Deciding your data model strategy
First you should decide which classes in the model package are appropriate, depending on the characteristics of your existing business data and your requirements.
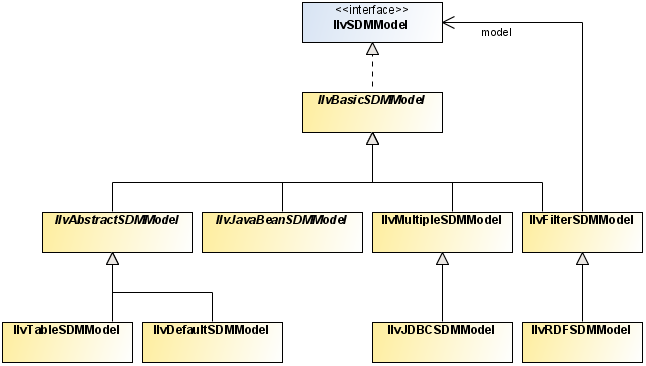
There are five levels of data model implementation, each appropriate for certain situations:
1. No use of existing data.
There are three possible situations:

You do not have existing data that you want to display and you will create your diagram(s) from scratch.

You have existing data, but you want to duplicate it before displaying it, and it does not matter how the data will be represented in memory.

You have exported your data to an XML file, and you want to read in the XML data.
The nodes and the links of the default model are instances of the classes
IlvDefaultSDMNode and
IlvDefaultSDMLink. These objects have an arbitrary set of user-defined properties, so the default model can represent all kinds of objects.
2. Display existing data in a database.
Your data is stored in a database, and you want to display it but not modify it directly in the diagram component.
The
model package provides a specific SDM model for this case:
IlvJDBCSDMModel. This model uses the JDBC™ API to access the database. All you need to do is configure the model with the database URL, the names of the tables containing the nodes and links, and a few other parameters.
3. Existing JavaBeans™.
You have existing data stored in classes which conform to the JavaBeans standard: there are accessor methods (
get and
set ) for each bean
property.
In this case, use the class
IlvJavaBeanSDMModel. This model uses your JavaBeans as the nodes and links of a
graph, so there is no duplication or additional memory consumption. The properties of nodes and links are read and written using the JavaBeans API. All you have to do is supply the set of JavaBeans that will make up your graph. For an example, see
JavaBeans example.
4. Existing Java™ classes that are not JavaBeans or existing data but no Java classes.
For example, you already have an implementation of a Swing JTree model that represents your data and you want to display the contents of the
tree without duplicating data.
One of the following cases applies:

You have existing data represented by Java classes that are not JavaBeans.

You want to display data that is not already represented in memory by Java classes.
In such cases, there are two possible approaches:

Subclass the basic model,
IlvBasicSDMModel, and implement the methods that list the objects and retrieve the properties of each object. This requires more work but is more open, and may be preferable if all objects already exist. For an example, see
NonJavaBeans example: basic model variant.
The following table summarizes the strategies described in this section.
Summary of data model strategies
Data Characteristics | Recommended Class |
New or from XML | |
Database (display only) | |
JavaBeans | |
Java classes or other existing objects (for example, Swing) | |
|
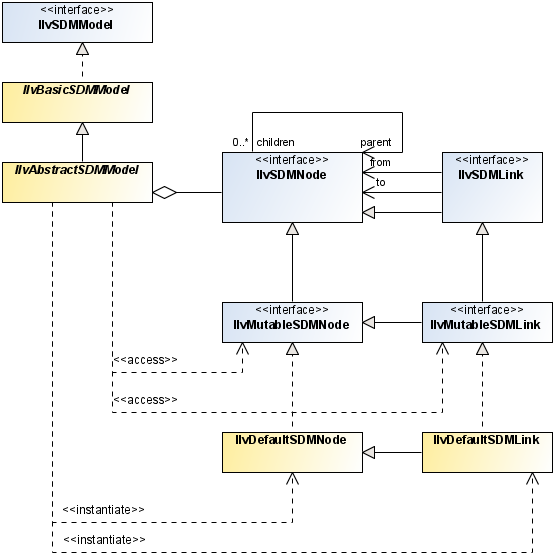
If the graphic objects are to be moved interactively, SDM tries to store the new object locations as x,y properties in the model. However, the model can refuse to set the x,y properties, for example when it is a read-only model. To cope with such a case, the SDM library provides a metadata system that manages new properties as if they were stored in the true model.
To enable metadata, call ilog.views.sdm.IlvSDMEngine.setMetadataEnabled(true). Metadata is saved only in XML files. Other persistent mechanisms are responsible for saving metadata if they need to.
The default model does not need metadata.
The SDM Model class relationships
The abstract SDM Model class relationships
Copyright © 2018, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.