Parameters
The Orthogonal Link Layout uses generic parameters, common to other graph layouts, and specific parameters applicable in orthogonal link layouts only. Refer to the following sections for general information on parameters among the graph layouts:
The Orthogonal Link Layout parameters are described in detail in this topic under:
Generic Parameters
The
IlvOrthogonalLinkLayout class supports the following
generic parameters as defined in the class
IlvGraphLayout:
The following comments describe the particular way in which these parameters are used by this subclass.
Allowed Time
The layout algorithm stops if the allowed time setting has elapsed. (For a description of this layout parameter in the
IlvGraphLayout class, see
Allowed Time.)
Preserve Fixed Links
The layout algorithm does not reshape the links that are specified as fixed. (For more information on link parameters in the
IlvGraphLayout class, see
Preserve Fixed Links.)
Specific Parameters
The following parameters are specific to the
IlvOrthogonalLinkLayout class:
Dimensional Parameters
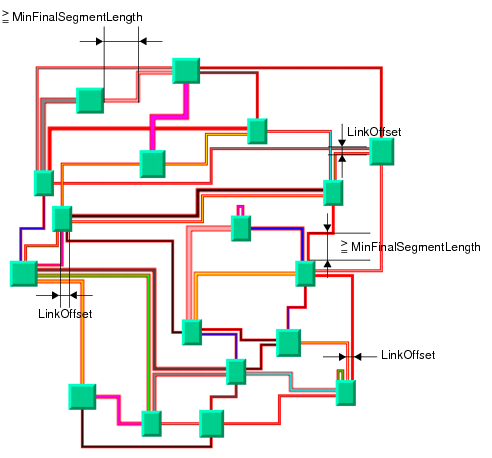
Figure 4.39 illustrates the dimensional parameters used in the Orthogonal Link Layout algorithm. These parameters are:
Figure 4.39 Dimensional Parameters for the Orthogonal Link Layout Algorithm
Link Offset
The layout algorithm computes the final connecting segments of the links (that is, the segments near the origin and destination nodes) in order to obtain parallel lines spaced at a user-defined distance. Since the links can have different widths, it takes into account the width of the links, when computing the offset. To specify the offset, use the method:
To obtain the current value, use the method:
Minimum Final Segment Length
You can specify a minimum value for the length of the final connecting segments of the links (that is, the segments near the origin and destination nodes) using the method:
To obtain the current value, use the method:
The default value is 10.
Link Style
The layout algorithm provides two link styles. To specify the link style, the following method can be used:
The valid values for style are:
 IlvLayoutOrthogonalLinkStyle
IlvLayoutOrthogonalLinkStyle The links are reshaped to a polygonal line of alternating horizontal and vertical segments.
Figure 4.37 shows a layout produced with this style. This is the default.
 IlvLayoutDirectLinkStyle
IlvLayoutDirectLinkStyle The links are reshaped to a polygonal line composed of three segments: a straight-line segment that starts and ends with a small horizontal or vertical segment.
Figure 4.38 shows a layout produced with this style.
Note: The layout algorithm calls the method ensureReshapeableLinks on the attached graph model to ensure that all the links can be reshaped as needed, including their connection points. With an IlvGrapher, this method may replace links with the appropriate type of link and install the appropriate link connector on the nodes. For details on this method, see the Reference Manual. For details on the graph model, see Using the Graph Model. |
Note: The link style requires links in an IlvGrapher that can be reshaped. Links of type IlvLinkImage, IlvOneLinkImage, IlvDoubleLinkImage, IlvOneSplineLinkImage, and IlvDoubleSplineLinkImage cannot be reshaped. You can use the class IlvPolylineLinkImage instead. |
To obtain the current choice, use the following method:
Number of Optimization Iterations
The link shape optimization is stopped if the number of iterations exceeds the allowed number of iterations or the time exceeds the
allowed time. To specify this number, use the method:
To obtain the current value, use the method:
Note: You may want to disable the link shape optimization by setting the number of iterations to zero in order to increase the speed of the layout process. |
Same Shape for Multiple Links
You can force the layout algorithm to compute the same shape for all the links having common origin and destination nodes. The links will have parallel shapes. To enable or disable this option, use the method:
To obtain the current value, use the method:
The default value is IlFalse.
Link Crossing Penalty
The computation of the shape of the links is driven by the objective to minimize a cost function, which is proportional to the number of link-to-link and link-to-node crossings. By default, these two types of crossings have equal weights. You can increase or decrease the weight of the link-to-node crossings using the method:
The default value is 1. To increase the possibility of obtaining a layout with no link-to-node crossings (or with only a few crossings), set the parameter to a value greater than one. For example, set penalty to 5.
To obtain the current value, use the method:
You can also increase or decrease the weight of the link-to-link crossings using the method:
The default value is 1. To increase the possibility of obtaining a layout with no link-to-link crossings (or with a only few crossings), set the parameter to a value greater than one. For example, set penalty to 5.
To obtain the current value, use the method:
Version 6.0
Copyright © 2015, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.