Singular Value Decomposition
The singular value decomposition (SVD) is perhaps the most revealing decomposition in numerical linear algebra. It provides a wealth of information to the analyst, including orthogonal bases for the domain and range spaces, the 2-norm and Frobenius norm of the matrix, and a determination of the numerical rank of a matrix. The SVD of a matrix A is:
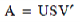
where the elements of the diagonal matrix S are the singular values, and the columns of U and V are the left and right singular vectors of A. Here's an example program that reads a matrix from standard input and prints the components of its SVD:
#include <rw/dgenmat.h>
#include <rw/rstream.h>
#include <rw/lapack/sv.h>
#include <rw/lapack/svdcalc.h>
int main()
{
RWGenMat<float> A; // 1
std::cin >> A;
RWSVDecomp<double, RWSVDCalc<double> > svd(A); // 2
std::cout << "singular values: " // 3
<< svd.singularValues() << std::endl;
std::cout << "left vectors" << svd.leftVectors() << std::endl;
std::cout << "right vectors" << svd.rightVectors()
<< std::endl;
return 0;
}
// 1 Here we define the matrix A and read it from standard input.
// 2 This line constructs the singular value decomposition object.
// 3 In the next few lines, we print out the components of the singular value decomposition. Refer to the SourcePro API Reference for a complete list of the member functions available to manipulate the SVD object.