Architecture of the table component
Like the other
JViews TGO components, the table component is based on the MVC architecture, which means that it has a model, a view and a controller associated with it. For a general introduction to the MVC architecture, see
Architecture of graphic components which describes the classes and features of the table component specific to each of the three modules of the MVC architecture, and also explains the role of the adapter.

Gives an overview of the MVC architecture of the table component.

Describes how to manage attributes (columns) and representation objects (rows) in the table.

Describes how to customize the representation of table cells.

Describes how to attach a controller to a table view.

Describes the classes of the table adapter.
Class overview
This topic describes the classes that you can use to create and manage tables. For a more detailed description, refer to the
overview-summary in the Rogue Wave®
JViews TGO Java API Reference Documentation. The classes are organized as follows:
MVC (model, view, controller) architecture
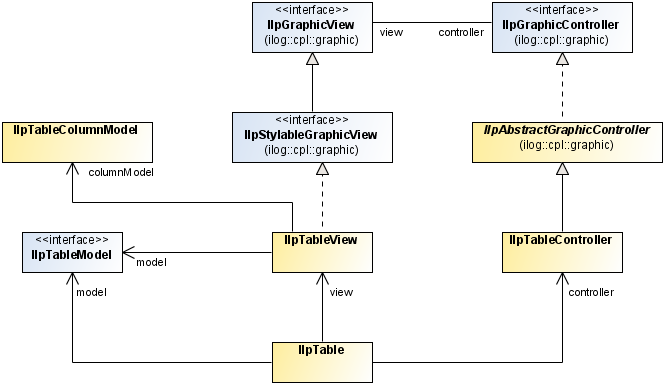
The MVC architecture for the table component is implemented by the following classes (see
Model, view, and controller for the table component):

The
IlpTableView class is the view module of the MVC architecture. It defines a Swing-based table used to display representation objects. It uses an
IlpTableModel as entry model.

The
IlpTableModel interface defines how the
IlpTableView can access representation objects and attributes. Implementations of this interface relate to the model module of the MVC architecture.

The
IlpTableColumnModel class defines which columns of the table model are visible, which are fixed, as well as the order and the size of the columns.

The
IlpTableController class represents the controller module of the MVC architecture. This class is used to define the behavior of the
IlpTableView. Its API contains methods to sort the table columns and to set interactors to the table.
Model, view, and controller for the table component
For general information about the model, the view, and the controller, see
Architecture of graphic components.
Representation model and representation objects
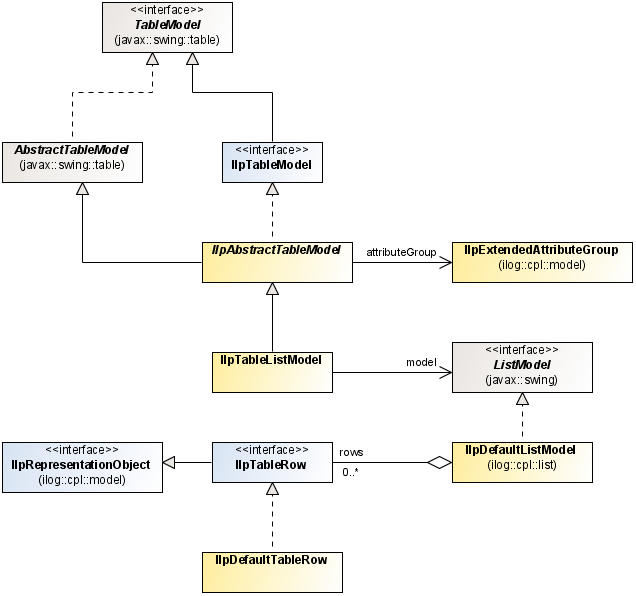
The representation model for the table component is implemented by the following classes (see
Representation model and representation objects for the table component):

The
IlpDefaultTableRow class is the default implementation of
IlpTableRow. It can use the attribute values of the representation object directly or take the attribute values of the corresponding business object.

The
IlpDefaultListModel class is provided to contain representation objects (
IlpTableRow instances) stored as a list.
Representation model and representation objects for the table component
For general information about the representation model and the representation objects, see
Architecture of graphic components.
Graphic view and renderers
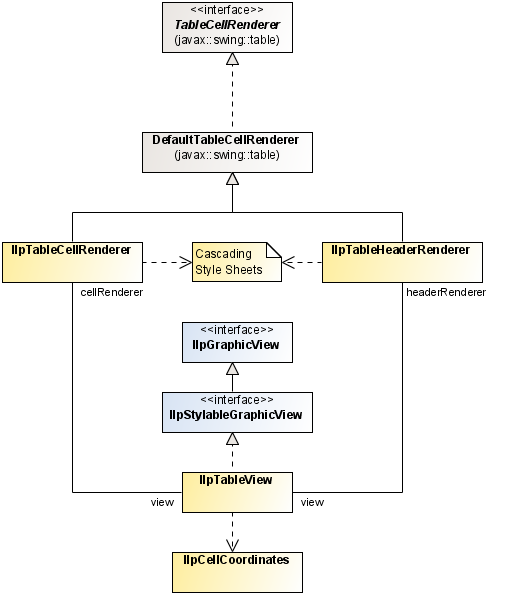
The graphic view and the renderers are implemented by the following classes (see
Graphic view and renderers for the table component):

The
IlpTableHeaderRenderer is used to render the column headers of the table (view). In each column header, it displays an icon, indicating the sorting direction and sorting order of the columns, and uses the style sheet information set to the table to get the column label and description.

The
IlpTableCellRenderer is used to render the cells of the table. It uses the style sheet information set to the table to retrieve the graphic characteristics needed to display the cell contents, such as label, icon, font, or color.
Graphic view and renderers for the table component
For general information about the graphic view and the rendering, see
Architecture of graphic components.
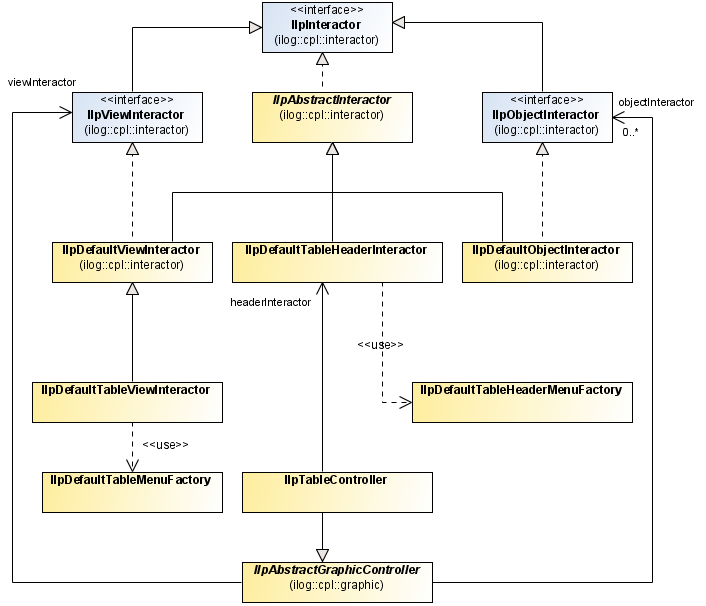
Controller and interactors
The controller and interactors of the table component are implemented by the following classes:
Controller and interactors for the table component
For general information about the controller and interactors, see
Architecture of graphic components.
The model
The table model provides the representation objects to be displayed in the associated table. It can be connected to a back-end application by means of an adapter. It refers to an attribute group
IlpExtendedAttributeGroup to determine which attributes of the representation objects are to be displayed. Each time an attribute is added to or removed from this attribute group, a column is added to or removed from the table. (For more information on attributes, see
Attribute API in the
Business Objects and Data Sourcesdocumentation.)
NOTE Each added column is arbitrarily placed at the end of the table, unless its position is defined as property index in the style sheets set to the table.
By default, the
IlpTableView creates an instance of
IlpTableListModel. This table model could be filled through an
IlpDefaultListModel connected to a back end or could be used directly.
When the table is to be connected to a back-end application, a data source and a list adapter must be instantiated. Both the data source and the default list model must be connected to the adapter.
Managing attributes (columns)
Attributes contain the values of the representation objects, or of the business objects related to the representation objects, to be shown in the table. Attributes are displayed in the columns of the table.
The
IlpAbstractTableModel class provides the following methods to manage these attributes:
 setAttributeGroup
setAttributeGroup sets the attribute group used by the table model to determine which attributes are to be shown. A call to this method does not empty the table model (which keeps its representation objects.)
NOTE The representation objects and the table model do not necessarily use the same attribute group: the table model can provide computed attributes with values that are not in the representation objects.
After a nonordered attribute group has been set to the table model, the attributes are alphabetically sorted in the table model. This constitutes the default order of the columns in the table. Each attribute added after the attribute group has been set to the table model is placed at the end of the table. This arbitrary order is modified when the property tableColumnOrder is defined for the accepted business class or when the property index is defined for the attribute represented in the column.
 getColumns
getColumns returns the attribute at the specified index.
 getColumnCount
getColumnCount returns the number of columns (attributes) contained in the table model.
 getColumnName
getColumnNamereturns the name of the column, the index of which is given as parameter. The column name is the same as the attribute name.
Managing representation objects (rows)
The
IlpTableListModel class, which extends
IlpAbstractTableModel, provides the following methods to manage the representation objects in a table. The representation objects correspond to the rows in the table. These rows must be instances of an implementation of
IlpTableRow.
 getRow
getRow returns the representation object (
IlpTableRow ) at the specified index.
 getRowCount
getRowCount returns the number of representation objects in the table model.
To add or remove representation objects when you do not use an adapter and a data source, you must use the following
IlpDefaultListModel methods:
 add
add adds a representation object,
o, to the table model (
o must be an
IlpTableRow).
 addAll
addAll adds a set of representation objects,
c, to the table model (
c must contain only
IlpTableRow instances).
 remove
remove removes the representation object whose index is given as parameter.
 remove
remove removes the specified representation object from the table model.
 clear
clear removes all the representation objects from the table model.
The view
The table view is responsible for displaying the graphic objects (table cells) and as such corresponds to the visible part of the architecture.
You can customize the representation of table cells by:
These ways are provided in addition to the CSS-based customization of the default table cell renderer as explained in
Customizing table cells in the
Styling documentation.
Using your own graphic representation
You can create an
IlvGraphic or a
JComponent directly by declaring the
class property and setting it in a CSS file.
The class property name is a reserved keyword that indicates the class name of the generated graphic object. JViews TGO provides a predefined representation for the objects in all graphic components, which means that the class property is optional. It can be used when you want to replace the predefined representation.
object."ilog.tgo.model.IltNetworkElement/label" {
class: ilog.views.sdm.graphic.IlvGeneralNode;
foreground: red;
label: @label;
}
IlpTableCellRenderer takes the information present in the CSS files to define how a table cell is rendered. If the property
class is specified, it defines the
IlvGraphic or
JComponent that will be used to render the table cell.
To use a cascading style sheet class property in a table view, do the following:
1. Implement your own graphic object or use an existing one, either as an IlvGraphic or as a JComponent.
2. Configure the properties of the objects or classes you want to represent with this property using CSS.
Using an arbitrary TableCellRenderer
The renderer used by an
IlpTableView is an
IlpTableCellRenderer. You can replace it with you own renderer, using the
setDefaultRenderer method. This renderer must implement the
TableCellRenderer interface.
To write your own renderer, do the following:
1. Implement the javax.swing.table.TableCellRenderer interface.
2. Configure your table component to use your renderer.
The following code extract shows how to configure an
IlpTableView to use the
MyTableCellRenderer class to render all table cells:
IlpTableView view = //access the table view
view.setDefaultRenderer(new MyTableCellRenderer());
The controller
The
IlpTableController class represents the controller module of the MVC architecture. It can be attached to a table view by using the following code.
How to attach a controller to the table view
IlpTableView tableView = new IlpTableView();
IlpTableController tableController = new IlpTableController();
tableView.setController(tableController);
Note that a controller is automatically attached to a table view when a table component is instantiated:
IlpTable tableComponent = new IlpTable();
IlpTableController controller = tableComponent.getController();
// tableComponent.getView().getController() == controller
When a controller is attached to a table view, the controller listens to the keyboard, mouse, and focus events that occur in the table and transfers them to the view interactor set to the controller.
Only one controller can be attached to a view at a time.
By default, the
IlpTableController delegates event management to an
IlpDefaultTableViewInteractor. However, you can specify another interactor by using the following code:
tableController.setViewInteractor(new MyInteractor());
When an interactor receives mouse events from the controller, it tries to recognize the associated user gestures. For example, when it receives an event MOUSE_PRESSED followed by an event MOUSE_RELEASED, the interactor recognizes the gesture BUTTON1_CLICKED. The set of basic gestures recognized by an interactor is defined in the class IlpGesture.
Interactors allow you to associate behavior with user gestures by means of Java™ actions. You can also associate actions with keyboard events.
The
IlpDefaultViewInteractor manages the events received from the controller in the following way:

If the event is a keyboard event, it checks whether an action has been associated with this key. If so, it triggers the action.

If the event occurred on an
IlpGraphic object or on a representation object, it delegates the event management to the
IlpObjectInteractor set to the controller, if any.

It checks whether the event corresponds to the display of a pop-up menu. If so, and if a pop-up menu is set to this interactor, it will display the pop-up menu and stop.

It tries to recognize gestures from the event. When a gesture is recognized, it triggers the action associated with this gesture, if any.
The API of the
IlpTableController also contains methods to sort the columns and filter the rows of the table view. See
Table component services.
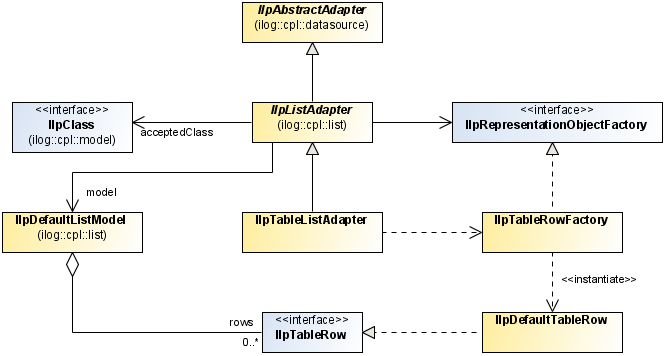
The adapter
The table adapter converts business objects retrieved from the associated data source to table rows. The table adapter is defined by the interface
IlpListAdapter. This adapter does not create representation objects in a table model but in a list model. This list model and the representation objects it contains are transformed into a table model at the level of the table component.
The default table adapter implementation provides the following services:
The following figure shows the table adapter classes:
Table adapter classes
A given
IlpListAdapter instance can only represent
IlpClass objects of the same type. So that only objects of a specific class or of one of its subclasses be represented, you should set this class with the
setAcceptedClass method.
How to create a table adapter by instantiating a table component
IlpTable ilpTable = new IlpTable();
IltDefaultDataSource dataSource = new IltDefaultDataSource();
ilpTable.setDataSource(dataSource, acceptedClass);
How to retrieve a table adapter
IlpTableListAdapter adapter = ilpTable.getAdapter();
How to set your own adapter to the table component
IlpTable ilpTable= new IlpTable();
IlpTableListAdapter adapter = new IlpTableListAdapter();
ilpTable.setAdapter(adapter);
ilpTable.setAcceptedClass(acceptedClass);
IltDefaultDataSource dataSource = new IltDefaultDataSource();
ilpTable.setDataSource(dataSource);
List adapters use by default an
IlpTableRowFactory that creates representation objects of type
IlpDefaultTableRow.
You can create a table adapter implicitly by instantiating the IlpTable component, as shown in the following example.
Representation object factory
The table adapter converts business objects retrieved from the associated data source to table rows. The new representation objects are created by a representation object factory. The factory interface varies according to the type of adapter. The table adapter uses by default an
IlpTableRowFactory that creates representation objects of type
IlpDefaultTableRow.
Editing
Adapter interfaces are read-only, meaning that they do not perform editing operations on the representation objects they create.
Copyright © 2018, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.