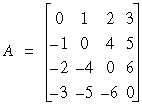
then the line of code:
A.leadingSubMatrix(2); //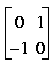
yields the 2 x 2 skew symmetric matrix shown in the comment above.
Like a matrix created by subscripting, a leading submatrix views the same data as the matrix from which it was extracted. The code:
DoubleSkewMat Atopleft = A.leadingSubmatrix(2);
sets the matrix Atopleft to be a reference to the data in the matrix A. It is a view of just the upper-left corner 2 x 2 matrix. If you subsequently change Atopleft, A also changes.
©Copyright 1999, Rogue Wave Software, Inc.
Contact Rogue Wave about documentation or support issues.