The class diagram for layers
and styles is shown in Layer and Style UML Diagram.
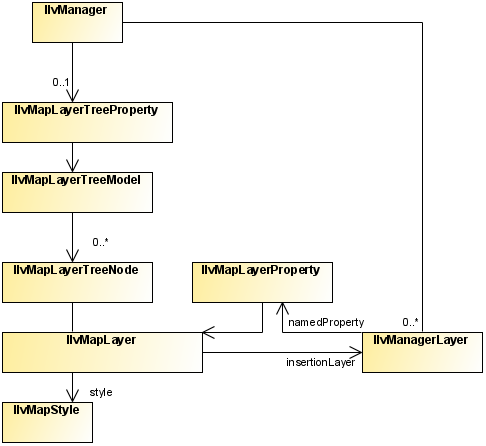
Layer and Style UML Diagram
The source code for the Map Builder demonstration, which contains
all of the code described in this section, can be found at <installdir> /jviews-maps810/samples/mapbuilder/index.html.
About map layers
The IlvMapLayer class represents a map layer,
that is, a cartographic theme. It associates a style ( IlvMapStyle or one of its subclasses) with
an IlvManagerLayer containing graphic objects.
Map Layers are arranged in a tree
structure, and stored in the manager using the IlvMapLayerTreeProperty, see Map layer tree.
Each map layer is attached to an IlvMapLayerTreeNode, which contains the
necessary information on parent and child layers. You can use
this node to step through layer hierarchy as follows:
String SVGpath = "C:/maps/map.svg"; IlvSVGDataSource source = new IlvSVGDataSource(SVGpath); source.setManager(getView().getManager()); source.setDestinationBounds(lonMinRad,latMinRad,lonMaxRad,latMaxRad);
Note
Alternatively you can use a tailored
transformation by calling
IlvSVGDataSource.setInternalTransformation.
source.start();
IlvMapLayerTreeNode node = mapLayer.getNode();
for (int i = 0; i < node.getChildCount(); i++) {
IlvMapLayerTreeNode child=(IlvMapLayerTreeNode) node.getChildAt(i);
IlvMapLayer childLayer = (IlvMapLayer) node.getUserObject();
... do something with child layer
}
Most map layers are attached to a data source, which is responsible for
populating the manager layer with the correct graphic objects
when the map data is loaded (possibly on-demand-loading) and
reprojection times. The exception to this rule is the composite
layer. Composite layers are only used to group a set of
sub-layers and manage their styles using attribute inheritance
(See below).
About map styles
Every style in JViews
Maps is a subclass of the base IlvMapStyle class.
This class provides access to a set of
attributes, usually also accessible by a setter/getter pair,
depending on each style subclass.
For example, you can change the view
visibility setting using on of:
style.setAttribute(IlvMapStyle.VISIBLE_IN_VIEW,Boolean.TRUE);
style.setVisibleInView(true);
You can catch any change in the map style
by writing and registering a listener on it. For example:
StyleListener listener = new StyleListener() {
public void styleChanged(StyleEvent event) {
if(IlvMapStyle.ALPHA.equals(event.getAttribute())) {
// ... do something when transparency changes
}
}
};
...
myStyle.addStyleListener(listener);
Style hierarchy
Styles form a hierarchy and attribute
values can be inherited through this hierarchy. If a style
attribute is inherited from a parent style, that parent attribute
value is used when displaying objects using that style.
Although not enforced in the API, it is
recommended that you make the style hierarchy the same as the map
layer hierarchy. This can be done when the map layer is inserted
in the layer tree model:
IlvMapLayerTreeModel ltm = IlvMapLayerTreeProperty.GetMapLayerTreeModel(manager); ltm.addChild(parentLayer, layer); IlvMapStyle parentStyle = layer.getParent().getStyle(); IlvMapStyle childStyle = layer.getStyle(); childStyle.setParent(parentStyle);
Common styling properties
Whatever the type of layer, its style
always has the following base properties.
Common Styling Properties
Property
name |
Contents |
|---|---|
VISIBLE_IN_VIEW |
Indicates whether the IlvManagerLayer is displayed on the map
view.
|
VISIBLE_IN_OVERVIEW |
Indicates whether the IlvManagerLayer is displayed on the map
overview.
|
ATTRIBUTE_INFO |
Contains the IlvAttributeInfoProperty used to
describe all object properties. This is used to provide the
list of possible property names displayed in the label
attribute check box. This attribute cannot be changed by the
user in the map layer tree panel.
|
LABEL_ATTRIBUTE |
Contains
either a null value, or the name of the property used when
labeling this map layer (chosen usually in the list provided
by the ATTRIBUTE_INFO attribute). |
ALWAYS_ON_TOP |
Indicates
whether the attached map layer is placed on a normal or
superimposing plane. This should be used only for overlay
layers such as grids, labels, measures, and so on. |
LEGEND_GROUP |
A
logical name, used and displayed to group map layers in the
legend. |
CATEGORY |
An
identifying name to group more than one layer on the same
legend line. |
ALPHA |
The
level of transparency of the manager layer. |