Calculation Methods for Linear Regression
Given the linear regression model Y = bx + e, finding the least squares solution 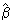 is equivalent to solving the normal equations
is equivalent to solving the normal equations  . Thus the solution for
. Thus the solution for 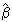 is given by:
is given by:
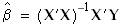
The Business Analysis Module includes three classes for calculating multiple linear regression parameters: RWLeastSqQRCalc, RWLeastSqQRPvtCalc, and RWLeastSqSVDCalc. The following three sections provide a brief description of the method encapsulated by each class, and its pros and cons.
RWLeastSqQRCalc
Class RWLeastSqQRCalc encapsulates the QR method. This method begins by decomposing the regression matrix X into the product of an orthogonal matrix Q and an upper triangular matrix R. The QR representation is then substituted into the equation in Calculation Methods for Linear Regression to obtain the solution 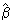 .
.
|
Pros: |
Good performance. Parameter values are recalculated very quickly when adding or removing predictor variables. Model selection performance is best with this calculation method. |
|
Cons: |
Calculation fails when the regression matrix X has less than full rank. (A matrix has less than full rank if the columns of X are linearly dependent.) Results may not be accurate if X is extremely ill-conditioned. |
RWLeastSqQRPvtCalc
Class RWLeastSqQRPvtCalc uses essentially the same QR method described in RWLeastSqQRCalc, except that the QR decomposition is formed using pivoting.
|
Pros: |
Calculation succeeds for regression matrices of less than full rank. However, calculations fail if the regression matrix contains a column of all 0s. |
|
Cons: |
Slower than the straight QR technique described in RWLeastSqQRCalc. |
RWLeastSqSVDCalc
Class RWLeastSqSVDCalc employs singular value decomposition (SVD). The method solves the least squares problem by decomposing the regression matrix into the form 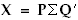 , where P is an
, where P is an 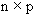 matrix consisting of p orthonormalized eigenvectors associated with the p largest eigenvalues of
matrix consisting of p orthonormalized eigenvectors associated with the p largest eigenvalues of 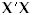 , Q is a
, Q is a 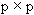 orthogonal matrix consisting of the orthonormalized eigenvectors of
orthogonal matrix consisting of the orthonormalized eigenvectors of 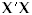 , and S = diag(s1, s2, ... , sp) is a
, and S = diag(s1, s2, ... , sp) is a  diagonal matrix of singular values of X. This singular value decomposition of X is used to solve the equation in Calculation Methods for Linear Regression.
diagonal matrix of singular values of X. This singular value decomposition of X is used to solve the equation in Calculation Methods for Linear Regression.
|
Pros: |
Works on matrices of less than full rank. Produces accurate results when X has full rank, but is highly ill-conditioned. |
|
Cons: |
Slower than the straight QR technique described in RWLeastSqQRCalc. |