Map layers and map styles
Describes map layers and map styles.

Describes the classes provided for layers and styling.

Describes the classes that provide map layers for graphic objects.

Describes the class that provides composite layers.

Describes the class that provides label layers.

Describes the classes that provide grid layers.

Describes the facilities for map scales and layer styles.

Describes the facilities for map attribute filters.
Introduction to layers and styles
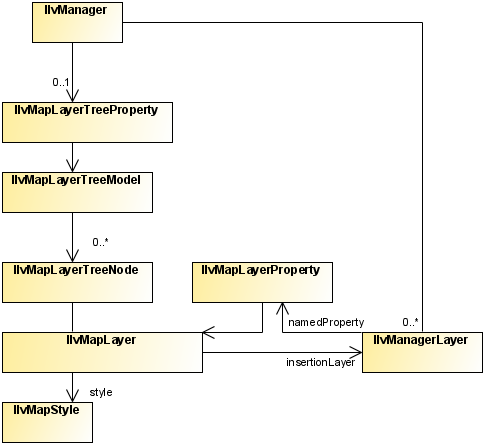
The class diagram for
layers and styles is shown in
Layer and Style UML Diagram.
Layer and Style UML Diagram
The source code for the Map Builder demonstration, which contains all of the code described in this section, can be found at
<installdir> /jviews-maps/samples/mapbuilder/index.html.
About map layers
The
IlvMapLayer class represents a map layer, that is, a cartographic
theme. It associates a style (
IlvMapStyle or one of its subclasses) with an
IlvManagerLayer containing graphic objects.
Map Layers are arranged in a tree structure, and stored in the manager using the
IlvMapLayerTreeProperty, see
Map layer tree.
Each map layer is attached to an
IlvMapLayerTreeNode, which contains the necessary information on parent and child layers. You can use this node to step through layer hierarchy as follows:
String SVGpath = "C:/maps/map.svg";
IlvSVGDataSource source = new IlvSVGDataSource(SVGpath);
source.setManager(getView().getManager());
source.setDestinationBounds(lonMinRad,latMinRad,lonMaxRad,latMaxRad);
NOTE Alternatively you can use a tailored transformation by calling IlvSVGDataSource.setInternalTransformation.
source.start();
IlvMapLayerTreeNode node = mapLayer.getNode();
for (int i = 0; i < node.getChildCount(); i++) {
IlvMapLayerTreeNode child=(IlvMapLayerTreeNode) node.getChildAt(i);
IlvMapLayer childLayer = (IlvMapLayer) node.getUserObject();
... do something with child layer
}
Most map layers are attached to a
data source, which is responsible for populating the manager layer with the correct graphic objects when the map data is loaded (possibly on-demand-loading) and reprojection times. The exception to this rule is the composite layer. Composite layers are only used to group a set of sub-layers and manage their styles using attribute inheritance (See below).
About map styles
Every style in
JViews Maps is a subclass of the base
IlvMapStyle class.
This class provides access to a set of attributes, usually also accessible by a setter/getter pair, depending on each style subclass.
For example, you can change the view visibility setting using on of:
style.setAttribute(IlvMapStyle.VISIBLE_IN_VIEW,Boolean.TRUE);
style.setVisibleInView(true);
You can catch any change in the map style by writing and registering a listener on it. For example:
StyleListener listener = new StyleListener() {
public void styleChanged(StyleEvent event) {
if(IlvMapStyle.ALPHA.equals(event.getAttribute())) {
// ... do something when transparency changes
}
}
};
...
myStyle.addStyleListener(listener);
Style hierarchy
Styles form a hierarchy and attribute values can be inherited through this hierarchy. If a style attribute is inherited from a parent style, that parent attribute value is used when displaying objects using that style.
Although not enforced in the API, it is recommended that you make the style hierarchy the same as the map layer hierarchy. This can be done when the map layer is inserted in the layer tree model:
IlvMapLayerTreeModel ltm =
IlvMapLayerTreeProperty.GetMapLayerTreeModel(manager);
ltm.addChild(parentLayer, layer);
IlvMapStyle parentStyle = layer.getParent().getStyle();
IlvMapStyle childStyle = layer.getStyle();
childStyle.setParent(parentStyle);
Common styling properties
Whatever the type of layer, its style always has the following base properties.
Common Styling Properties
Property name | Contents |
VISIBLE_IN_VIEW | Indicates whether the IlvManagerLayer is displayed on the map view. |
VISIBLE_IN_OVERVIEW | Indicates whether the IlvManagerLayer is displayed on the map overview. |
ATTRIBUTE_INFO | Contains the IlvAttributeInfoProperty used to describe all object properties. This is used to provide the list of possible property names displayed in the label attribute check box. This attribute cannot be changed by the user in the map layer tree panel. |
LABEL_ATTRIBUTE | Contains either a null value, or the name of the property used when labeling this map layer (chosen usually in the list provided by the ATTRIBUTE_INFO attribute). |
ALWAYS_ON_TOP | Indicates whether the attached map layer is placed on a normal or superimposing plane. This should be used only for overlay layers such as grids, labels, measures, and so on. |
LEGEND_GROUP | A logical name, used and displayed to group map layers in the legend. |
CATEGORY | An identifying name to group more than one layer on the same legend line. |
ALPHA | The level of transparency of the manager layer. |
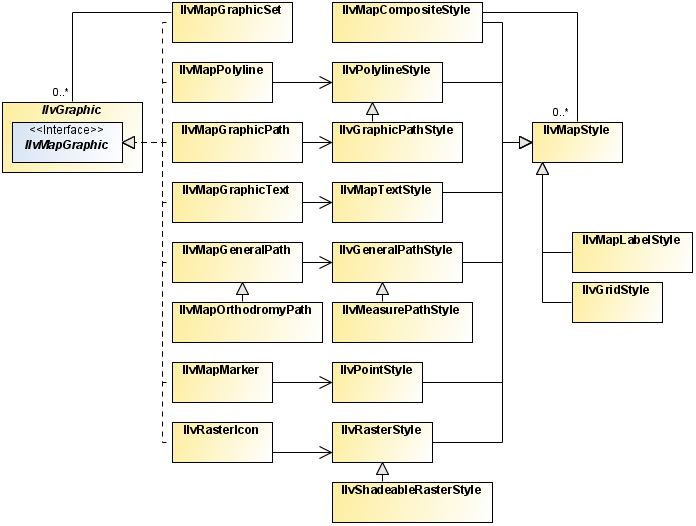
Map layers for graphic objects
The class diagram for map layers for graphic objects is shown in
Layers for Graphic Objects UML Diagram.
Layers for Graphic Objects UML Diagram
Most map layers are used to manage graphic objects created from map features imported from various map data files. The styling options differ according to the content of each file and the map features imported by the different readers. For example, you do not style a polygon the same way you do an altitude raster image.
The IlvGeneralPathStyle class
The
IlvGeneralPathStyle class is used for
IlvMapGeneralPath stylable graphic objects. Generally, most vectorial map renderers provide a
setUsingGeneralPath method to allow a choice between using general paths, which give a better aspect and capabilities, or regular polygons, which provide better performance.
General Path Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
FILL_PAINT | Paint object used to fill the shape. |
STROKE_PAINT | Paint object used when stroking the path. |
FILL_ON | Boolean indicating whether the inside of the object is filled. |
STROKE_ON | Boolean indicating whether the shape of the object is stroked. |
PAINT_ABSOLUTE | Boolean indicating whether the fill paint is adapted to the bounding rectangle of the object. |
STROKE_WIDTH | Stroke width. |
PAINT_ZOOMED | Boolean indicating whether the paint is zoomed according to the shape when the object is zoomed. |
END_CAP | Type of decoration applied to the ends of unclosed subpaths (see java.awt.BasicStroke ). |
LINE_JOIN | Type of decoration applied at the intersection of two path segments (see java.awt.BasicStroke ). |
LINE_STYLE | Float table indicating how to make a dash pattern by alternating between opaque and transparent sections (see java.awt.BasicStroke ). |
STROKE | Object used for stroking the path. This attribute is dependant on all stroke attributes and is recomputed when one of them changes.This attribute is not visible in the Map Layer Tree Panel. |
The IlvPolylineStyle class
The
IlvPolylineStyle class is used for
IlvMapPolyline stylable objects (polygons or polylines without fill).
Polyline Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
FOREGROUND | Color object used when drawing the polygon borders. |
LINE_WIDTH | Polygon borders line width. |
END_CAP | Type of decoration applied to the ends of unclosed subpaths (see java.awt.BasicStroke ). |
LINE_JOIN | Type of decoration applied at the intersection of two path segments (see java.awt.BasicStroke ). |
LINE_STYLE | Float table indicating how to make a dash pattern by alternating between opaque and transparent sections (see java.awt.BasicStroke ). |
DECORATION | Additional IlvPathDecoration object used for stroking the polygon. |
DECORATION_ONLY | Boolean indicating whether only the decoration is displayed. |
DECORATION_PAINT | Paint color of the decoration. By default (when this attribute is null), the decoration is colored using the FOREGROUND attribute. |
The IlvGraphicPathStyle class
The
IlvGraphicPathStyle class is a subclass of
IlvPolylineStyle and so provides all the attributes in
The IlvPolylineStyle class. It provides the style for
IlvMapGraphicPath objects (filled polygon areas), by adding:
Graphic Path Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
PAINT | Paint object used to fill the polygon area. |
DO_FILL | Boolean indicating whether the inside of the polygon is filled. |
DO_STROKE | Boolean indicating whether the borders of the polygon are stroked. |
The IlvPointStyle class
The
IlvPointStyle class controls the style of map point (
IlvMapPoint) objects. It provides the following attributes:
Point Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
FOREGROUND | Color object used for displaying the point. |
MARKER_SIZE | The size of the marker. |
MARKER_TYPE | The type of marker to use. |
The IlvMapTextStyle class
The
IlvMapTextStyle class controls the style of map stylable label objects (
IlvMapText). It provides the following attributes:
Map Text Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
ANTIALIASING | Boolean indicating whether text should be specifically antialiased (even if the view setting itself is different). |
ATTACHMENT | The label attachment. |
FILL_PAINT | Paint object used to fill the characters of the text. |
FONT | The label Font. |
FRAME_PAINT | Paint object used to draw the frame of the label. |
INNER_MARGIN | Spacing between the frame of the label and the text. |
INTERLINE | Spacing between two lines of text. |
MAXIMUM_HEIGHT | The maximum height of the label. |
MINIMUM_HEIGHT | The minimum height of the label. |
STROKE_PAINT | Paint object used to draw the shape of the text character. |
BACKGROUND_PAINT | Paint object used to fill the frame of the label. |
ALIGNMENT | Alignment of the multi-line text. |
The IlvRasterStyle class
The
IlvRasterStyle class is used with
IlvRasterIcon graphic objects, and provides attributes to control the appearance of the image:
Raster Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
BRIGHTNESS | A Double percentage applied to the color model to make the entire image brighter or darker. 0% gives a black image. |
CONTRAST | A Double percentage applied to the color model to increase the color difference. 0% gives a completely grey image. |
SATURATION | A Double percentage applied to the color model of the image to change the color saturation. 0% gives a completely grey image. |
COLOR_MODEL | The ColorModel object used to transform the pixel values of the image into RGBA colors. |
Composite layers
The IlvMapCompositeStyle class
The
IlvMapCompositeStyle class does not define any additional attributes. Its attribute list grows with its child list.
When adding a child style in a composite style, all the attributes of that child are added (if they did not exist) into the parent style. Those values can then be inherited for each child style – allowing the attributes for all children to be changed in one single place.
You can change the inheritance setting of each attribute by calling the
setInherited method.
Label layer
Label layers are created automatically on demand by the
IlvMapLabeler property installed on the manager when the LABEL_ATTRIBUTE style attribute is changed on a registered layer.
The IlvMapLabelStyle class
The
IlvMapLabelStyle class is used by the
IlvMapAreaLabel,
IlvMapLineLabel and
IlvMapPointLabel classes, and controls the labeling parameters:
Map Label Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
FOREGROUND | The Color used to display labels. |
LABEL_FONT | The Font of the labels. |
LABEL_STROKE | The Stroke object used to display label outlines (not visible to users). |
OUTLINE_COLOR | The Color of the label outline. |
DRAW_OUTLINE | Boolean indicating whether the outline is displayed. |
LABELLING_SMALL_AREAS | Boolean indicating whether areas too small to enclose their label are labeled. |
FOLLOW_PATH | Boolean indicating whether labels on polygons follow those polygons or are placed horizontally. |
Grid layers
The source code for the Map Builder demonstration, which contains all of the code described in this section, can be found at
<installdir> /jviews-maps/samples/mapbuilder/index.html.
The IlvAbstractBaseGrid class
The
IlvAbstractBaseGrid base class has subclasses
IlvMGRSGrid and
IlvLatLonGrid. It is a manager layer that, instead of drawing graphic objects (
IlvGraphic instances) added to it, displays a grid adapted to the current zoom level of the map.
This base grid also implements the
IlvManagerViewDecoration interface, which allows you to display the grid on the screen, but prevents it from being displayed on printed material.
The IlvMGRSGrid class
The
IlvMGRSGrid class displays a set of auto-adaptive MGRS standard grids and labels on top of a geographic view. This grid displays a list of Grid zones (either
UPS or
UTM zones), and their sub grids (100000m, 10000m, 1000m). Each grid or sub-grid is labeled using the standardized MGRS name for the current area.
You can create and add an MGRS grid on any geo-referenced manager view (that is, any view that supports the
IlvCoordinateSystemProperty). For example, to add an MGRS grid containing all MGRS zones as a decoration of the view:
IlvMGRSGrid grid = new IlvMGRSGrid();
IlvMGRSGridZone.addAllZones(grid);
view.addViewDecoration(grid);
The IlvLatLonGrid class
The
IlvLatLonGrid class displays a set of auto-adaptive grids and labels along latitude or longitude lines on top of a geographic view. If the grid is auto-adaptive, the step between each successive lat/lon line is dependant on the scale of the current view.
You can create and add an MGRS grid on any geo-referenced manager view (that is, any view that supports the
IlvCoordinateSystemProperty). For example, to create a lat/lon grid layer:
view.getManager().addLayer(new IlvLatLonGrid()-1);
By default, the
IlvLatLonGrid creates only the points at the corners of each grid square. If you are using a coordinate system that transforms the map in a non-linear way (such as Orthographic projection, UTM projection, and so on), you can increase the number of intermediate points on each grid square in order to show a smoother version of the grid:
lgrid.setSmoothness(4);
Writing specific grids
The easiest way to implement your own grid system is to start with an empty MGRS grid and then add your own zones to it. For examples of this, see the Map Builder GridManager class.
Integrating grids into map layers
As the grids are implemented as manager layers, you only need to connect these to an
IlvMapLayer.
This map layer must be created, styled and integrated in the map layer tree model:
IlvMapLayerTreeModel ltm =
IlvMapLayerTreeProperty.GetMapLayerTreeModel(view.getManager());
IlvMapLayer mapInsertionLayer = new IlvMapLayer();
mapInsertionLayer.setStyle(new IlvGridStyle());
ltm.addChild(null, mapInsertionLayer);
Then you can integrate the grid manager layer into it:
mapInsertionLayer.insert(grid);
You can also use an
IlvDelayedDecoration manager layer to encapsulate the grid. Whenever the user moves or zooms the grid rapidly, a simplified version of the grid is used, which displays more quickly. When the user stops moving or zooming the grid, the full grid is displayed:
IlvDelayedDecoration delayedGrid = new IlvDelayedDecoration(200);
delayedGrid.setDecoration(grid);
mapInsertionLayer.insert(delayedGrid);
The IlvGridStyle class
The
IlvGridStyle class is used when displaying grids. It defines the following attributes:
Grid Styling Properties
Property name | Content |
GRID_COLOR | The Color used to display grid lines. |
TEXT_FONT | The Font of grid labels. |
TEXT_COLOR | The Color used to display grid labels. |
OUTLINE_COLOR | The Color of the outline of the grid labels. |
Map scales and layer styles
As a result of the use of the
IlvMapStyleControllerProperty property of the manager (and its underlying
IlvMapStyleController), layer styles are dependant on the current scale of the map. Every style attribute of a map layer can be different at different scales.
One of the most widely used attribute changes is the VISIBLE_IN_VIEW attribute, which is used to show and hide different map layers at particular scales. Using the same mechanism, your users can also change colors, line thickness, decorations and so on. Whenever the scale changes, the scale controller can change the current map layer styles, if required. This change of style usually triggers a view repaint, because the attributes of the objects have changed.
Some objects also listen to these style changes in order to re-render themselves. For example, if the color model of a raster style changes, all the images that depend on the style need to be re-created.
You can add dynamic styles with API calls such as:
IlvMapStyleController themeControl=
IlvMapStyleControllerProperty.GetMapStyleController(view.getManager());
themeControl.addTheme(0.001,mapLayer,"new style");
themeControl.getStyle(mapLayer,0.001).setVisibleInView(true);
When you add dynamic styles, be careful to ensure that you still manage style inheritance. When adding a new map layer into a parent layer, you can do this as follows:
IlvMapDynamicStyle []t=themeControl.getThemes(mapLayer);
for (int i = 0; i < t.length; i++) {
t[i].getStyle().setParent(parentLayer.getStyle());
}
The source code for the Map Builder demonstration, which contains all of the code described in this section, can be found at
<installdir> /jviews-maps/samples/mapbuilder/index.html.
Map attribute filters
A
IlvMapAttributeFilter object is used to compute the value of a styling attribute from a value found in an
IlvGraphic instance. Typically, this value is retrieved from the
IlvFeatureAttributeProperty named property attached to a
IlvGraphic object. To install such a filter, you set it to an
IlvMapStyle object.
The following example shows a custom filter class that defines the foreground of map graphic objects according to their “VALUE” feature attribute.
/**
* Computes the foreground from a graphic's IlvFeatureAttribute
*/
class ColorAttributeFilter implements IlvMapAttributeFilter {
/**
* Method that returns the new color computed from the "VALUE"
* feature attribute. If DEFAULT_VALUE is returned, the style value on which
* the filter is installed will not be affected.
*/
public Object get(IlvGraphic g, String attributeName) {
if(IlvPolylineStyle.FOREGROUND.equals(attributeName)) {
IlvAttributeProperty p = (IlvAttributeProperty)
g.getNamedProperty(IlvAttributeProperty.NAME);
if(p == null)
return DEFAULT_VALUE;
Object o = p.getValue("VALUE");
Object ret = convertObjectToColor(o);
if(ret == null)
return DEFAULT_VALUE;
return ret;
}
}
The following code example shows how to install a custom filter class in a map layer style.
IlvMapAttributeFilter filter = new ColorAttributeFilter();
IlvMapLayer layer = getLayer();
IlvMapStyle style = layer.getStyle();
style.setAttributeFilter(filter);
Once the filter is installed, each request to retrieve an attribute value is passed to the get method of the filter.
Copyright © 2018, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.