- java.lang.Object
-
- ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout
-
- ilog.views.graphlayout.hierarchical.IlvHierarchicalLayout
-
public class IlvHierarchicalLayout extends IlvGraphLayout
The main class for the Hierarchical Layout algorithm.The Hierarchical Layout arranges the nodes in horizontal or vertical levels such that the majority of the links point in the same direction and the number of link crossings is small.
Here is a sample drawing produced by the Hierarchical Layout algorithm with two levels of nodes that are top-justified within each level:
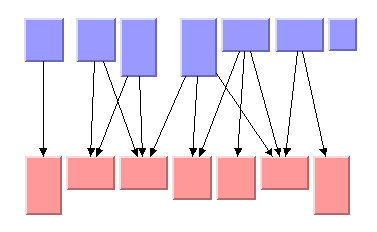
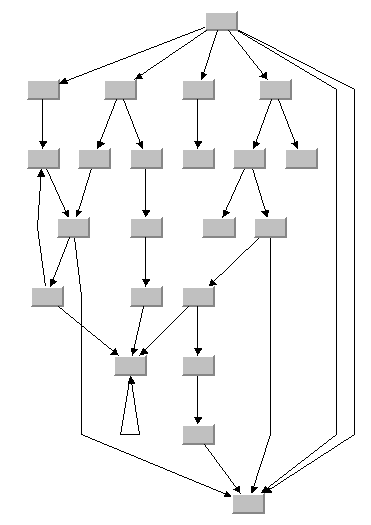
Another sample drawing with eight levels follows. This graph contains a cycle and a self-loop. The direction of the flow is from top to bottom. The nodes are organized in horizontal levels.
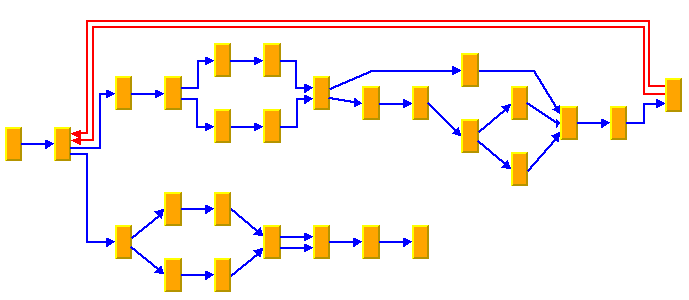
The Hierarchical Layout algorithm supports different styles of links in the same drawing. The following sample drawing shows orthogonal, straight, and polyline links. The direction of the flow is to the right and the node levels are vertical.
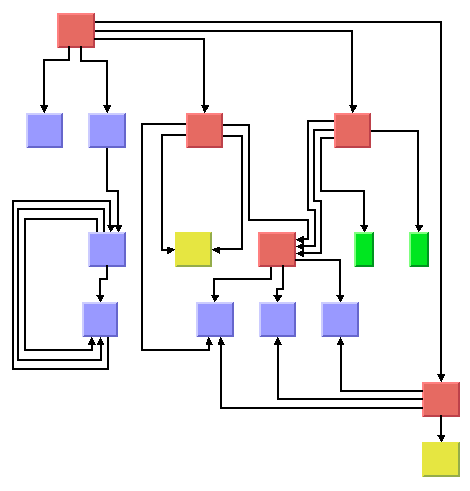
The Hierarchical Layout algorithm supports port specifications. The side and index of the port where a link connects to a node can be specified. The following sample drawing shows a drawing with port specifications and orthogonal link style. The direction of the flow is from top to bottom.
To simplify the explanations of the layout parameters, we use the compass directions north, south, east, and west. The first level of the layout is the north pole. If the flow direction is top to bottom, north is always upwards, south towards the bottom, west towards the left, and east towards the right side of the layout. If the flow direction is left to right, north is left and south is right.
See the corresponding chapter of the User's Manual for details on the algorithm, the types of graphs for which this algorithm can be used, the features and limitations, code samples, and so on.
Note the following points:
- The layout algorithm always takes into account the direction of links.
- The initial position of the nodes (at the moment you start the layout) does not affect the resulting layout.
- The algorithm supports self-links, cycles, and multiple links between the same pair of nodes.
CSS example:
SDM {
GraphLayout : true;
}
GraphLayout {
graphLayout : @#layout;
// optional settings for the graph layout renderer
}
Subobject#layout {
class : "ilog.views.graphlayout.hierarchical.IlvHierarchicalLayout";
allowedTime : "3";
backtrackCrossingReductionEnabled : "false";
connectorStyle : "2";
coordinatesMode : "MANAGER_COORDINATES";
crossingReductionDuringIncremental : "false";
flowDirection : "2";
fromFork : "false";
globalDestinationPointMode : "2";
globalIncrementalNodeMovementMode : "2";
globalLinkStyle : "2";
globalOriginPointMode : "2";
horizontalLinkOffset : "3.0";
horizontalNodeLinkOffset : "3.0";
horizontalNodeOffset : "3.0";
incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositioning : "false";
incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionRange : "3.0";
incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionTendency : "3.0";
incrementalMode : "false";
intergraphConnectivityMode : "false";
labelLayoutEnabledDuringRecLayoutMode : "false";
layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled : "false";
levelingStrategy : "2";
levelJustification : "2";
linkCrossingFineTuningEnabled : "false";
linkStraighteningEnabled : "false";
linkWidthUsed : "false";
longLinkCrossingReductionDuringIncremental : "false";
maxInterLevelApertureAngle : "3.0";
medianCrossingValueEnabled : "false";
minBusyTime : "3";
minEndSegmentLength : "3.0";
minForkSegmentLength : "3.0";
minStartSegmentLength : "3.0";
multiLinkOptimizationEnabled : "false";
multiLinkOptimizationMaxSpread : "3.0";
multiLinkOptimizationOffset : "3.0";
neighborLinksAligned : "false";
nonorthogonalBendEliminationEnabled : "false";
numberOfLinkCrossingSweeps : "2";
orthogonalStairCaseEliminationEnabled : "false";
polylineLinkOverlapReductionEnabled : "false";
position : "10,10";
preferredForkAxisLength : "3.0";
recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed : "false";
recursiveLayoutMode : "false";
selfLinkFromPortSide : "EAST";
selfLinksSameSideNested : "false";
selfLinkToPortSide : "EAST";
toFork : "false";
verticalLinkOffset : "3.0";
verticalNodeLinkOffset : "3.0";
verticalNodeOffset : "3.0";
}
link.tag {
DestinationPointMode : "FREE_MODE";
FromPortIndex : "2";
FromPortSide : "EAST";
LinkPriority : "2.0";
LinkStyle : "POLYLINE_STYLE";
OriginPointMode : "FREE_MODE";
ToPortIndex : "2";
ToPortSide : "EAST";
}
node.tag {
EastNumberOfPorts : "2";
IncrementalNodeBoxForExpand : "10,10,400,400";
IncrementalNodeMovementMode : "FREE_MODE";
NorthNumberOfPorts : "2";
SouthNumberOfPorts : "2";
SpecNodeLevelIndex : "2";
SpecNodePositionIndex : "2";
WestNumberOfPorts : "2";
}
CSS specification of per-node and per-link layout parameters:The following table lists the per-object rendering properties of the
GraphLayoutrenderer:PropertyTypeDefaultDescriptionGraphLayoutIlvGraphLayoutnullLets you define a different graph layout algorithm for each subgraph. If one is not specified, the same algorithm is applied recursively to all subgraphs.LayoutFixedStringfalseDeprecated, replaced by Fixed.FixedStringfalseLets you specify that the node or link must not be moved or reshaped by the layout algorithm.LayoutGroupStringnullLets you apply the algorithm to different groups of objects, one group after the other.LayoutIgnoredbooleanfalseIftrue, the object is ignored by the layout.The per-node and per-link layout parameters are specified in the style sheet through the CSS rules for nodes and links, not through the CSS rule for graph layout. For instance:
link.tag {
LinkStyle : "ORTHOGONAL_STYLE";
}
Note that the names of the node and link layout parameters use an initial capital, unlike the regular properties.See also the documentation of the classes
IlvGraphLayoutRenderer, IlvSwimLanesRenderer, IlvLaneRenderer.
-
-
Property Summary
Properties Modifier and Type Property and Description longallowedTime
Sets the upper limit for the duration of the layout algorithm.booleanbacktrackCrossingReductionEnabled
Sets whether the backtrack mechanism of the link crossing reduction phase is enabled.java.lang.Stringclass
Default constructor.intconnectorStyle
Sets the style of connectors.intcoordinatesMode
Sets the coordinates mode to be used during layout.booleancrossingReductionDuringIncremental
Sets whether crossing reduction during incremental layout is enabled.intDestinationPointMode
Sets the mode for the connection point of an individual link on the destination node.intEastNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the east side of a node.intflowDirection
Sets the direction of the link flow.booleanfromFork
Sets whether a fork shape is created for links that start at the same source point.intFromPortIndex
Sets the port index of a link at the "from" side.intFromPortSide
Sets the port side of a link at the "from" side.intglobalDestinationPointMode
Sets the global mode for the connection point of the links on the destination nodes.intglobalIncrementalNodeMovementMode
Sets the node movement mode used during incremental layout.intglobalLinkStyle
Sets the global style of the shapes of links.intglobalOriginPointMode
Sets the global mode for the connection point of the links on the origin nodes.doublehorizontalLinkOffset
Sets the horizontal offset between parallel segments of links.doublehorizontalNodeLinkOffset
Sets the horizontal offset between a node and a link segment that is parallel to the node border.doublehorizontalNodeOffset
Sets the horizontal offset between nodes.booleanincrementalAbsoluteLevelPositioning
Sets whether it is enabled to place nodes within the level to absolute positions that are close to the previous positions during incremental layout.doubleincrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionRange
Sets the range that is considered very close to the previous node position.doubleincrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionTendency
Sets the percentage how much the layout algorithm tries to place nodes to absolute positions within the level that are close to the previous positions during incremental layout.booleanincrementalMode
Sets whether the incremental layout mode is enabled.ilog.views.IlvRectIncrementalNodeBoxForExpand
Sets the effective bounding rectangle of an expanded node during incremental layout.intIncrementalNodeMovementMode
Sets the movement mode of an individual node used during incremental layout.booleanintergraphConnectivityMode
Sets whether the intergraph link connectivity is considered for the partitioning of the layout into levels.booleanlabelLayoutEnabledDuringRecLayoutMode
Sets whether the recursive layout mode places also the labels of the graph.booleanlayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled
Sets whether the generic connected component layout mechanism is enabled.intlevelingStrategy
Sets the hierarchical layout leveling strategy.intlevelJustification
Sets the justification within the levels.booleanlinkCrossingFineTuningEnabled
Sets whether the link crossing fine tuning phase is enabled.floatLinkPriority
Sets the priority of a link.booleanlinkStraighteningEnabled
Sets whether the link straightening phase is enabled.intLinkStyle
Sets the style of the shape of an individual link.booleanlinkWidthUsed
Sets whether the layout respects the width of links.booleanlongLinkCrossingReductionDuringIncremental
Sets whether the handling of long links for crossing reduction during incremental layout is enabled.doublemaxInterLevelApertureAngle
Sets the maximum aperture angle of the links incident to a node.booleanmedianCrossingValueEnabled
Sets whether the median crossing value is used during crossing reduction.longminBusyTime
Sets the minimal time that the layout algorithm can be busy.doubleminEndSegmentLength
Sets the minimum length of the last segment of each link, that is, the segment that is incident to the "to" node.doubleminForkSegmentLength
Sets the minimum length of the start or end segment of links if a fork shape is used for these links.doubleminStartSegmentLength
Sets the minimum length of the first segment of each link, that is, the segment that is incident to the "from" node.booleanmultiLinkOptimizationEnabled
Sets whether the optimization of overlapping multiple links is enabled.doublemultiLinkOptimizationMaxSpread
Sets the maximum spread width for the bends introduced by the optimization of overlapping multiple links.doublemultiLinkOptimizationOffset
Sets the minimum distance between bends introduced by the optimization of overlapping multiple links.booleanneighborLinksAligned
Sets whether links between neighbor nodes of the same level are aligned so that they are strictly horizontal or vertical.booleannonorthogonalBendEliminationEnabled
Sets whether the bend elimination phase for nonorthogonal links is enabled.intNorthNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the north side of a node.intnumberOfLinkCrossingSweeps
Sets the number of layer sweeps to remove link crossings.intOriginPointMode
Sets the mode for the connection point on an individual link on the origin node.booleanorthogonalStairCaseEliminationEnabled
Sets whether the stair case elimination phase for orthogonal links is enabled.booleanpolylineLinkOverlapReductionEnabled
Sets whether optimization of polyline links to avoid links overlapping large neighbor nodes is enabled.ilog.views.IlvPointposition
Sets the position of the layout.doublepreferredForkAxisLength
Sets the preferred length of the axis of a fork shape.booleanrecursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed
Sets whether the layout instance of the ancestor graph is in principle allowed to treat this subgraph in a recursive layout.booleanrecursiveLayoutMode
Sets whether this layout instance handles all subgraphs recursively that are nested into this graph.intselfLinkFromPortSide
Sets the default port side of a self-link at the "from" side.booleanselfLinksSameSideNested
Sets whether self-links that attach the same side of a node are nested.intselfLinkToPortSide
Sets the default port side of a self-link at the "to" side.intSouthNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the south side of a node.intSpecNodeLevelIndex
Sets the index of the specified level for a node.intSpecNodePositionIndex
Sets the index of the specified position of a node within a level.booleantoFork
Sets whether a fork shape is created for links that end at the same target point.intToPortIndex
Sets the port index of a link at the "to" side.intToPortSide
Sets the port side of a link at the "to" side.doubleverticalLinkOffset
Sets the vertical offset between parallel segments of links.doubleverticalNodeLinkOffset
Sets the vertical offset between a node and a link segment that is parallel to the node border.doubleverticalNodeOffset
Sets the vertical offset between nodes.intWestNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the west side of a node.
-
-
-
Property Detail
-
class
public java.lang.String class
Default constructor.
CSS example:class : "ilog.views.graphlayout.hierarchical.IlvHierarchicalLayout";
-
allowedTime
public long allowedTime
Sets the upper limit for the duration of the layout algorithm.The default value for Hierarchical layout is
100000000(100000 seconds).
CSS example:allowedTime : "3";
-
backtrackCrossingReductionEnabled
public boolean backtrackCrossingReductionEnabled
Sets whether the backtrack mechanism of the link crossing reduction phase is enabled. The layout algorithm uses a sweep heuristic to resolve link crossings which includes a backtracking mechanism. If a sweep made the result worse, it sets the results back to the previous situation.This is an expert option. It is enabled by default. It is normally not necessary to disable the backtrack mechanism, except if you need to speed up the layout.
CSS example:backtrackCrossingReductionEnabled : "false";
-
connectorStyle
public int connectorStyle
Sets the style of connectors. Valid values are:-
#CENTERED_PINS- The link connector pins are placed in the center of the border the link is attached to. -
#CLIPPED_PINS- Each link pointing to the center of the node is clipped at the node border. -
#EVENLY_SPACED_PINS- The link connector pins are evenly spaced along the node border. -
#AUTOMATIC_PINS- The connector style is selected depending on the link style.
The default value is
#AUTOMATIC_PINS.The connector style is used to place the connector pins of links that have the free origin or destination point mode and no specified port index. Links with fixed point mode do not change their connection point at the origin node. Links with specified port indexes are connected to the corresponding connector pin of the port instead. The placement of connector pins also depends on the link clip interface and the connection box interface, in the following way:
- First, the bounding box of an end node is obtained. If a link
connection box interface was set via
IlvGraphLayout#setLinkConnectionBoxInterface, the bounding box and offsets are delivered by that interface. Otherwise, the node bounding box delivered by the graph model (seeIlvGraphModel#boundingBox(Object)) is used. - Next, the initial connector pin of the link is placed at this bounding box in the manner specified by the connector style.
- Finally, if a link clip interface was set via
IlvGraphLayout#setLinkClipInterface(IlvLinkClipInterface), the connector pins are corrected by clipping with that interface.
If you specify port sides but no port numbers for links (see
#setFromPortSide(Object, int)and#setToPortSide(Object, int)), then it is recommended to avoid#CLIPPED_PINS, since they do not reflect the port side precisely enough. Only centered or evenly spaced link connector pins display the port side precisely.Note that when the graph attached to the layout is of type
IlvGrapher, the effect of the connector style depends on the type of the connectors installed at the node. For links that have free origin or destination point mode, we recommend using link connectors of typeIlvFreeLinkConnector. Other connector types may cause anIlvInappropriateLinkExceptionduring layout. You can use the methodIlvGraphLayoutUtil#EnsureAppropriateLinkswhen the exception is caught to install the appropriate connectors.
CSS example:connectorStyle : "2"; -
-
coordinatesMode
public int coordinatesMode
Sets the coordinates mode to be used during layout.Valid values are:
-
ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout#MANAGER_COORDINATES- The geometry of the graph is computed using the coordinate space of the manager (that is, the attachedIlvGrapher) without applying any transformation.This mode should be used if you visualize the graph at zoom level 1, or you do not visualize it at all, or the graph contains only fully zoomable objects. In all these cases there is no need to take the transformer into account during the layout.
Note that in this mode the dimensional parameters of the layout algorithms are considered as being specified in manager coordinates.
-
ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout#VIEW_COORDINATES- The geometry of the graph is computed in the coordinate space of the manager view. More exactly, all the coordinates are transformed using the current reference transformer.This mode should be used if you want the dimensional parameters of the layout algorithms to be considered as being specified in manager view coordinates.
-
ilog.views.graphlayout.IlvGraphLayout#INVERSE_VIEW_COORDINATES- The geometry of the graph is computed using the coordinate space of the manager view and then applying the inverse transformation. This mode is equivalent to the "manager coordinates" mode if the geometry of the graphic objects strictly obeys the transformer. (A small difference may exist because of the limited precision of the computations.)On the contrary, if some graphic objects are either nonzoomable (see
IlvGraphic#zoomable) or semizoomable (for example, links with a maximum line width), this mode gives different results than the manager coordinates mode. These results are optimal if the graph is visualized using the same transformer as the one taken into account during the layout.Note that in this mode the dimensional parameters of the layout algorithms are considered as being specified in manager coordinates.
The default value is
IlvGraphLayout#INVERSE_VIEW_COORDINATES.This option is useful only if the attached graph model is an
IlvGrapherAdapter(or a subclass). Otherwise, it has no effect. Note: the coordinates mode of the layout is used only while this layout is running. If layout is not running, operations on the grapher adapter use the coordinates mode that was set on the grapher adapter directly (seeIlvGrapherAdapter#setCoordinatesMode).
CSS example:coordinatesMode : "MANAGER_COORDINATES";
Allowed values: MANAGER_COORDINATESVIEW_COORDINATESINVERSE_VIEW_COORDINATES -
-
crossingReductionDuringIncremental
public boolean crossingReductionDuringIncremental
Sets whether crossing reduction during incremental layout is enabled. This option has no effect if the incremental mode is disabled. If the incremental mode is enabled and the argument isfalse, the layout preserves the relative order of the nodes and the links within the levels. If the argument istrue, the layout preserves the level structure but reorders the nodes within the levels to avoid link crossings.It is disabled by default.
CSS example:crossingReductionDuringIncremental : "false";
-
DestinationPointMode
public int DestinationPointMode
Sets the mode for the connection point of an individual link on the destination node. This mode is used only if the global "from" point mode is set to#MIXED_MODE. Otherwise, the connection points on the destination nodes have, for all the links, the mode that is specified as the global destination point mode.Valid values are:
-
#FREE_MODE- The layout is free to choose, for this link, the appropriate position of the connection point on the destination node, except for "pinned" connection points (seeIlvGraphModel#hasPinnedConnectionPoint(Object, boolean)). The choice can further be influenced by specifying the side and the port index of the links. -
#FIXED_MODE- The layout must keep, for this link, the current position of the connection point on the destination node. This can be useful, in particular, if the node has fixed pins where the link is attached (as, for instance, withIlvPinLinkConnector) and the pins should not be moved by the layout algorithm.The fixed mode works only if the link connector delivers consistently the same connection point when called multiple times. If a link is not connected to a link connector, or if the
IlvClippingLinkConnectoris used, the real connection point is calculated on the fly and may change when called multiple times with changing link bends. In this case, the fixed mode cannot ensure a correct routing of the links.Note that if the mode is fixed, specifications of the port index of links at the "to" side are ignored.
The default value is
#FREE_MODE.
CSS example:DestinationPointMode : "FREE_MODE";
Allowed values: FREE_MODEFree FIXED_MODEFixed
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
- See Also:
globalDestinationPointMode
-
-
EastNumberOfPorts
public int EastNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the east side of a node.
CSS example:EastNumberOfPorts : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
flowDirection
public int flowDirection
Sets the direction of the link flow. Valid values are:-
IlvDirection#Right- the majority of the links flow to the right. -
IlvDirection#Left- the majority of the links flow to the left. -
IlvDirection#Bottom- the majority of the links flow to the bottom. -
IlvDirection#Top- the majority of the links flow to the top.
This feature sets the direction of the flow for the majority of the links in a directed graph. The layout algorithm may need to direct some links in the opposite direction of the general link flow. If the links flow to the left or right, the nodes are placed in vertical levels. If the links flow to the top or bottom, the nodes are placed in horizontal levels.
The default value is
IlvDirection#Right.
CSS example:flowDirection : "2"; -
-
fromFork
public boolean fromFork
Sets whether a fork shape is created for links that start at the same source point. A fork shape is a link shape where several links start at the same point, share a link segment, and then branch into separate link paths. The fork shape is used only in the orthogonal link style, and only in the following cases: if the connector style is#CENTERED_PINS, or if the links start at the same specified port index at the north or south side of a node, or if the links have the fixed origin point mode and are placed at exactly the same coordinate.The default value is
false.
CSS example:fromFork : "false";
-
FromPortIndex
public int FromPortIndex
Sets the port index of a link at the "from" side. This allows you to specify the relative ports of the links on the node border. Using relative ports is a way to specify the relative order of how the links connect to the "from" node. The specification is only used if the free origin point mode is used for the link.Port numbers are between
0andn - 1, wherenis the number of ports at the node side where the link is connected. Links with an unspecified or negative port index are connected on the node border according to the global connector style. A link with a specified port indexiis connected at the ith relative port, and the connector pins of ports are evenly spaced on the corresponding node border.
CSS example:FromPortIndex : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
FromPortSide
public int FromPortSide
Sets the port side of a link at the "from" side. This allows you to specify at which side of the node the starting point of the link is connected.Possible values for the
sideparameter are#EAST,#WEST,#NORTH,#SOUTH, and the default#UNSPECIFIED.If a port side is unspecified, the link can connect to any border side of the node. Otherwise, the link connects only to the specified node border.
CSS example:FromPortSide : "EAST";
Allowed values: EASTWESTNORTHSOUTHUNSPECIFIED
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
globalDestinationPointMode
public int globalDestinationPointMode
Sets the global mode for the connection point of the links on the destination nodes. Valid values are:-
#FREE_MODE- For all links, the layout is free to choose the appropriate position of the connection point on the destination node, except for "pinned" connection points (seeIlvGraphModel#hasPinnedConnectionPoint(Object, boolean)). The choice can further be influenced by specifying the side and the port index of the links. -
#FIXED_MODE- For all links, the layout must keep the current position of the connection point on the destination node. This can be useful, in particular, if the node has fixed pins where the link is attached (as, for instance, withIlvPinLinkConnector) and the pins should not be moved by the layout algorithm.The fixed mode works only if the link connector delivers consistently the same connection point when called multiple times. If a link is not connected to a link connector, or if the
IlvClippingLinkConnectoris used, the real connection point is calculated on the fly and may change when called multiple times with changing link bends. In this case, the fixed mode cannot ensure a correct routing of the links.Note that if the mode is fixed, specifications of the port index of links at the "to" side are ignored.
-
#MIXED_MODE- Each link can have a different mode for the connection point on the destination node. The mode of each individual link can be set by the method#setDestinationPointMode(Object, int).
Unless the global mode is
#MIXED_MODE, the connection points on the destination node have the same mode for all the links.The default value is
#FREE_MODE.
CSS example:globalDestinationPointMode : "2"; -
-
globalIncrementalNodeMovementMode
public int globalIncrementalNodeMovementMode
Sets the node movement mode used during incremental layout. This option has no effect if the incremental mode is disabled. Valid values are:-
#FREE_MODE- The incremental layout preserves the relative order of nodes but does not preserve the exact position of nodes. It may move the nodes a little bit to optimize the space usage. The shifting does not change the level structure of the graph. If crossing reduction is disabled during incremental layout (see#setCrossingReductionDuringIncremental(boolean)), the shifting also does not change the order of the nodes within the levels. -
#FIXED_IN_X_MODE- The incremental layout preserves the relative order of nodes and keeps the nodes fixed in the x direction. The nodes may shift in the y direction. -
#FIXED_IN_Y_MODE- The incremental layout preserves the relative order of nodes and keeps the nodes fixed in the y direction. The nodes may shift in the x direction. -
#FIXED_MODE- The nodes do not move at all during incremental layout. Only nodes that are marked for incremental repositioning will be moved, and links are rerouted. -
#MIXED_MODE- Each node that is not marked for incremental can have a different mode. The mode of each individual node can be set by the method#setIncrementalNodeMovementMode(Object, int). Mixing fixed and free nodes should only be done in exceptional cases, because it may create overlaps or a messy arrangement.
Nodes that are marked for incremental are placed in a nonincremental way without respecting the previous position. The incremental movement mode has no effect for these nodes. Unless the global mode is
#MIXED_MODE, all nodes that are not marked for incremental are placed according to the same mode.The default mode is
#FREE_MODE.If the incremental mode is enabled and nodes are fixed in the x or y direction, it works well if the graph has a coarsely level structure (for example, if it was created by a previous layout in free mode or in nonincremental mode) but it may create overlaps or a messy arrangement otherwise. Fixing nodes has several consequences: The spacing options are obeyed only if there is enough space between the fixed nodes. The specified position of the layout is not obeyed, because it would require shifting the fixed nodes. The crossing reduction during incremental layout has no effect (see
#isCrossingReductionDuringIncremental()). However, you can decide whether to enable the crossing reduction of long links (see#isLongLinkCrossingReductionDuringIncremental()). If the long link crossing reduction is enabled, it will rearrange the long links that span several levels to avoid crossings.Furthermore, note that if the generic connected component layout mechanism of the
IlvGraphLayoutbase class is enabled, it will move nodes even if they are specified as fixed. Therefore, it is recommended disabling the generic connected component layout mechanism.
CSS example:globalIncrementalNodeMovementMode : "2"; -
-
globalLinkStyle
public int globalLinkStyle
Sets the global style of the shapes of links. Valid values are:-
#POLYLINE_STYLE- All links get a polyline shape, that is, a shape consisting of a sequence of line segments. -
#ORTHOGONAL_STYLE- All links get an orthogonal shape, that is, a shape consisting of a sequence of orthogonal line segments. -
#STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE- All links get a straight-line shape. -
#NO_RESHAPE_STYLE- No reshape is performed on any link. -
#MIXED_STYLE- Each link can have a different link style. The style of each individual link can be set by the method#setLinkStyle(Object, int)so that different link shapes can occur in the same graph.
Unless the global link style is
#MIXED_STYLE, all links have the same style of shape.The default value is
#POLYLINE_STYLE.Note that when the graph attached to the layout is of type
IlvGrapher, the effect of the link reshaping depends on the type of the links and the connectors installed at the node. For all link styles, we recommend using links of typeIlvPolylineLinkImageand, for links that have free origin or destination point mode, link connectors of typeIlvFreeLinkConnector. Other link or connector types may cause anIlvInappropriateLinkExceptionduring layout. You can use the methodIlvGraphLayoutUtil#EnsureAppropriateLinksbefore layout or when the exception is caught to convert all links and link connectors to an appropriate type.
CSS example:globalLinkStyle : "2"; -
-
globalOriginPointMode
public int globalOriginPointMode
Sets the global mode for the connection point of the links on the origin nodes. Valid values are:-
#FREE_MODE- For all links, the layout is free to choose the appropriate position of the connection point on the origin node, except for "pinned" connection points (seeIlvGraphModel#hasPinnedConnectionPoint(Object, boolean)). The choice can further be influenced by specifying the side and the port index of the links. -
#FIXED_MODE- For all links, the layout must keep the current position of the connection point on the origin node. This can be useful, in particular, if the node has fixed pins where the link is attached (as, for instance, withIlvPinLinkConnector) and the pins should not be moved by the layout algorithm.The fixed mode works only if the link connector delivers consistently the same connection point when called multiple times. If a link is not connected to a link connector, or if the
IlvClippingLinkConnectoris used, the real connection point is calculated on the fly and may change when called multiple times with changing link bends. In this case, the fixed mode cannot ensure a correct routing of the links.Note that if the mode is fixed, specifications of the port index of links at the "from" side are ignored.
-
#MIXED_MODE- Each link can have a different mode for the connection point on the origin node. The mode of each individual link can be set by the method#setOriginPointMode(Object, int).
Unless the global mode is
#MIXED_MODE, the connection points on the origin node have the same mode for all the links.The default value is
#FREE_MODE.
CSS example:globalOriginPointMode : "2"; -
-
horizontalLinkOffset
public double horizontalLinkOffset
Sets the horizontal offset between parallel segments of links. In the orthogonal link style, the segments attached directly to the node may have a smaller offset if the node is too small or the number of incident links is too large to satisfy the specified offset.The default value is
15.
CSS example:horizontalLinkOffset : "3.0";
-
horizontalNodeLinkOffset
public double horizontalNodeLinkOffset
Sets the horizontal offset between a node and a link segment that is parallel to the node border.The default value is
20.
CSS example:horizontalNodeLinkOffset : "3.0";
-
horizontalNodeOffset
public double horizontalNodeOffset
Sets the horizontal offset between nodes. If the levels are horizontal, this is the minimum distance between the nodes of the same level. If the levels are vertical, this is the minimum distance between the nodes of different levels.The default value is
40.
CSS example:horizontalNodeOffset : "3.0";
-
incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositioning
public boolean incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositioning
Sets whether it is enabled to place nodes within the level to absolute positions that are close to the previous positions during incremental layout. This option has no effect if the incremental mode is disabled. It has also no effect if crossing reduction during incremental layout is enabled.If the incremental mode is enabled and crossing reduction during incremental layout is disabled, the layout arranges the nodes such that the relative order of the nodes within each level is preserved. If this parameter is set to
false, nodes may be placed at absolute positions far from the previous positions, even though their relative order does not change, because the main objective of the algorithm is to produce a balanced layout.To help the user preserve a mental map of the graph, this parameter should be set to
true. In this case, the nodes are placed closer to their previous positions, even though this may result in a less balanced layout.The freedom of incremental level positioning can be controlled by the tendency to preserve the previous node position (see
#setIncrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionTendency(double)) and the range that is considered to be close enough to the previous node position#setIncrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionRange(double)).It is enabled by default.
CSS example:incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositioning : "false";
-
incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionRange
public double incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionRange
Sets the range that is considered very close to the previous node position. This option has an effect only if the incremental absolute level positioning is used.In nonincremental mode, nodes are placed within the level in order to balance the layout. If the incremental absolute level positioning is used, nodes should be placed close to their previous positions, but the layout should also be balanced. Both criteria compete with each other. The position range influences how the competing criteria are resolved. If a node is placed within this range to its previous position, the balance criteria is used to determine its position. If the node is placed farther away from its previous position, the position tendency is used to determine its position.
A node that is placed within the incremental position range to its previous position is placed at the best balanced position. This avoids having the balance of nodes that are already close to the previous position being disturbed by an additional tendency towards the previous position.
The default value is
20.
CSS example:incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionRange : "3.0";
-
incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionTendency
public double incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionTendency
Sets the percentage how much the layout algorithm tries to place nodes to absolute positions within the level that are close to the previous positions during incremental layout. This option has an effect only if the incremental absolute level positioning is used.In nonincremental mode, nodes are placed within the level in order to balance the layout. If the incremental absolute level positioning is used, nodes should be placed close to their previous positions, but the layout should also be balanced. Both criteria compete with each other. The position tendency influences how the competing criteria are resolved. A high position tendency has the effect that the nodes stay closer to their previous positions, and a low position tendency has the effect that the nodes stay closer to the balanced position. Passing the position tendency 0 has basically the same effect as disabling the incremental absolute level positioning.
The input value is a percentage between
0and100. The default value is70percent.
CSS example:incrementalAbsoluteLevelPositionTendency : "3.0";
-
incrementalMode
public boolean incrementalMode
Sets whether the incremental layout mode is enabled. If the argument istrue, the layout respects the current coordinates of nodes and links, and it tries to create a layout with similar positions. Depending on the incremental node movement mode, the layout may need to shift all nodes to optimize the space usage, but the shifting does not change the relative order of the nodes and links, so that the diagram after an incremental layout looks very similar to the previous diagram.The levels are arranged based on the current coordinates of the nodes. Thus, the specified node level and position indexes are ignored during incremental layout.
The incremental mode is disabled by default.
CSS example:incrementalMode : "false";
-
IncrementalNodeBoxForExpand
public ilog.views.IlvRect IncrementalNodeBoxForExpand
Sets the effective bounding rectangle of an expanded node during incremental layout.In this context, we call expand any interactive operation that changes the size of the node to make it very large while preserving the center position of the node. The typical purpose of an expand operation is to change the graphical representation of the node to show more details in the inner of the node. For instance, an expand operation may show a subgraph in the inner of the node. Often, an incremental re-layout is desired after an expand operation.
The challenge of the re-layout after an expand operation consists of the fact that the node may become so large that it overlaps many nodes. This may yield undesired effects during incremental layout, because incremental layout is unable to determine the level structure from the coordinates of the nodes if some node overlaps many other nodes completely.
To facilitate the incremental layout, the old bounding box of the expanded node, as it was before the expand operation, must be specified as the effective bounding box. This helps the incremental layout determine the proper level structure.
The effective bounding box has no effect if incremental layout is disabled, or if the node is marked for incremental recalculation. The effective bounding box is transient, that is, it is automatically removed after each successful layout and not stored into
.ivlfiles.
CSS example:IncrementalNodeBoxForExpand : "10,10,400,400";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
IncrementalNodeMovementMode
public int IncrementalNodeMovementMode
Sets the movement mode of an individual node used during incremental layout. This movement mode is used only if the incremental mode is enabled, the global movement mode is set to#MIXED_MODE, and the node is not marked for incremental recalculation. If the global movement mode is not#MIXED_MODE, all nodes have the mode that is specified as the global movement mode.Valid values are:
-
#FREE_MODE- The incremental layout preserves the relative order of the node with respect to all other nodes (except those that are marked for incremental recalculation). It does not preserve the exact position. It may move the node a little bit to optimize the space usage. The shifting does not change the level structure of the graph. If the crossing reduction is disabled during incremental layout (see#setCrossingReductionDuringIncremental(boolean)), the shifting also does not change the order of the node within the levels with respect to the other nodes. -
#FIXED_IN_X_MODE- The incremental layout preserves the relative order of the node with respect to all other nodes (except those that are marked for incremental recalculation), and it keeps the node fixed in the x direction. The node may shift in the y direction. -
#FIXED_IN_Y_MODE- The incremental layout preserves the relative order of the node with respect to all other nodes (except those that are marked for incremental recalculation), and it keeps the node fixed in the y direction. The nodes may shift in the x direction. -
#FIXED_MODE- The node does not move at all during incremental layout.
The default mode is
#FREE_MODE.If the incremental mode is enabled and some nodes are fixed in the x or y direction, it often works well if the graph has a coarsely level structure (for example, if it was created by a previous layout in free mode or in nonincremental mode) but it may create overlaps or a messy arrangement otherwise, in particular if only few nodes are fixed and many nodes are free to move. Fixing nodes has several consequences: The spacing options are obeyed only if there is enough space between the fixed nodes. The specified position of the layout is not obeyed, because it would require shifting the fixed nodes. The crossing reduction during incremental layout has no effect (see
#isCrossingReductionDuringIncremental()). However, you can decide whether to enable the crossing reduction of long links (see#isLongLinkCrossingReductionDuringIncremental()). If the long link crossing reduction is enabled, it will rearrange the long links that span several levels to avoid crossings.Furthermore, note that if the generic connected component layout mechanism of the
IlvGraphLayoutbase class is enabled, it will move nodes even if they are specified as fixed. Therefore it is recommended disabling the generic connected component layout mechanism.
CSS example:IncrementalNodeMovementMode : "FREE_MODE";
Allowed values: FREE_MODEFree FIXED_MODEFixed
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
- See Also:
globalIncrementalNodeMovementMode
-
-
intergraphConnectivityMode
public boolean intergraphConnectivityMode
Sets whether the intergraph link connectivity is considered for the partitioning of the layout into levels. If this option is enabled, the algorithm tries to distribute the nodes that represent subgraphs into the levels so that the majority of intergraph links point roughly in the flow direction.This is an expert option. It is disabled by default.
Note that this option has no effect if the generic disconnected node placement is enabled (see
#setLayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled(boolean)).Even if this option is enabled, the Hierarchical Layout algorithm does not route intergraph links. They should be routed by applying a Link Layout after the Hierarchical Layout.
CSS example:intergraphConnectivityMode : "false";
-
labelLayoutEnabledDuringRecLayoutMode
public boolean labelLayoutEnabledDuringRecLayoutMode
Sets whether the recursive layout mode places also the labels of the graph. This option has only an effect when the recursive layout mode is enabled. It places the labels obtained from#getLabelLayout(), which is attached at the same grapher as this layout instance. The placement of labels is enabled by default.
CSS example:labelLayoutEnabledDuringRecLayoutMode : "false";
-
layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled
public boolean layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled
Sets whether the generic connected component layout mechanism is enabled. If enabled on a layout class that supports this mechanism (see#supportsLayoutOfConnectedComponents()), the method#performLayout(boolean, boolean, boolean)cuts the attached graph model into connected components and lays out each connected component separately. Then the connected components are placed using the layout instance returned by the method#getLayoutOfConnectedComponents().Notice that the connected component layout is not used if the graph is connected.
A
RuntimeExceptionis thrown if the layout does not support this mechanism.The default value is the value returned by the method
#isLayoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabledByDefault().
CSS example:layoutOfConnectedComponentsEnabled : "false";
-
levelingStrategy
public int levelingStrategy
Sets the hierarchical layout leveling strategy.This strategy determines how nodes are distributed in the hierarchical levels. Valid values are:
-
#OPTIMAL: the optimal leveling strategy. The layout algorithm tries to minimize the sum of level distances for all edges. -
#SEMI_OPTIMAL: the semioptimal leveling strategy. This strategy often gives the same result as the optimal strategy. The layout algorithm tries a quick heuristic to minimize the sum of level distances for all edges. It pulls root nodes to the highest-numbered level possible and leaf nodes to the lowest-numbered level possible. -
#HIGHER_LEVELS: the leveling strategy to utilize higher numbered levels. This layout algorithm pulls nodes to the highest-numbered level possible. Root nodes in particular are effected. -
#LOWER_LEVELS: the leveling strategy to utilize lower numbered levels. the layout algorithm pulls nodes to the lowest-numbered level possible. Leaf nodes in particular are effected. -
#SPREAD_OUT: the leveling strategy to spread the nodes out over all levels. This can be considered as the inverse of the semioptimal leveling strategy. It pulls root nodes to the lowest-numbered level possible and leaf nodes to the highest-numbered level possible.
#SEMI_OPTIMAL.The calculation of node levels can also be influenced by the following node constraints:
IlvRelativeLevelConstraintIlvSameLevelConstraintIlvLevelRangeConstraint
If the incremental mode is switched on, the leveling strategy has no effect. The levels are calculated from the node positions, except for those nodes that are marked for incremental recalculation. See
#markForIncremental(Object)for more information.
CSS example:levelingStrategy : "2"; -
-
levelJustification
public int levelJustification
Sets the justification within the levels. Valid values are:-
IlvDirection#Center -
IlvDirection#Left -
IlvDirection#Right -
IlvDirection#Top -
IlvDirection#Bottom
This feature sets the justification of the nodes within each level. If the nodes are center-justified, all nodes of the same level are placed with their centers along a line. Otherwise, all nodes of the same level are placed with the specified border justified to a line. If the link flow direction is to the left or right, the nodes can be justified to the left, center, or right. If the link flow direction is to the top or bottom, the nodes can be justified to the top, center, or bottom.
The default value is
IlvDirection#Center.
CSS example:levelJustification : "2"; -
-
linkCrossingFineTuningEnabled
public boolean linkCrossingFineTuningEnabled
Sets whether the link crossing fine tuning phase is enabled. This is an additional heuristic that tries to resolve more link crossings.This is an expert option. It is enabled by default. It is normally not necessary to disable fine tuning, except if you need to speed up the layout.
CSS example:linkCrossingFineTuningEnabled : "false";
-
LinkPriority
public float LinkPriority
Sets the priority of a link. The layout algorithm tries to place the links in such a way that the majority of the links are short and point in the same direction. However, this is not always possible for all links. Low priority links are more likely to be longer or point in the opposite direction than the high priority links. The link priority should be smaller than 10000.
CSS example:LinkPriority : "2.0";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
linkStraighteningEnabled
public boolean linkStraighteningEnabled
Sets whether the link straightening phase is enabled. This phase analyzes long orthogonal links and tries to remove bends.This is an expert option. It is enabled by default. It is normally not necessary to disable link straightening, except if you need to speed up the layout.
CSS example:linkStraighteningEnabled : "false";
-
LinkStyle
public int LinkStyle
Sets the style of the shape of an individual link. This link style is used only if the global link style is set to#MIXED_STYLE. Otherwise, all links have the style that is specified as the global link style.Valid values are:
-
#POLYLINE_STYLE- The link gets a polyline shape, that is, a shape consisting of a sequence of line segments. -
#ORTHOGONAL_STYLE- The link gets an orthogonal shape, that is, a shape consisting of a sequence of orthogonal line segments. -
#STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLE- The link gets a straight-line shape. -
#NO_RESHAPE_STYLE- No reshape is performed on the link.
The default value is
#POLYLINE_STYLE.Note that when the graph attached to the layout is of type
IlvGrapher, the effect of the link reshaping depends on the type of the links and the connectors installed at the node. For all link styles, we recommend using links of typeIlvPolylineLinkImageand, for links that have free origin or destination point mode, link connectors of typeIlvFreeLinkConnector. Other link or connector types may cause anIlvInappropriateLinkExceptionduring layout. You can use the methodIlvGraphLayoutUtil#EnsureAppropriateLinksbefore layout or when the exception is caught to convert all links to an appropriate type.
CSS example:LinkStyle : "POLYLINE_STYLE";
Allowed values: POLYLINE_STYLEPolyline links ORTHOGONAL_STYLEOrthogonal links STRAIGHT_LINE_STYLEStraight-line links NO_RESHAPE_STYLENo link reshape
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
- See Also:
globalLinkStyle
-
-
linkWidthUsed
public boolean linkWidthUsed
Sets whether the layout respects the width of links. This option affects the calculation of connector pins that must be evenly spaced. It has no effect on the link connector pins with the connector style#CLIPPED_PINSor#CENTERED_PINS.If
trueis passed as the argument, the distribution of the connector pins varies depending on the link width. The horizontal or vertical offset between pairs of links or links and nodes is with respect to the link border. Iffalseis passed as the argument, the distribution of connector pins is independent of the link width. The horizontal or vertical offset between pairs of links or links and nodes is with respect to the link center.The default is
false.
CSS example:linkWidthUsed : "false";
-
longLinkCrossingReductionDuringIncremental
public boolean longLinkCrossingReductionDuringIncremental
Sets whether the handling of long links for crossing reduction during incremental layout is enabled. This option has no effect if the incremental mode is disabled. If the incremental mode is enabled and the argument isfalse, the layout preserves the relative order of the nodes and the links within the levels. If the argument istrue, the layout preserves the level structure and the relative order of the nodes, but reroutes the links in order to avoid link crossings. This means a long link may cross a level between a different pair of nodes than before layout.It is disabled by default.
CSS example:longLinkCrossingReductionDuringIncremental : "false";
-
maxInterLevelApertureAngle
public double maxInterLevelApertureAngle
Sets the maximum aperture angle of the links incident to a node.This parameter only has an effect if none of the links has the orthogonal link style. It is best suited if the link style is for polyline links. It defines the maximum angle of the link segments that run between the levels of the hierarchical layout.
The maximum angle is given in degrees, it must be between 10 and 90 degrees.
If the flow direction of the layout is vertical, that is, to the bottom or to the top, a strictly vertical link segment has an aperture of 0, and a strictly horizontal link segment has aperture of 90. By limiting the maximum aperture angle, you ensure that the slope of segments between levels is more vertical than horizontal. That is to say, the slope of the link is in the flow direction of the layout. To ensure the slope of the segments, the vertical space between the levels is enlarged.
If the flow direction of the layout is horizontal, that is, to the left or to the right, a strictly vertical link segment has an aperture of 90, and a strictly horizontal link segment has an aperture of 0. By limiting the maximum aperture angle, you ensure that the slope of segments between levels is more horizontal than vertical. To ensure the slope of the segments, the horizontal space between the levels is enlarged.
If the maximum aperture is set to 90, the aperture angle has no influence on the space between levels. This is the default.
Very small maximum aperture angles are not recommended. The resulting layout may waste too much space between the node levels.
CSS example:maxInterLevelApertureAngle : "3.0";
-
medianCrossingValueEnabled
public boolean medianCrossingValueEnabled
Sets whether the median crossing value is used during crossing reduction. The layout algorithm uses a heuristic to resolve link crossings. This heuristic uses a "barycenter" weight on the nodes to determine how the crossings are resolved. If this option is enabled, it additionally uses a "median" weight as a tie breaker if two nodes have the same "barycenter" weight. Statistically, this results in fewer crossings.This is an expert option. It is enabled by default. It is normally not necessary to change this value. However, if many nodes have very high numbers of incoming or outgoing links, the calculation of the "median" weight may slow down the layout. In this case, you can switch this option off.
CSS example:medianCrossingValueEnabled : "false";
-
minBusyTime
public long minBusyTime
Sets the minimal time that the layout algorithm can be busy. This is the time between two calls of#layoutStepPerformed()when the method#callLayoutStepPerformedIfNeeded()is used.The objective is to avoid the overhead of
#layoutStepPerformed()becoming too high if the method is called too often. Internal routines of layout algorithms usually call#callLayoutStepPerformedIfNeeded(), which calls#layoutStepPerformed()if the time since the last call was at least the minimal busy time.The default value is 50 (milliseconds).
CSS example:minBusyTime : "3";
-
minEndSegmentLength
public double minEndSegmentLength
Sets the minimum length of the last segment of each link, that is, the segment that is incident to the "to" node.The default value is
0.
CSS example:minEndSegmentLength : "3.0";
-
minForkSegmentLength
public double minForkSegmentLength
Sets the minimum length of the start or end segment of links if a fork shape is used for these links.The default value is
10.
CSS example:minForkSegmentLength : "3.0";
-
minStartSegmentLength
public double minStartSegmentLength
Sets the minimum length of the first segment of each link, that is, the segment that is incident to the "from" node.The default value is
0.
CSS example:minStartSegmentLength : "3.0";
-
multiLinkOptimizationEnabled
public boolean multiLinkOptimizationEnabled
Sets whether the optimization of overlapping multiple links is enabled. If you have multiple links between the same pair of directly neighbored nodes, and this option is disabled, it may happen that these links overlap. If the option is enabled and the link style of the links allow bend points, then additional bends are introduced to avoid those overlaps. The offset between these bends of the same multilink bundle can be controlled by#setMultiLinkOptimizationOffset.The optimization is enabled by default.
CSS example:multiLinkOptimizationEnabled : "false";
-
multiLinkOptimizationMaxSpread
public double multiLinkOptimizationMaxSpread
Sets the maximum spread width for the bends introduced by the optimization of overlapping multiple links. These are bends of links in the same bundle between nodes that are directly neighbored. These bends are shifted relative to each other by the multi link optimization offset unless the number of links times the offset exceeds the max spread value. In that case, the offset is limited by the max spread value.The default value is
50.
CSS example:multiLinkOptimizationMaxSpread : "3.0";
- See Also:
multiLinkOptimizationEnabled
-
multiLinkOptimizationOffset
public double multiLinkOptimizationOffset
Sets the minimum distance between bends introduced by the optimization of overlapping multiple links. These are bends of links in the same bundle between nodes that are directly neighbored. These bends are shifted relative to each other by the multi link optimization offset unless the number of links times the offset exceeds the max spread value. In that case, the offset is limited by the max spread value.The default value is
10.
CSS example:multiLinkOptimizationOffset : "3.0";
- See Also:
multiLinkOptimizationEnabled
-
neighborLinksAligned
public boolean neighborLinksAligned
Sets whether links between neighbor nodes of the same level are aligned so that they are strictly horizontal or vertical. For instance, in a top-down layout, the links between neighbor nodes of the same level can be drawn roughly horizontal while all other links are drawn roughly vertical. However, if one end node is larger than the other end node and both nodes are aligned at the top, the link between both would normally not be drawn strictly horizontal because it connects to the smaller node at a different y coordinate than to the larger node. (Reason: the y coordinate of the center of the nodes is different when they are aligned at the top and do not have the same size). In the orthogonal link style, the link would have a bend. If the alignment mode is enabled, these links between neighbor nodes are connected to the nodes so that they are strictly straight and have no bends. The connector style is ignored for these links.It is enabled by default.
If neighbor links are not aligned and have the orthogonal style, the spacing between the link segments may be slightly smaller than the specified offset between links. If the incremental node movement mode is fixed, it is not always possible to create aligned links between neighbor nodes, due to the fixed positions of the nodes.
CSS example:neighborLinksAligned : "false";
-
nonorthogonalBendEliminationEnabled
public boolean nonorthogonalBendEliminationEnabled
Sets whether the bend elimination phase for nonorthogonal links is enabled. This phase analyzes nonorthogonal links and tries to remove bends in the links shape. This is not always desired for very long links since they often look aesthetically better if they are split by two bend into an orthogonal middle part and nonorthogonal end parts.This is an expert option. It is disabled by default. Enabling the bend elimination produces more straight links but also slows down the algorithm. In recursive mode, it might be useful to enable this option since the recursive mode produces many small link segments between bends.
CSS example:nonorthogonalBendEliminationEnabled : "false";
-
NorthNumberOfPorts
public int NorthNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the north side of a node.
CSS example:NorthNumberOfPorts : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
numberOfLinkCrossingSweeps
public int numberOfLinkCrossingSweeps
Sets the number of layer sweeps to remove link crossings. The layout algorithm uses a sweep algorithm to resolve link crossings. This is a heuristic that cannot always remove all link crossings. The number of sweeps influences the number of crossings that are resolved. However, there is no simple formula to decide whether more sweeps would resolve more crossings or result in the converse. On some occasions it may be useful to increase or decrease the number of sweeps in order to resolve more link crossings.This is an expert option. The default value is 5. It is normally not necessary to change this value.
CSS example:numberOfLinkCrossingSweeps : "2";
-
OriginPointMode
public int OriginPointMode
Sets the mode for the connection point on an individual link on the origin node. This mode is used only if the global "from" point mode is set to#MIXED_MODE. Otherwise, the connection points on the origin nodes have, for all the links, the mode that is specified as the global origin point mode.Valid values are:
-
#FREE_MODE- The layout is free to choose, for this link, the appropriate position of the connection point on the origin node, except for "pinned" connection points (seeIlvGraphModel#hasPinnedConnectionPoint(Object, boolean)). The choice can further be influenced by specifying the side and the port index of the links. -
#FIXED_MODE- The layout must keep, for this link, the current position of the connection point on the origin node. This can be useful, in particular, if the node has fixed pins where the link is attached (as, for instance, withIlvPinLinkConnector) and the pins should not be moved by the layout algorithm.The fixed mode works only if the link connector delivers consistently the same connection point when called multiple times. If a link is not connected to a link connector, or if the
IlvClippingLinkConnectoris used, the real connection point is calculated on the fly and may change when called multiple times with changing link bends. In this case, the fixed mode cannot ensure a correct routing of the links.Note that if the mode is fixed, specifications of the port index of links at the "from" side are ignored.
The default value is
#FREE_MODE.
CSS example:OriginPointMode : "FREE_MODE";
Allowed values: FREE_MODEFree FIXED_MODEFixed
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
- See Also:
globalOriginPointMode
-
-
orthogonalStairCaseEliminationEnabled
public boolean orthogonalStairCaseEliminationEnabled
Sets whether the stair case elimination phase for orthogonal links is enabled. This phase analyzes orthogonal links and tries to remove staircase pattens in the links shape.This is an expert option. It is enabled by default. It is normally not necessary to disable stair case elimination, except if you need to speed up the layout.
CSS example:orthogonalStairCaseEliminationEnabled : "false";
-
polylineLinkOverlapReductionEnabled
public boolean polylineLinkOverlapReductionEnabled
Sets whether optimization of polyline links to avoid links overlapping large neighbor nodes is enabled. If this option is enabled, the algorithm introduces additional bends if polyline links are routed at a flat angle, to avoid overlapping large neighbor nodes. The option does not affect orthogonal links.If the graph has a huge number of links, it is recommended switching this optimization off, because it is very time-consuming.
The optimization is enabled by default.
CSS example:polylineLinkOverlapReductionEnabled : "false";
-
position
public ilog.views.IlvPoint position
Sets the position of the layout. This can be used if connected component processing is disabled or if the graph is fully connected. It has no effect otherwise.If a position is specified, the layout algorithm places the graph such that the specified point is the upper-left corner. If no position is specified, in incremental mode the layout algorithm places the graph close to its previous position before layout started, and in nonincremental mode it places the graph so that
(0, 0)is the upper-left corner.The default value is
null.
CSS example:position : "10,10";
-
preferredForkAxisLength
public double preferredForkAxisLength
Sets the preferred length of the axis of a fork shape. If a fork shape is used for n links that start at the same point, and the flow direction is towards the bottom, then the fork will have a horizontal segment as the axis. This horizontal segment has the preferred length calculated from this parameter multiplied by n.Note this length is only a hint for the layout algorithm. If there is not enough free space, the layout algorithm decreases the length of the axis below the preferred length. If there is enough free space, it may also increase the length of the axis in order to reduce unnecessary link bends.
The default value is
10.
CSS example:preferredForkAxisLength : "3.0";
-
recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed
public boolean recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed
Sets whether the layout instance of the ancestor graph is in principle allowed to treat this subgraph in a recursive layout. Whether the layout of the ancestor graph can handle the subgraph attached to this layout instance depends on the parameter settings of the ancestor layout. The layout instance of the ancestor graph must also be a hierarchical layout and must have the recursive layout mode enabled, otherwise the ancestor layout does not try to handle this subgraph.This option is enabled by default.
CSS example:recursiveLayoutFromAncestorAllowed : "false";
-
recursiveLayoutMode
public boolean recursiveLayoutMode
Sets whether this layout instance handles all subgraphs recursively that are nested into this graph. Normally, the hierarchical layout handles only the flat graph attached to this layout. If the recursive layout is enabled, it handles also all subgraphs recursively nested into this layout and also routes all intergraph links. The recursive mode is disabled by default.In detail: the recursive mode causes the hierarchical layout instances of the subgraphs to delegate the work to this layout. If the layout instance of a subgraph is no
IlvHierarchicalLayout, the subgraph is not handled by this layout. Layout parameters per node and link must be set on the layout instance of the subgraph the node or link belongs to.
CSS example:recursiveLayoutMode : "false";
-
selfLinkFromPortSide
public int selfLinkFromPortSide
Sets the default port side of a self-link at the "from" side. Self-links are links that start and end at the same node. This is used as port side for those self-links that have no explicit port side specification at the "from" side. It specifies at which side of the node the starting point of the self-link is connected.Possible values for the
sideparameter are#EAST,#WEST,#NORTH,#SOUTH. The default value is#SOUTH.
CSS example:selfLinkFromPortSide : "EAST";
Allowed values: EASTWESTNORTHSOUTH
-
selfLinksSameSideNested
public boolean selfLinksSameSideNested
Sets whether self-links that attach the same side of a node are nested. If multiple self-links attach the same side of a node and they are not nested, they are routed next to each other. If they are nested, they are routed link a multilink bundle.This is an expert option. It is enabled by default.
CSS example:selfLinksSameSideNested : "false";
-
selfLinkToPortSide
public int selfLinkToPortSide
Sets the default port side of a self-link at the "to" side. Self-links are links that start and end at the same node. This is used as port side for those self-links that have no explicit port side specification at the "to" side. It specifies at which side of the node the end point of the self-link is connected.Possible values for the
sideparameter are#EAST,#WEST,#NORTH,#SOUTH. The default value is#WEST.
CSS example:selfLinkToPortSide : "EAST";
Allowed values: EASTWESTNORTHSOUTH
-
SouthNumberOfPorts
public int SouthNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the south side of a node.
CSS example:SouthNumberOfPorts : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
SpecNodeLevelIndex
public int SpecNodeLevelIndex
Sets the index of the specified level for a node. Nodes are organized in horizontal or vertical levels numbered from0ton. If the link flow direction is from top to bottom, the nodes with level index0are placed in the topmost level, and the nodes with higher level indexes are placed in the levels below. If the link flow direction is from left to right, the nodes with level index0are placed in the leftmost level, and the nodes with higher level indexes are placed in the levels farther to the right.This method allows you to specify the level where a node should be placed. If the level index of a node is set to a negative value, it means that there is no preference for the level of the node. In this case, the layout algorithm calculates an appropriate level index.
The default level index of a node is
-1; that is, the layout algorithm determines the appropriate level automatically.Note that specified level indexes can cause conflicts to constraints that are solved depending on the constraint priorities. The index specification or some of the constraints may be ignored in this case. Furthermore, note that if the generic connected component layout mechanism of the
IlvGraphLayoutbase class is enabled, each connected component uses its own level structure. If it is disabled, there is only one global level structure.
CSS example:SpecNodeLevelIndex : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
SpecNodePositionIndex
public int SpecNodePositionIndex
Sets the index of the specified position of a node within a level. Nodes are organized in horizontal or vertical levels. Within each level, the nodes are placed sequentially at relative positions numbered from0ton. If the link flow direction is from top to bottom, the node with position index0is placed leftmost within its level, and the nodes with higher position indexes are placed farther to the right. If the link flow direction is from right to left, the node with position index0is placed topmost within its level, and the nodes with higher position indexes are placed below.This method allows you to specify the relative position where a node should be placed within its level. If the position index of a node is set to a negative value, it means that there is no preference for the position of the node. In this case, the layout algorithm calculates an appropriate position index. If the position index is higher than the number of nodes in the level, the position index is ignored. If two nodes of the same level have the same position index, one of the indexes is ignored. The layout algorithm calculates an appropriate position index for the nodes that have inappropriate or conflicting position indexes.
The default position index of a node is
-1; that is, the layout algorithm determines the appropriate position automatically.Note that specified position indexes can cause conflicts to constraints that are solved depending on the constraint priorities. The index specification or some of the constraints may be ignored in this case. Furthermore, note that if the generic connected component layout mechanism of the
IlvGraphLayoutbase class is enabled, each connected component uses its own level structure. If it is disabled, there is only one global level structure.
CSS example:SpecNodePositionIndex : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
toFork
public boolean toFork
Sets whether a fork shape is created for links that end at the same target point. A fork shape is a link shape where several links join from different branches into a final link segment that ends at the same point. The fork shape is used only in the orthogonal link style, and only in the following cases: if the connector style is#CENTERED_PINS, or if the links start at the same specified port index at the north or south side of a node, or if the links have the fixed origin point mode and are placed at exactly the same coordinate.The default value is
false.
CSS example:toFork : "false";
-
ToPortIndex
public int ToPortIndex
Sets the port index of a link at the "to" side. This allows you to specify the relative ports of the links on the node border. Using the relative ports is a way to specify the relative order of how the links connect to the "to" node. The specification is only used if the free destination point mode is used for the link.Port numbers are between
0andn - 1, wherenis the number of ports at the node side where the link is connected. Links with an unspecified or negative port index are connected on the node border according to the global connector style. A link with specified port indexiis connected at the ith relative port, and the connector pins of ports are evenly spaced on the corresponding node border.
CSS example:ToPortIndex : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
ToPortSide
public int ToPortSide
Sets the port side of a link at the "to" side. This allows you to specify at which side of the node the end point of the link is connected.Possible values for the
sideparameter are#EAST,#WEST,#NORTH,#SOUTH, and the default#UNSPECIFIED.If a port side is unspecified, the link can connect to any border side of the node. Otherwise, the link connects only to the specified node border.
CSS example:ToPortSide : "EAST";
Allowed values: EASTWESTNORTHSOUTHUNSPECIFIED
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of links. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for links. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
verticalLinkOffset
public double verticalLinkOffset
Sets the vertical offset between parallel segments of links. In the orthogonal link style, the segments attached directly to the node may have a smaller offset if the node is too small or the number of incident links is too large to satisfy the specified offset.The default value is
15.
CSS example:verticalLinkOffset : "3.0";
-
verticalNodeLinkOffset
public double verticalNodeLinkOffset
Sets the vertical offset between a node and a link segment that is parallel to the node border.The default value is
20.
CSS example:verticalNodeLinkOffset : "3.0";
-
verticalNodeOffset
public double verticalNodeOffset
Sets the vertical offset between nodes. If the levels are vertical, this is the minimum distance between the nodes of the same level. If the levels are horizontal, this is the minimum distance between the nodes of different levels.The default value is
40.
CSS example:verticalNodeOffset : "3.0";
-
WestNumberOfPorts
public int WestNumberOfPorts
Sets the number of relative ports on the west side of a node.
CSS example:WestNumberOfPorts : "2";
Important: This layout parameter applies to subsets of nodes. Therefore, the CSS declaration must be added to the corresponding CSS rule for nodes. Note also that the name of such layout parameters uses an initial capital, unlike the regular properties which hold for the entire content of the graph.
-
-