Random layout (RL)
Describes the Random layout algorithm.

Gives some samples of the random layout and explains where it is used.

Gives a list of features and limitations.

Describes the placement of the nodes and gives samples of the specifications.

Describes the generic features and parameters of the layout.

Describes the parameters specific to the Random layout.
RL sample
Describes the
Random Layout algorithm (class
IlvRandomLayout from the package
ilog.views.graphlayout.random).
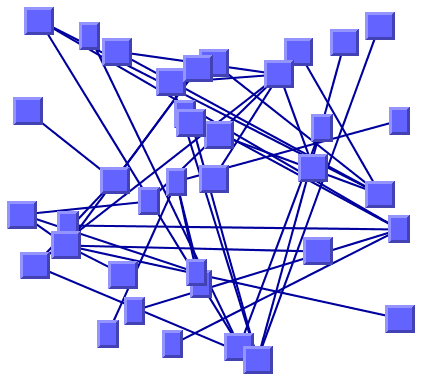
The following figure shows a sample drawing produced with the Random Layout (RL).
Graph drawing produced with the Random Layout
What types of graphs suit the RL?
Any type of graph:
Features and limitations of the RL
Features
Random placement of the nodes of a grapher inside a specified region.
Limitations

The algorithm computes random coordinates for the upper-left corner of the graphic objects representing the nodes. In some cases, it might not be appropriate.

To ensure that the nodes do not overlap the margins of the layout region, the algorithm computes the coordinates randomly inside a region whose width and height are those of the specified layout region reduced by the maximum width and height of the nodes. In some cases, it might not be appropriate.
The RL algorithm
The Random Layout (RL) algorithm is not really a layout algorithm. It simply places the nodes at randomly computed positions inside a user-defined region. Nevertheless, the Random Layout algorithm can be useful when a random, initial placement is needed by another layout algorithm or in cases where an aesthetic, readable drawing is not important.
Example of RL
In CSS
The following sample CSS specification uses the Random Layout algorithm. The CSS specification can be loaded as style file into an application that uses the
IlvDiagrammer class (see
Graph layout in Rogue Wave JViews Diagrammer).
SDM {
GraphLayout : "true";
LinkLayout : "false";
}
GraphLayout {
linkStyle : "STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE";
}
In Java™
The following code sample uses the
IlvRandomLayout class. This code sample shows how to perform a Random Layout on a grapher directly without using a diagram component or any style sheet:
...
import ilog.views.*;
import ilog.views.graphlayout.*;
import ilog.views.graphlayout.random.*;
...
IlvGrapher grapher = new IlvGrapher();
IlvManagerView view = new IlvManagerView(grapher);
... /* Fill in here the grapher with nodes and links in */
IlvRandomLayout layout = new IlvRandomLayout();
layout.attach(grapher);
try {
IlvGraphLayoutReport layoutReport = layout.performLayout();
int code = layoutReport.getCode();
System.out.println("Layout completed (" +
layoutReport.codeToString(code) + ")");
}
catch (IlvGraphLayoutException e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
Generic features and parameters of the RL
The
IlvRandomLayout class supports the following generic parameters defined in the
IlvGraphLayout class. See
Base class parameters and features:
The following sections describe the particular way in which these parameters are used by this subclass.
Allowed time (RL)
The layout algorithm stops if the allowed time setting elapses. See
Allowed time.
Layout of connected components (RL)
The layout algorithm can use the generic mechanism to lay out connected components. In this case, each connected component is placed separately. For more information about this mechanism, see
Layout of connected components.
Layout region (RL)
The layout algorithm uses the layout region setting (either your own or the default setting) to control the size and the position of the graph drawing. All three ways to specify the layout region are available for this subclass. See
Layout region.
Link clipping (RL)
The layout algorithm can use a link clip interface to clip the end points of a link. See
Link clipping. The link clipping parameter is useful when the nodes have a shape other than a rectangle, such as a triangle, rhombus, or circle. If no link-clip interface is used, the links are normally connected to the bounding boxes of the nodes, not to the border of the node shapes.
Link connection box (RL)
The layout algorithm can use a link connection box interface to calculate the center of a node. See
Link connection box. This interface is only used when the link style is straight line.
This interface is used when one or other of the following features is enabled:

Connect links to node centers

Link clipping
This interface is also used for self-links and multilinks, depending on the mode of the self-link or multilinks.
Percentage of completion calculation (RL)
The layout algorithm calculates the estimated percentage of completion. This value can be obtained from the layout report during the run of the layout. For a detailed description of this feature, see
Percentage of completion calculation and
Graph layout event listeners.
Preserve fixed links (RL)
The layout algorithm does not reshape the links that are specified as fixed. See
Preserve fixed links.
Preserve fixed nodes (RL)
The layout algorithm does not move the nodes that are specified as fixed. See
Preserve fixed nodes.
Random generator seed value (RL)
The Random Layout uses a random number generator to compute the coordinates. You can specify a particular value to be used as a
seed value. (See
Random generator seed value) For the default behavior, the random generator is initialized using the current system clock. Therefore, different layouts are obtained if you perform the layout repeatedly on the same graph.
Save Parameters to Named Properties (RL)
The layout algorithm can save its layout parameters into named properties. This can be used to save layout parameters to
.ivl files. For a detailed description of this feature, see
Save parameters to named properties and
Saving layout parameters and preferred layouts.
Stop immediately (RL)
The layout algorithm stops after cleanup if the method
stopImmediately is called. For a description of this method in the
IlvGraphLayout class, see
Stop immediately. If the layout stops early because the allowed time has elapsed, the result code in the layout report is
IlvGraphLayoutReport.STOPPED_AND_INVALID.
Specific parameters of the RL
Link style (RL)
When the layout algorithm moves the nodes,
straight-line links (such as instances of
IlvLinkImage) automatically “follow” the new positions of their end nodes. If the grapher contains other types of links (for example,
IlvPolylineLinkImage or
IlvSplineLinkImage), the shape of the link might not be appropriate because the intermediate points of the link is not moved. In this case, you can ask the layout algorithm to automatically remove all the intermediate points of the links (if any).
Example of removing intermediate link points (RL algorithm)
To specify that the layout algorithm automatically removes all the intermediate points of the links (if any):
In CSS
Add to the GraphLayout section:
linkStyle : "STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE ";
In Java™
Use the method:
void setLinkStyle(int style)
The valid values for style are:
 IlvRandomLayout.NO_RESHAPE_STYLE
IlvRandomLayout.NO_RESHAPE_STYLENone of the links is reshaped in any manner.
 IlvRandomLayout.STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE
IlvRandomLayout.STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLEAll the intermediate points of the links (if any) are removed. It is the default value.
Connect links to node center (RL)
This feature is shared by all subclasses of the Basic Link Style Layout. See
Connect links to node center for details.
Multilink and self-link features (RL)
This feature is shared by all subclasses of the Basic Link Style Layout. See
Multilink and self-link features for details.
Copyright © 2018, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.