Data and Views
The vector, matrix, and array classes are built on a powerful and simple architecture which we call the data-view model. Understanding this architecture will help you use the Essential Math Module to write efficient, simple code that is easy to maintain. Here is the key point:
As an example of the data-view model, consider Figure 141:
Figure 141. Different views into a single data block
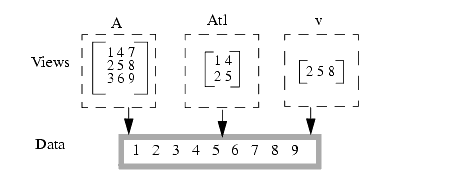
Figure 141 illustrates a 3 x 3 matrix A, a 2 x 2 matrix Atl, which is a view of the top left corner of A, and a vector v, which is a view of A's middle row. All three of these objects are different views into a single data block. Since the views share the same data, changing the middle element 5 in the vector v, for example, also changes the corresponding element in A and Atl. Assigning different names to views of the same data is sometimes called aliasing. In later sections, we will show how to use the data-view concept effectively, why it leads to efficient code, and how to avoid aliasing when necessary.