- java.lang.Object
-
- ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout
-
- ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.annealing.IlvAnnealingLabelLayout
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- LabelingModelListener, Serializable, EventListener
- Direct Known Subclasses:
- IltAnnealingLabelLayout
public class IlvAnnealingLabelLayout extends IlvLabelLayout
The main class for the Simulated Annealing Label Layout algorithm.This performs a simulated annealing label positioning algorithm. Each label is moved according to its label descriptor, such that the overlaps among labels, and between labels and obstacles is small. The label descriptor defines the area where a label can be placed. For instance, to specify an area close to a given point, use the
IlvAnnealingPointLabelDescriptor(seesetLabelDescriptor(Object, IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor)), or to specify an area along a polyline, use theIlvAnnealingPolylineLabelDescriptor.In the following sample drawings, the labels were placed by the Annealing Label Layout algorithm. They show point labeling with the
IlvAnnealingPointLabelDescriptorto place the labels at nodes of a network or at cities of a map.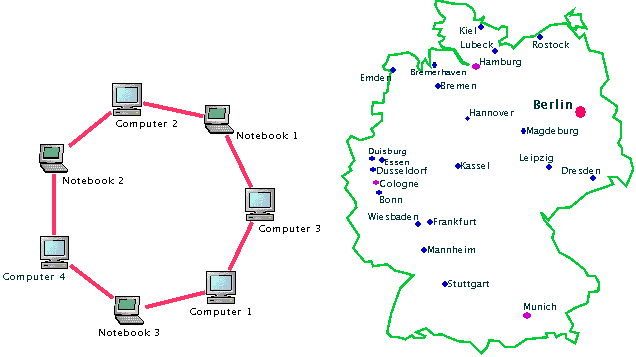
The following are two sample drawings that show link/line labeling with the
IlvAnnealingPolylineLabelDescriptor. Many options are provided to tailor the placement. In the left drawing, the "Start Label", "End Label" and "Center Label" were specified to be at the start, end, center, respectively, of the corresponding link. The right drawing shows a link with multiple labels. It is possible to specify the side of the link where labels are placed.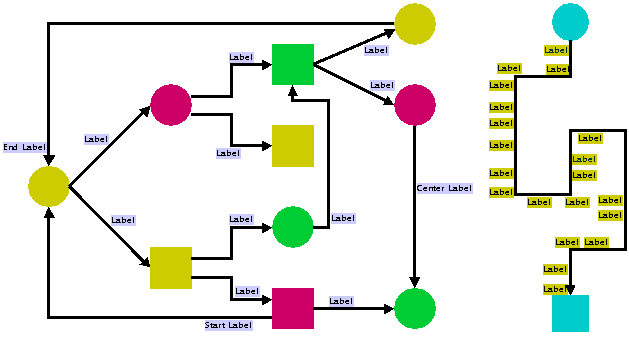
Simulated annealing is a quality controlled, randomized iterative heuristic. The labels are placed according to a temperature scheme, and the quality of the placement increases when the temperature decreases. The quality is defined by the amount of overlaps between pairs of labels and between labels and obstacles. The fewer overlaps the higher the quality. Simulated annealing, as randomized algorithm, does not guarantee a placement of the labels without overlaps. However, it produces a quality layout with a high probability. The more iterations the higher the probability of high quality.
See the corresponding chapter of the User's Manual for details on the algorithm, the features and limitations, code samples, and so on.
Note that the initial position of the labels (at the moment you start the layout) does not affect the resulting layout.
- Since:
- JViews 5.0
- See Also:
- Serialized Form
-
-
Field Summary
-
Fields inherited from class ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout
INVERSE_VIEW_COORDINATES, MANAGER_COORDINATES, VIEW_COORDINATES
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description IlvAnnealingLabelLayout()Creates a new instance of the Annealing Layout algorithm.IlvAnnealingLabelLayout(IlvAnnealingLabelLayout source)Creates a new label layout instance by copying an existing one.
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description voidcleanLabel(IlvLabelingModel labelingModel, Object label)Cleans a label.voidcleanObstacle(IlvLabelingModel labelingModel, Object obstacle)Cleans an obstacle.voidcontentsChanged(LabelingModelEvent event)Overridden version of the base class method to allow the layout to automatically update the label positions when a related obstacle is moved.IlvLabelLayoutcopy()Copies the layout instance.voidcopyParameters(IlvLabelLayout source)Copies the parameters from a given layout instance.protected IlvLabelLayoutLabelPropertycreateLayoutLabelProperty(String name, IlvGraphic label, boolean withDefaults)Returns a new instance ofIlvAnnealingLabelLayoutLabelPropertythat stores the parameter settings of this layout class for labels.protected IlvLabelLayoutManagerPropertycreateLayoutManagerProperty(String name, boolean withDefaults)Returns a new instance ofIlvAnnealingLabelLayoutManagerPropertythat stores the parameter settings of this layout class.voiddetach()Detaches the labeling model from the layout instance.intgetAllowedNumberOfIterations()Returns the maximum allowed number of iterations of the layout algorithm.IlvAutoLayoutHandlergetAutoLayoutHandler()Returns the auto layout handler.IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptorgetLabelDescriptor(Object label)Returns the descriptor of the label.IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptorProvidergetLabelDescriptorProvider()Returns the label descriptor provider.IlvLabelMovementPolicygetLabelMovementPolicy()Returns the label movement policy used during layout.doublegetLabelOffset()Returns the minimum offset between labels.EnumerationgetLabelsOfObstacle(Object obstacle)Returns the labels associated with an obstacle.intgetMaxNumberOfFailIterations()Returns the maximum number of iterations that doesn't improve the layout quality before the layout algorithm stops.doublegetMinImprovementPercentageToContinue()Returns the minimum required percentage the layout needs to improve over a couple of rounds before the layout algorithm stops.intgetNumberIterationsForMinImprovement()Returns the number of iterations performed to reach the minimum required percentage of layout quality improvement.doublegetObstacleOffset()Returns the global minimum offset between a label and an unrelated obstacle.IlvObstacleOffsetInterfacegetObstacleOffsetInterface()Returns the obstacle offset interface used during layout.protected voidinit()Initializes instance variables.booleanisAutoUpdate()Returnstrueif the automatic update of labels on geometry changes is enabled.booleanisUseQuadtree()Returnstrueif the quadtree is enabled.protected voidlayout(boolean redraw)Computes the layout using the Annealing Layout algorithm.voidrefreshAllLabelsOfObstacles()Refreshes all the labels associated with obstacles.voidrefreshLabelsOfObstacle(Object obstacle)Refreshes the labels associated with an obstacle.voidsetAllowedNumberOfIterations(int iterations)Sets the maximum allowed number of iterations of the layout algorithm.voidsetAutoLayoutHandler(IlvAutoLayoutHandler handler)Sets the auto layout handler.voidsetAutoUpdate(boolean flag)Enables the automatic update of labels on geometry changes.voidsetLabelDescriptor(Object label, IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor descriptor)Sets the descriptor of the label.voidsetLabelDescriptorProvider(IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptorProvider provider)Allows you to install a label descriptor provider.voidsetLabelMovementPolicy(IlvLabelMovementPolicy policy)Allows you to install a label movement policy, that is, an object that allows or prohibits a label being moved by the layout algorithm.voidsetLabelOffset(double offset)Sets the minimum offset between the border of neighbored labels.voidsetMaxNumberOfFailIterations(int iterations)Sets the maximum number of iterations that doesn't improve the layout quality before the layout algorithm stops.voidsetMinImprovementPercentageToContinue(double percentage)Sets the minimum required percentage the layout needs to improve over a couple of rounds before the layout algorithm stops.voidsetNumberIterationsForMinImprovement(int iterations)Sets the number of iterations performed to reach the minimum required percentage of layout quality improvement specified bysetMinImprovementPercentageToContinue(double).voidsetObstacleOffset(double offset)Sets the global minimum offset between a label and an unrelated obstacle.voidsetObstacleOffsetInterface(IlvObstacleOffsetInterface ifc)Allows you to install an obstacle offset interface, that is, an object that allows selecting specific minimum offsets between certain label/obstacle pairs.voidsetUseQuadtree(boolean flag)Enables the quadtree.booleansupportsAllowedTime()Indicates that this layout class can stop the layout computation when the user-defined allowed time is exceeded.booleansupportsPercentageComplete()Indicates that this layout class can estimate the percentage of completion during the run of layout.booleansupportsRandomGenerator()Indicates that this layout class uses randomly-generated numbers that can be initialized with a user-defined seed value.booleansupportsSaveParametersToNamedProperties()Indicates whether the layout class can transfer the layout parameters to named properties.booleansupportsStopImmediately()Indicates that this layout class can interrupt the current run of the layout immediately in a controlled way.voidupdateLabelPosition(Object label, boolean redraw)Update the position of the input label when the related obstacle has moved.-
Methods inherited from class ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout
addLabelLayoutEventListener, addLabelLayoutParameterEventListener, attach, attach, callLayoutStepPerformedIfNeeded, cleanLabelingModel, createLayoutReport, getAllowedTime, getCoordinatesMode, getInstanceId, getLabelingModel, getLayoutReport, getManager, getMinBusyTime, getSeedValueForRandomGenerator, increasePercentageComplete, isGeometryUpToDate, isInputCheckEnabled, isLayoutNeeded, isLayoutRunning, isLayoutRunning, isLayoutTimeElapsed, isParametersUpToDate, isStoppedImmediately, isStoppedPrematurely, isStructureUpToDate, isUseDefaultParameters, isUseSeedValueForRandomGenerator, layoutStepPerformed, onParameterChanged, onParameterChanged, performLayout, performLayout, removeLabelLayoutEventListener, removeLabelLayoutParameterEventListener, setAllowedTime, setCoordinatesMode, setGeometryUpToDate, setInputCheckEnabled, setLayoutReport, setLayoutRunning, setManager, setMinBusyTime, setParametersUpToDate, setSeedValueForRandomGenerator, setStructureUpToDate, setUseDefaultParameters, setUseSeedValueForRandomGenerator, stopImmediately
-
-
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
IlvAnnealingLabelLayout
public IlvAnnealingLabelLayout()
Creates a new instance of the Annealing Layout algorithm.
To indicate the manager you want to lay out, use the methodattach(IlvManager).
To indicate the labeling model you want to lay out, use the methodattach(IlvLabelingModel).
To perform the layout, use the methodperformLayout.
To modify the layout parameters, use the different methods provided in this class and its superclass.
-
IlvAnnealingLabelLayout
public IlvAnnealingLabelLayout(IlvAnnealingLabelLayout source)
Creates a new label layout instance by copying an existing one. This constructor is used by thecopy()method. Any subclass should provide a copy constructor.Note that layout parameters which are specific to a label or obstacle are not copied. Global layout parameters are copied.
- Parameters:
source- The layout instance that is copied.
-
-
Method Detail
-
init
protected void init()
Initializes instance variables.You should not call this method directly. The method is called internally by the constructor without arguments and by the copy constructor. The method must be overridden by subclasses that need to initialize additional instance variables.
- Overrides:
initin classIlvLabelLayout
-
copy
public IlvLabelLayout copy()
Copies the layout instance.This method copies the layout instance by calling the copy constructor.
- Specified by:
copyin classIlvLabelLayout- Returns:
- A copy of the layout instance.
- See Also:
IlvAnnealingLabelLayout(IlvAnnealingLabelLayout),copyParameters(IlvLabelLayout)
-
copyParameters
public void copyParameters(IlvLabelLayout source)
Copies the parameters from a given layout instance.Note that layout parameters which are specific to a label or obstacle are not copied. Global layout parameters are copied.
- Overrides:
copyParametersin classIlvLabelLayout- Parameters:
source- The layout instance from which the parameters are copied.- See Also:
copy()
-
detach
public void detach()
Detaches the labeling model from the layout instance.When a new labeling model is attached to the layout instance, it is not necessary to detach the previously attached labeling model because this is done automatically when the method
IlvLabelLayout.attach(IlvLabelingModel)is called.This method performs cleaning operations on the labeling model. In addition to the cleaning operations in the base class, Annealing Label Layout removes the label descriptors per label.
Note that you must call this method when you no longer need the layout instance; otherwise, some objects may not be garbage collected.
- Overrides:
detachin classIlvLabelLayout- See Also:
IlvLabelLayout.attach(IlvLabelingModel),setLabelDescriptor(Object, IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor)
-
cleanLabel
public void cleanLabel(IlvLabelingModel labelingModel, Object label)
Cleans a label. This method removes any data that has been stored by the layout algorithm on a label. In addition to the cleaning operations in the base class, Annealing Label Layout removes the label descriptors of the label.- Overrides:
cleanLabelin classIlvLabelLayout- Parameters:
labelingModel- The graph model thelabelbelongs tolabel- The label to be cleaned- See Also:
detach()
-
cleanObstacle
public void cleanObstacle(IlvLabelingModel labelingModel, Object obstacle)
Cleans an obstacle. This method removes any data that has been stored by the layout algorithm on an obstacle.- Overrides:
cleanObstaclein classIlvLabelLayout- Parameters:
labelingModel- The graph model theobstaclebelongs toobstacle- The obstacle to be cleaned- See Also:
detach()
-
contentsChanged
public void contentsChanged(LabelingModelEvent event)
Overridden version of the base class method to allow the layout to automatically update the label positions when a related obstacle is moved.If the auto update is enabled (that is,
isAutoUpdate()returnstrue) the method checks whether an auto layout handler is installed. If a handler is installed, it callsIlvAutoLayoutHandler.performAutoLayout(Object, Vector), passingthisas layout and the vector of changed objects. Otherwise it simply calls the methodupdateLabelPosition(Object, boolean)in order to reposition the labels accordingly.- Specified by:
contentsChangedin interfaceLabelingModelListener- Overrides:
contentsChangedin classIlvLabelLayout- Parameters:
event- The event indicating the change that has occurred in the labeling model.- See Also:
setAutoUpdate(boolean),setAutoLayoutHandler(IlvAutoLayoutHandler),updateLabelPosition(Object, boolean)
-
setAutoLayoutHandler
public void setAutoLayoutHandler(IlvAutoLayoutHandler handler)
Sets the auto layout handler.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
getAutoLayoutHandler(),setAutoUpdate(boolean),contentsChanged(LabelingModelEvent)
-
getAutoLayoutHandler
public IlvAutoLayoutHandler getAutoLayoutHandler()
Returns the auto layout handler.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
setAutoLayoutHandler(IlvAutoLayoutHandler),setAutoUpdate(boolean),contentsChanged(LabelingModelEvent)
-
updateLabelPosition
public void updateLabelPosition(Object label, boolean redraw)
Update the position of the input label when the related obstacle has moved. For instance this is useful if a label assigned to a node should follow the node on movements. It does not perform a full layout and does not try to avoid overlaps.The normal usage of this method is to install a listener on the related object of the label that gets notified about the object movements. When notified, the listener should call this method to update the label position depending on the new position of the related object.
- Parameters:
label- The input label.redraw- The flag indicating if the label must be redraw immediately.- See Also:
LabelingModelListener,contentsChanged(LabelingModelEvent),setAutoUpdate(boolean)
-
layout
protected void layout(boolean redraw)
Computes the layout using the Annealing Layout algorithm. To start the layout, call the methodIlvLabelLayout.performLayout(boolean, boolean).- Specified by:
layoutin classIlvLabelLayout- Parameters:
redraw- Iftrue, the attached labeling model will be asked to redraw the manager after layout. When the layout algorithm moves the labels, it is required to pass the value of theredrawargument to the methodIlvLabelingModel.moveLabel(Object, double, double, boolean).- See Also:
IlvLabelLayout.performLayout(boolean, boolean)
-
getLabelsOfObstacle
public Enumeration getLabelsOfObstacle(Object obstacle)
Returns the labels associated with an obstacle. Returns all labels that have a label descriptor that has the input object as related obstacle.- Parameters:
obstacle- The input obstacle.- Returns:
- The labels associated with the given obstacle.
- Since:
- JViews 8.0
- See Also:
IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor.getRelatedObstacle()
-
refreshLabelsOfObstacle
public void refreshLabelsOfObstacle(Object obstacle)
Refreshes the labels associated with an obstacle. After replacing a node in a graph, the link obstacles forget their labels associated with them. This method allows to refresh the labels associated with an obstacle in this case, so that the methodgetLabelsOfObstacle(Object)returns the correct associated labels.- Parameters:
obstacle- The input obstacle.- Since:
- JViews 8.1
- See Also:
getLabelsOfObstacle(Object),refreshAllLabelsOfObstacles()
-
refreshAllLabelsOfObstacles
public void refreshAllLabelsOfObstacles()
Refreshes all the labels associated with obstacles. After replacing a node in a graph, the link obstacles forget their labels associated with them. This method allows to refresh the labels associated with an obstacle in this case, so that the methodgetLabelsOfObstacle(Object)returns the correct associated labels.- Since:
- JViews 8.1
- See Also:
getLabelsOfObstacle(Object),refreshLabelsOfObstacle(Object)
-
setLabelDescriptor
public void setLabelDescriptor(Object label, IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor descriptor)
Sets the descriptor of the label. In order to perform layout, the Simulated Annealing algorithm needs to know to which place a label should move. This is the purpose of the label descriptor. The algorithm will only move labels that have a descriptor.For instance, to specify that a label should move close to an
IlvGraphicthat represents a city on a geographic map, use anIlvAnnealingPointLabelDescriptor. In order to specify that a label should be placed on a link, use anIlvAnnealingLinkLabelDescriptor.Label descriptors cannot be shared. You have to allocate a different label descriptor for each label.
There are two possibilities to specify the label descriptor: either iterate over the labels and call
setLabelDescriptorfor each label, or specify a label descriptor provider that allocates the label descriptors on the fly when needed.- Parameters:
label- The label.descriptor- The label descriptor.- See Also:
setLabelDescriptorProvider(IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptorProvider),getLabelDescriptor(Object),IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor,IlvAnnealingPointLabelDescriptor,IlvAnnealingPolylineLabelDescriptor
-
getLabelDescriptor
public IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor getLabelDescriptor(Object label)
Returns the descriptor of the label.- Parameters:
label- The label.- Returns:
- The label descriptor.
- See Also:
setLabelDescriptor(Object, IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor)
-
setLabelDescriptorProvider
public final void setLabelDescriptorProvider(IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptorProvider provider)
Allows you to install a label descriptor provider. In order to perform layout, the Simulated Annealing algorithm needs to know to which place a label should move. This is the purpose of the label descriptor. The algorithm will only move labels that have a descriptor.For instance, to specify that a label should move close to an
IlvGraphicthat represents a city on a geographic map, use anIlvAnnealingPointLabelDescriptor. In order to specify that a label should be placed on a link, use anIlvAnnealingLinkLabelDescriptor.Label descriptors cannot be shared. You have to allocate a different label descriptor for each label.
There are two possibilities to specify the label descriptor: either iterate over the labels and call
setLabelDescriptor(Object, IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor)for each label, or specify a label descriptor provider that allocates the label descriptors on the fly when needed. The label descriptor provider is in particular useful if your application knows which labels belong to which related obstacle through the design of the data structures of labels and obstacles, so that there is no need to specify label descriptors in advance.- Parameters:
provider- The label descriptor provider.- Since:
- JViews 8.5
- See Also:
setLabelDescriptor(Object, IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor),getLabelDescriptorProvider()
-
getLabelDescriptorProvider
public final IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptorProvider getLabelDescriptorProvider()
Returns the label descriptor provider. Returnsnullif none is specified.- Since:
- JViews 8.5
- See Also:
setLabelDescriptorProvider(IlvAnnealingLabelDescriptorProvider)
-
setLabelOffset
public final void setLabelOffset(double offset)
Sets the minimum offset between the border of neighbored labels. Simulated annealing is a quality controlled iterative heuristic. It will not always satisfy the minimum offset, but it will include the minimum offset in the calculation of the quality after each iteration step, hence, the majority of labels will most likely preserve the minimum offset at the end of layout.Very large minimum offsets may slow down the layout considerably.
The default value is
0.- See Also:
getLabelOffset()
-
getLabelOffset
public final double getLabelOffset()
Returns the minimum offset between labels.- See Also:
setLabelOffset(double)
-
setObstacleOffset
public final void setObstacleOffset(double offset)
Sets the global minimum offset between a label and an unrelated obstacle. Typically, a label should not be placed too close to unrelated obstacles. The global obstacle offset is used if no obstacle offset interface is installed. Otherwise, seesetObstacleOffsetInterface(IlvObstacleOffsetInterface). The minimum offset is not used for the related obstacle of the label, if any (seeIlvAnnealingPointLabelDescriptor.getRelatedObstacle()andIlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor.considerObstacle(Object)).Simulated annealing is a quality controlled iterative heuristic. It will not always satisfy the minimum offset, but it will include the minimum offset in the calculation of the quality after each iteration step; hence, the majority of labels will most likely preserve the minimum offset at the end of layout.
Very large minimum offsets may slow down the layout considerably. It is not recommended to set the global obstacle offset to an unreasonably high value such as
Double.MAX_VALUE, because this causes computational problems inside quadtree operations (seesetUseQuadtree(boolean)).The default value is
0.- Parameters:
offset- The offset value to set.- See Also:
getObstacleOffset(),setObstacleOffsetInterface(IlvObstacleOffsetInterface)
-
getObstacleOffset
public final double getObstacleOffset()
Returns the global minimum offset between a label and an unrelated obstacle.- See Also:
setObstacleOffset(double)
-
setObstacleOffsetInterface
public final void setObstacleOffsetInterface(IlvObstacleOffsetInterface ifc)
Allows you to install an obstacle offset interface, that is, an object that allows selecting specific minimum offsets between certain label/obstacle pairs. It can be used to modify the effect of the global obstacle offset parameter. Typically, a label should not be placed too close to unrelated obstacles. The global obstacle offset (seesetObstacleOffset(double)) specifies globally the minimum offset between labels and unrelated obstacles. The obstacle offset interface can be used to make this minimum offset smaller for specific label/obstacle pairs, hence allowing the label to move closer to the corresponding obstacle than specified by the global obstacle offset. The obstacle offset is not used for the related obstacle of the label, if any (seeIlvAnnealingPointLabelDescriptor.getRelatedObstacle()andIlvAnnealingLabelDescriptor.considerObstacle(Object)).If an obstacle offset interface is installed, the effective minimum offset between a label and an obstacle is the minimum of the value provided by
getObstacleOffset()and the value provided by the obstacle interface. As an example, assume the labels in general must be at least 10 units apart from unrelated obstacles, except for a specific label "X" that can move as close as 3 units to specific obstacles "A" and "B". You specify this by setting the global obstacle offset to 10, and by installing an obstacle offset interface that returns 3 for the callgetOffset(model, X, A)and for the callgetOffset(model, X, B), while it returnsDouble.MAX_VALUEfor all other combinations of labels and obstacles.The obstacle offset interface cannot be used to make a minimum obstacle offset larger than the global obstacle offset. The global obstacle offset is always the upper limit, that is, if the obstacle offset interface returns larger values than the global obstacle offset, then the global offset is used.
- Parameters:
ifc- The obstacle offset interface to set.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
getObstacleOffsetInterface(),IlvObstacleOffsetInterface
-
getObstacleOffsetInterface
public final IlvObstacleOffsetInterface getObstacleOffsetInterface()
Returns the obstacle offset interface used during layout. The method returnsnullif none is specified.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
setObstacleOffsetInterface(IlvObstacleOffsetInterface)
-
setAllowedNumberOfIterations
public final void setAllowedNumberOfIterations(int iterations)
Sets the maximum allowed number of iterations of the layout algorithm.Simulated annealing is a quality controlled, randomized iterative heuristic. It does not guarantee a placement of the labels without overlaps. However, the more iterations, the higher the probability that the heuristic ends up with a high quality layout without overlaps.
- See Also:
getAllowedNumberOfIterations()
-
getAllowedNumberOfIterations
public final int getAllowedNumberOfIterations()
Returns the maximum allowed number of iterations of the layout algorithm.- See Also:
setAllowedNumberOfIterations(int)
-
setMaxNumberOfFailIterations
public final void setMaxNumberOfFailIterations(int iterations)
Sets the maximum number of iterations that doesn't improve the layout quality before the layout algorithm stops.Simulated annealing is a quality controlled, randomized iterative heuristic. If after the specified number of iterations, the quality did not improve, the algorithm gives up. Hence, setting the maximum number to a high value avoids that the layout algorithm gives up too early, resulting in a better quality of the layout. Setting the maximum number to a low value speeds up the algorithm.
The default value is 20.
- See Also:
getMaxNumberOfFailIterations()
-
getMaxNumberOfFailIterations
public final int getMaxNumberOfFailIterations()
Returns the maximum number of iterations that doesn't improve the layout quality before the layout algorithm stops.- See Also:
setMaxNumberOfFailIterations(int)
-
setMinImprovementPercentageToContinue
public final void setMinImprovementPercentageToContinue(double percentage)
Sets the minimum required percentage the layout needs to improve over a couple of rounds before the layout algorithm stops.Simulated annealing is a quality controlled, randomized iterative heuristic. If, after the specified number of iterations, the quality did not improve at least by the specified percentage, the algorithm gives up. Hence, setting the percentage to 0 avoids that the layout algorithm gives up too early, resulting in a better quality of the layout. Setting the percentage to a high number speeds up the algorithm. Useful percentage values are between 0 and 5%.
The default value is 0.5%.
By default, the algorithm performs five iterations to reach at least 0.5% improvement of the quality. The number of iterations that are taken to reach the minimum percentage of improvement can be set by
setNumberIterationsForMinImprovement(int).- Parameters:
percentage- The minimum improvement value, as a percentage.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
getMinImprovementPercentageToContinue(),setNumberIterationsForMinImprovement(int)
-
getMinImprovementPercentageToContinue
public final double getMinImprovementPercentageToContinue()
Returns the minimum required percentage the layout needs to improve over a couple of rounds before the layout algorithm stops.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
setMinImprovementPercentageToContinue(double)
-
setNumberIterationsForMinImprovement
public final void setNumberIterationsForMinImprovement(int iterations)
Sets the number of iterations performed to reach the minimum required percentage of layout quality improvement specified bysetMinImprovementPercentageToContinue(double).Simulated annealing is a quality controlled, randomized iterative heuristic. If, after the specified number of iterations, the quality did not improve at least by the specified percentage, the algorithm gives up. Hence, setting the number of iterations to a high value avoids the layout algorithm giving up too early, resulting in a better quality of the layout. Setting the number of iterations to a small number speeds up the algorithm. Useful values are between 1 and 30.
The default value is 5.
- Parameters:
iterations- The number of iterations to reach the minimum improvement.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
getNumberIterationsForMinImprovement(),setMinImprovementPercentageToContinue(double)
-
getNumberIterationsForMinImprovement
public final int getNumberIterationsForMinImprovement()
Returns the number of iterations performed to reach the minimum required percentage of layout quality improvement.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
setNumberIterationsForMinImprovement(int)
-
setUseQuadtree
public final void setUseQuadtree(boolean flag)
Enables the quadtree. The quadtree speeds up the layout algorithm if there is a large amount of labels and the underlying labeling model is bounding box dependent.The quadtree is enabled by default.
-
isUseQuadtree
public final boolean isUseQuadtree()
Returnstrueif the quadtree is enabled.- See Also:
setUseQuadtree(boolean)
-
setLabelMovementPolicy
public final void setLabelMovementPolicy(IlvLabelMovementPolicy policy)
Allows you to install a label movement policy, that is, an object that allows or prohibits a label being moved by the layout algorithm.An example of a label movement policy is an application that has its own preprocessing phase for the label positions, so that the label layout should treat only the remaining labels that the preprocessing phase could not handle. For instance, the movement policy could check which labels overlap with other labels and obstacles, and then move only these overlapping labels, and keep those labels fixed that are initially overlap-free. (This particular policy is available by the class
IlvOverlappingLabelMovementPolicy).- Parameters:
policy- The label movement policy.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
getLabelMovementPolicy()
-
getLabelMovementPolicy
public final IlvLabelMovementPolicy getLabelMovementPolicy()
Returns the label movement policy used during layout. Returnsnullif none is specified.- Since:
- JViews 5.5
- See Also:
setLabelMovementPolicy(IlvLabelMovementPolicy)
-
setAutoUpdate
public final void setAutoUpdate(boolean flag)
Enables the automatic update of labels on geometry changes. If enabled, a label follows its related obstacle whenever the obstacle is moved or resized. It callsupdateLabelPosition(Object, boolean)for each label that has a point label descriptor or polyline label descriptor with a related obstacle that was moved or resized.It is disabled by default.
It is designed to automatically update the labels during interactions. Hence, it is optimized for speed: It does not perform a full layout and does not try to avoid overlaps.
If the default labeling model is used, the automatic update is not always performed on zoom level changes. This may lead to undesired results with nonzoomable objects (see
IlvGraphic.zoomable()). We recommend to use zoomable objects.
-
isAutoUpdate
public final boolean isAutoUpdate()
Returnstrueif the automatic update of labels on geometry changes is enabled.- See Also:
setAutoUpdate(boolean)
-
supportsPercentageComplete
public final boolean supportsPercentageComplete()
Indicates that this layout class can estimate the percentage of completion during the run of layout.- Overrides:
supportsPercentageCompletein classIlvLabelLayout- Returns:
- always
true. - See Also:
IlvLabelLayout.increasePercentageComplete(int),IlvLabelLayoutReport.getPercentageComplete()
-
supportsRandomGenerator
public final boolean supportsRandomGenerator()
Indicates that this layout class uses randomly-generated numbers that can be initialized with a user-defined seed value. When you perform the layout several times on the same graph and use the same user-defined seed value, you obtain the same drawing of the grapher. If you want different drawings each time you perform the layout, you should modify the seed value and call the methoduseSeedValueForRandomGeneratorwith atrueargument.- Overrides:
supportsRandomGeneratorin classIlvLabelLayout- Returns:
- always
true. - See Also:
IlvLabelLayout.setSeedValueForRandomGenerator(long),IlvLabelLayout.getSeedValueForRandomGenerator(),IlvLabelLayout.setUseSeedValueForRandomGenerator(boolean),IlvLabelLayout.isUseSeedValueForRandomGenerator()
-
supportsAllowedTime
public final boolean supportsAllowedTime()
Indicates that this layout class can stop the layout computation when the user-defined allowed time is exceeded. The result code in the layout report isIlvLabelLayoutReport.STOPPED_AND_VALIDin this case, if all labels were moved at least once to a better position, andIlvLabelLayoutReport.STOPPED_AND_INVALIDotherwise.- Overrides:
supportsAllowedTimein classIlvLabelLayout- Returns:
- always
true. - See Also:
IlvLabelLayout.setAllowedTime(long),IlvLabelLayout.getAllowedTime(),IlvLabelLayoutReport.getCode()
-
supportsStopImmediately
public boolean supportsStopImmediately()
Indicates that this layout class can interrupt the current run of the layout immediately in a controlled way. The result code in the layout report isIlvLabelLayoutReport.STOPPED_AND_VALIDin this case, if all labels were moved at least once to a better position, andIlvLabelLayoutReport.STOPPED_AND_INVALIDotherwise.- Overrides:
supportsStopImmediatelyin classIlvLabelLayout- Returns:
- always
true. - See Also:
IlvLabelLayout.stopImmediately(),IlvLabelLayout.isStoppedImmediately(),IlvLabelLayoutReport.getCode()
-
supportsSaveParametersToNamedProperties
public boolean supportsSaveParametersToNamedProperties()
Indicates whether the layout class can transfer the layout parameters to named properties. This mechanism can be used if layout parameters must be stored persistently in an.ivlfile.- Overrides:
supportsSaveParametersToNamedPropertiesin classIlvLabelLayout- Returns:
- Always
true. - See Also:
IlvDefaultLabelingModel.saveParametersToNamedProperties(ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout, boolean),IlvDefaultLabelingModel.loadParametersFromNamedProperties(ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout),IlvDefaultLabelingModel.removeParametersFromNamedProperties()
-
createLayoutManagerProperty
protected IlvLabelLayoutManagerProperty createLayoutManagerProperty(String name, boolean withDefaults)
Returns a new instance ofIlvAnnealingLabelLayoutManagerPropertythat stores the parameter settings of this layout class.The method is used by
IlvDefaultLabelingModel.saveParametersToNamedProperties(IlvLabelLayout, boolean)to create a named property that contains parameter settings of this layout instance.- Overrides:
createLayoutManagerPropertyin classIlvLabelLayout- See Also:
IlvLabelLayoutManagerProperty,IlvDefaultLabelingModel.saveParametersToNamedProperties(ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout, boolean),IlvDefaultLabelingModel.loadParametersFromNamedProperties(ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout),IlvDefaultLabelingModel.removeParametersFromNamedProperties()
-
createLayoutLabelProperty
protected IlvLabelLayoutLabelProperty createLayoutLabelProperty(String name, IlvGraphic label, boolean withDefaults)
Returns a new instance ofIlvAnnealingLabelLayoutLabelPropertythat stores the parameter settings of this layout class for labels.The method is used by
IlvDefaultLabelingModel.saveParametersToNamedProperties(IlvLabelLayout, boolean)to create a named property for a label that contains parameter settings of a layout instance for this label.- Overrides:
createLayoutLabelPropertyin classIlvLabelLayout- See Also:
supportsSaveParametersToNamedProperties(),IlvLabelLayoutLabelProperty,IlvDefaultLabelingModel.saveParametersToNamedProperties(ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout, boolean),IlvDefaultLabelingModel.loadParametersFromNamedProperties(ilog.views.graphlayout.labellayout.IlvLabelLayout),IlvDefaultLabelingModel.removeParametersFromNamedProperties()
-
-