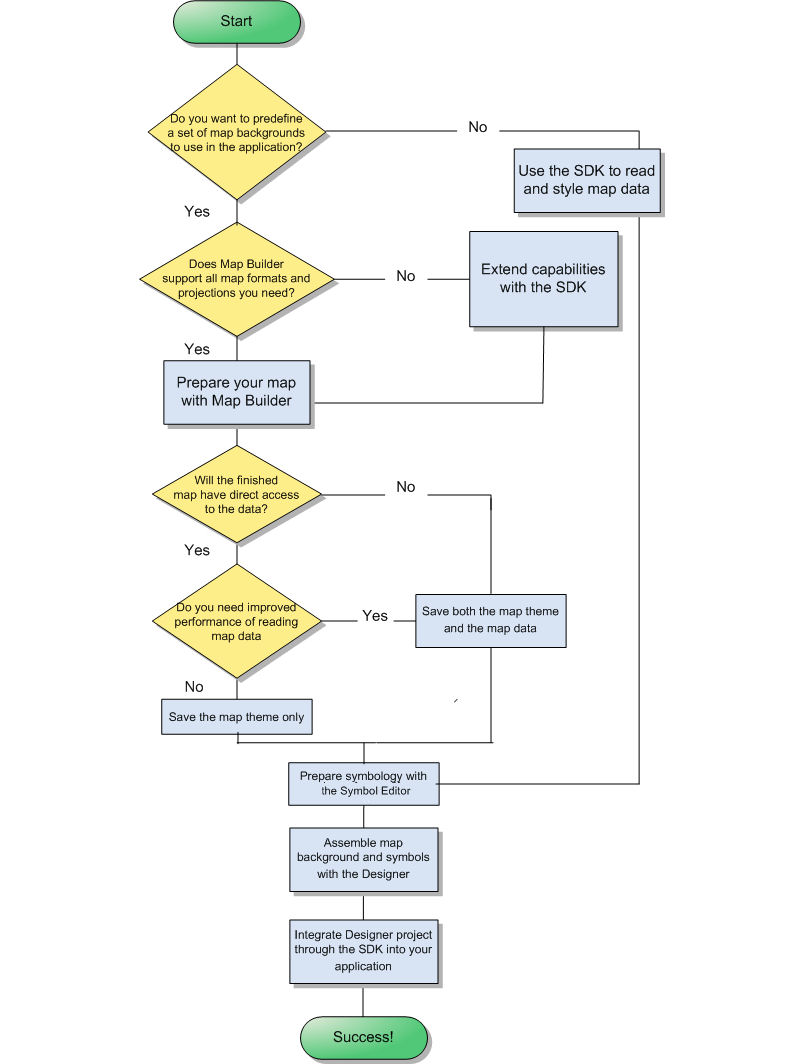
The process flow
Explains the process of building a map.

Illustrates with a diagram the process of building a map.

Explains how to define background maps with the Map Builder or with the SDK.

Explains the tools involved in creating an application without predefined background maps.
Overview
The Map Building Process
Defining a set of background maps
If you want to define a set of background maps to use later in your application, it is best to start with the Map Builder. If the Map Builder does not contain what you need, you can extend the code of the sample with the SDK.
Using the Map Builder
The Map Builder is a ready made sample for preparing and styling maps. You can use this sample code as is or customize it. The Map Builder supports the following types of map:

TIFF file-based interchange format for georeferenced raster imagery (
.tif ) (see
GeoTIFF format )

MapInfo Interchange Format (
.mif ) (see
MIF file )

Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing system ( see
TIGER/Line) files (
.rt* )

Drawing Interchange Format (AutoCAD
DXF format) files (
.dxf )

Google Earth™ Keyhole Markup Language (KML) and KML Zipped (KMZ) formats (
.kml,
.kmz )( see
KML/ KMZ)

Digital Terrain Elevation Data
0,
1 and
2 (see
DTED format)

Global Topographic Data
DEM (see
GTOPO30)

Scalable Vector Graphic (.SVG) files
It supports the following coordinate systems:

Geographical

Albers Equal Area

Azimuthal Equidistant

Cassini

Cylindrical Equal Area

Eckert IV and Eckert VI

Equidistant Cylindrical Projection

French Lambert

Gnomonic

Lambert Azimuthal Equal Area, Lambert Conformal Conic, and Lambert Equal Area Conic

Mercator, Oblique Mercator, and Transverse Mercator

Miller Cylindrical

Mollweide

Orthographic

Polyconic

Robinson

Sinusoidal

Stereographic

Universal Polar Stereographic and Universal Transverse Mercator

Wagner IV
See
Creating a map with the Map Builder for how to prepare a map using one of these format and coordinate systems.
Extending the Map Builder with the SDK
You can extend the Map Builder code through the SDK to integrate a different format or coordinate system. The following sample shows you how to do that:
You can then prepare the map as indicated in
Creating a map with the Map Builder.
Toolchain for an application without predefined background maps
The simplest flow, but not necessarily the easiest approach, is to use the SDK to develop an application that reads and styles map data. You will need to feel comfortable using the Java™ API and syntax. See
Developing with the SDKs for more information.
When you have processed your map data, you can add symbology with the Designer for
JViews Diagrammer to design symbols to place on the map. You can do this through an easy-to-use point-and-click GUI. See
Creating a Symbol with the Symbol Editor.
See
Handling symbols for more about adding symbology to a map.
You need to integrate the Designer project file into the application that you developed with the SDK. The integration requires a short piece of uncomplicated Java code. See the sample
Loading maps and symbols with JViews Diagrammer.
Copyright © 2018, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.