Transforming Data Models
Describes how data models can be transformed into different models referring to the same data.

Describes the three types of transform grouped in the IlvTreeTableDataSource data source.

Describes the adapters that are used to transform your model.
The IlvTreeTableDataSource data source
The
IlvTreeTableDataSource is the basic data source that can be displayed by a treemap chart. It groups together three types of transforms in an easy-to-use API: filtering, sorting and partitioning. These transforms are optional.
The
IlvTreeTableDataSource can be connected to one of the instances of
IlvModelWithColumns:
The
IlvTreeTableDataSource can filter, sort and partition the data. In all cases, the resulting
IlvTreeListModel, accessible through
getTreeModel, is the result of these model operations. It is the
IlvTreeListModel that is displayed by the treemap chart renderer.
Filtering
The filtering transform hides some model objects from the resulting model. You can set a filter object by means of the method
setFilterCriterion. This filter object defines the objects that are available in the resulting model. In a tree model, when a tree node is hidden, the entire tree branch below is hidden as well.
NOTE Filtering is not available when the input model is an IlvFlatTableModel.
Sorting
The sorting transform sorts the objects according to a specific criterion. In the case of a tree model, it sorts also the children set of each tree node. The sort criterion is set by means of
setSortCriterion and enabled through
setSorting.
NOTE Sorting is not available when the input model is an IlvFlatTableModel.
The package
ilog.views.chart.datax.adapter.sort contains several
Comparator implementations that are useful in this context, like the following ones.
Partitioning
The partitioning transform turns a flat model into a tree model, according to one or several rules that describe which objects should be grouped together and at which level. Such a rule is known as
partitioner. Partitioners can be set by means of
setPartitionerFactories.
NOTE Partitioning is currently not available when the input model is already a tree model. This limitation may be lifted in a future release.
The package
ilog.views.chart.datax.adapter.partition contains several
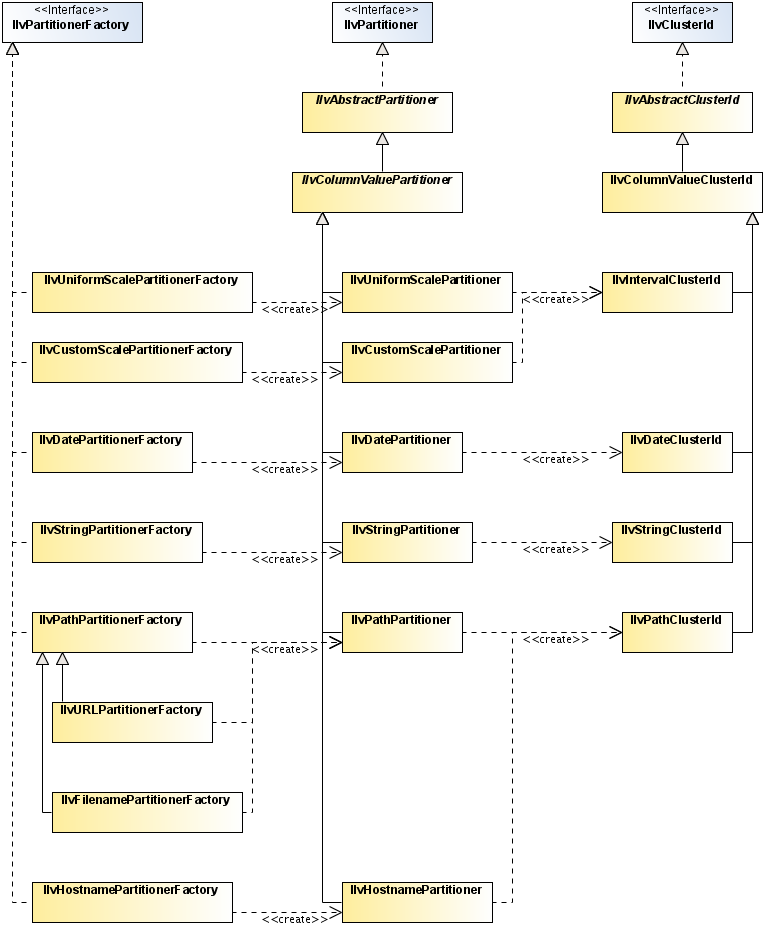
IlvPartitionerFactory implementations that are useful in this context. They all partition according to the value of the object in a given column, but act differently, depending on the value type and meaning.
 IlvPathPartitionerFactory
IlvPathPartitionerFactory partitions according to a string value, interpreting the string as a path, composed of path components separated through a given set of separators.
Here is an example showing the connection of an
IlvFlatListModel to an
IlvTreeTableDataSource, that groups the objects by country, sorts them alphabetically, and filters them to keep only those with positive performance.
final IlvFlatListModel model = ...;
IlvDataColumnInfo nameColumn = model.getColumn(0);
IlvDataColumnInfo countryColumn =
IlvColumnUtilities.getColumnByName(model, "Country");
final int performanceColumnIndex =
IlvColumnUtilities.getColumnIndexByName(model, "Performance");
// Create the data source.
IlvTreeTableDataSource dataSource = new IlvTreeTableDataSource();
dataSource.setUnderlyingModel(model);
// Activate filtering.
dataSource.setFilterCriterion(
new IlvAbstractFilter() {
public boolean evaluate(Object object) {
return model.getDoubleAt(object, performanceColumnIndex) >= 0;
}
});
// Activate sorting.
dataSource.setSortCriterion(
new IlvColumnValueComparator(model, nameColumn, null, false));
dataSource.setSorting(true);
// Activate partitioning.
dataSource.setPartitionerFactories(
new IlvPartitionerFactory[] {
new IlvStringPartitionerFactory(countryColumn)
});
Model adapters
The
IlvTreeTableDataSource uses some of the filtering, partitioning, and sorting adapters to perform the filtering, partitioning and sorting, as needed. However, sometimes it can be useful to perform these operations separately.
This can be the case when:

You need two filtering passes: one before partitioning and one after partitioning.

Your input model is not one of the five extended data models, but a Swing model.
To transform your model, you can use one of the following adapters:
All these adapters are located in the package
ilog.views.chart.datax.adapter.
Model Adapters Relationships
Adapters that Convert Models
The adapter listed in the table below convert one type of model into models of another type, as faithfully as possible.
| IlvTreeListToTreeSetModel IlvTreeListToFlatListModel IlvTreeListToFlatTableModel IlvTreeListToTreeTableModelFactory IlvTreeListToTreeModel |
| None |
| IlvFlatListToFlatSetModel IlvFlatListToFlatTableModel |
| IlvFlatSetToFlatTableModel |
| IlvFlatTableToFlatListModel IlvFlatTableToTableModel IlvFlatTableToListModel |
Adapters from IlvDataSource | IlvDataSourceToFlatTableModel |
Adapters from Swing TreeTableModel | IlvTreeTableToTreeListModel |
Adapters from Swing TreeModel | IlvTreeToTreeListModel IlvTreeToFlatTableModel |
Adapters from Swing TableModel | IlvTableToFlatTableModel |
Adapters from Swing ListModel | IlvListToFlatTableModel IlvListToFlatListModel |
Adapters for Filtering
These adapters perform the filtering transform of models, as discussed in the section
Filtering.
These adapters select a branch of a tree model.
Adapters for Sorting
These adapters perform the sorting transform of models, as discussed in the section
Sorting.
Adapters for Partitioning
These adapters perform the partitioning transform of models, as discussed in the section
Partitioning.
The partitioning transform introduces extra nodes in the resulting tree model. These extra nodes represent a group (cluster) of nodes and that were not present in the original model. These nodes are of the type
IlvClusterNode. By means of the method
getId you can retrieve information about the common properties of the cluster. This information is of the type
IlvClusterId. Each partitioner has a particular flavor of
IlvClusterId, as shown in the following table:
Partitioner | The IlvClusterId Class |
| IlvIntervalClusterId |
| IlvIntervalClusterId |
| IlvDateClusterId |
| IlvStringClusterId |
| IlvPathClusterId |
| IlvPathClusterId |
| IlvPathClusterId |
| IlvPathClusterId |
Here is an example showing how to convert a Swing
TableModel to an
IlvTreeListModel, that groups the rows by country, sorts them alphabetically, and filters them to keep only those with positive performance.
TableModel model = ...;
final int nameColumnIndex = 0;
final int countryColumnIndex = 2;
final int performanceColumnIndex = 3;
// Convert the model to a list of objects.
IlvFlatTableModel tableModel =
new IlvTableToFlatTableModel(model,
new IlvDataColumnInfo[] {
new IlvDefaultDataColumnInfo("Name", String.class),
new IlvDefaultDataColumnInfo("Founded", Date.class),
new IlvDefaultDataColumnInfo("Country", String.class),
new IlvDefaultDataColumnInfo("Performance", Double.class)
});
IlvDataColumnInfo nameColumn =
tableModel.getColumn(nameColumnIndex);
IlvDataColumnInfo countryColumn =
tableModel.getColumn(countryColumnIndex);
IlvFlatListModel listModel =
new IlvFlatTableToFlatListModel(tableModel);
// Add a filter.
IlvFlatListModel filteredModel =
new IlvFilteredFlatListModel(listModel,
new IlvAbstractFilter() {
public boolean evaluate(Object object) {
return model.getDoubleAt(object, performanceColumnIndex) >= 0;
}
});
// Add sorting.
IlvFlatListModel sortedModel =
new IlvSortedFlatListModel(filteredModel,
new IlvColumnValueComparator(sortedModel, nameColumn,
null, false));
// Add partitioning.
IlvTreeListModel partitionedModel =
new IlvFlatListToTreeListModel(sortedModel,
new IlvStringPartitionerFactory(countryColumn),
null, 1);
Copyright © 2018, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.