Active Objects and Data Input Streams
The example in this section implements the previous example’s corresponding input operation. It creates a synchronized data input stream RWSynchronizedDataInputStreamImp that connects to an RWNativeDataFromByteInputStreamImp stream, which restores C++ base types from a sequences of bytes. The RWNativeDataFromByteInputStreamImp stream is then connected to a buffered binary input stream that reads bytes from the file created in the previous example. The class RWBufferedByteInputStreamImp is connected to class RWByteFromStreambufInputStreamImp to provide the buffered byte input stream.
This example requires the Streams package, as well as the Execution Tracing, Thread-compatible Exception, Synchronization, Smart Pointer, Threading, Functor, and Interthread Communication packages from the Threads Module.
Figure 16 is a representation of the chain of streaming elements used in this example.
Figure 16 – Streaming with active objects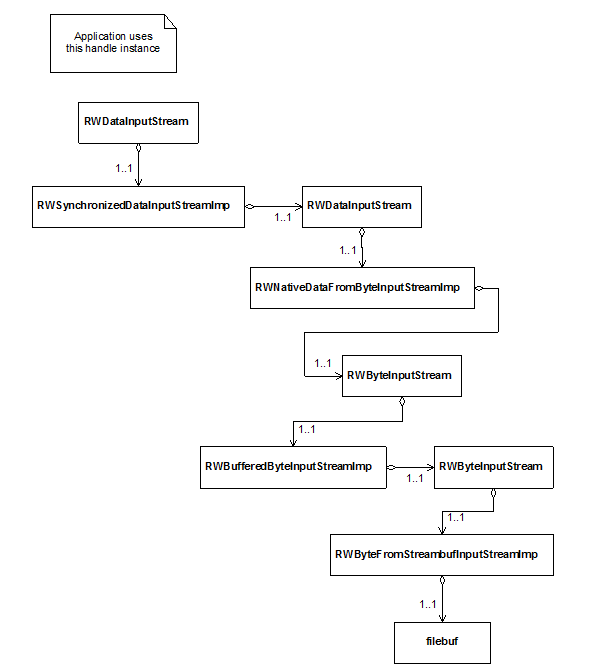

As in the previous example, this example uses active objects to carry out asynchronous operations on a unique thread-safe data stream. Only one type of active object is used. Its purpose is to read ten elements of one of the C++ base types from a data input stream, ensuring that the ten elements are read in one synchronized operation.
The complete example is located in directory ...\examples\stream in the file dataFilteredRead.cpp. The code for the active object class is presented below:
template <class T>
class readABunch {
public:
readABunch(RWDataInputStream& stream) // 1
:dataInputStream_(stream)
{
thread_= rwMakeThreadFunctionM(readABunch<T>,*this,
void,&readABunch<T>::func); // 2
thread_.start();
}
~readABunch() {
thread_.join(); // 3
thread_.raise();
}
void func() {
RWDataInputStream tmpStream =
RWGuardedDataInputStreamImp::make(dataInputStream_); // 4
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
tmpStream >> data_; // 5
cout << data_ << ' ';
rwYield();
}
}
private:
readABunch(const readABunch<T>&);
readABunch<T>& operator=(const readABunch<T>&);
RWDataInputStream dataInputStream_;
T data_;
RWThreadFunction thread_;
};
//1 The active object’s constructor takes a handle to the data input stream that is used internally as the source of data. The handle points to the thread-safe chain of streaming elements. If the first element of the chain of streaming elements pointed to by the data input stream handle is not of type RWSynchronizedDataInputStreamImp, then the active object does not enforce proper thread synchronization.
//2 Creates and starts a thread that executes the member function func().
//3 Upon destruction the active object waits for its thread to terminate execution and re-throws any exception raised while executing.
//4 Creates a temporary guarded input stream. All operations carried out on the guarded input stream are synchronized until its destruction. The guarded input stream uses the internal lock provided by the synchronized data input stream class to which it is attached to enforce synchronization. The guarded input stream acquires the synchronized data input stream lock in its constructor and releases it in its destructor. Once the guarded input stream is constructed, any other threads accessing the guarded input stream’s synchronized data input stream are blocked.
//5 Extracts the C++ base type from the temporary guarded data output stream and sends it to the standard output.