Presenting the Adapters
Server/JavaTM data sources provide an adapter for each data source to be represented graphically, as show in this table:
|
Server/Java Data Source |
Data Source |
Adapter |
|
Swing data sources |
||
|
List data source |
Java Swing JList/ |
and |
|
Table data source |
Java Swing JTable |
|
|
Tree data source |
Java Swing JTree |
|
|
JViews data sources |
||
|
Graph Data Source |
JViews IlvGrapher |
|
|
Gantt data source |
JViews Gantt charts |
|
|
SDM Data Source |
JViews SDM |
|
To create a Server/Java data source, you must:
-
Write a specification file to define a dynamic view and load it in the server. This specification file must follow predefined naming conventions to enable the representation objects to be mapped to the data sources.
-
Create a Java GUI and connect the graphic objects to the appropriate data sources through the corresponding adapters. The connection can be made with Java IDE supporting JavaBeans.
-
Open the dynamic view on the server.
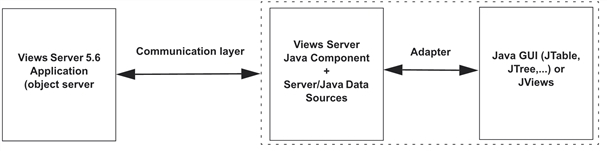
Server Java Data Source
Connecting Java Data Sources to a Java GUI
Adapters connect Java data sources to a Java GUI. These adapters operate in two ways:
-
Data Sources (Server) to GUI: Server notification.
-
GUI to Data Sources (Server): User interface updates.
The adapters provided with the Server libraries can be extended or reimplemented by the user. Adapters are connected to Java Swing gadgets or with JViews gadgets. However, the architecture of the adapters is designed to be run in a multithread-safe Swing-based application. Practically, the adapters work by buffering the notification messages sent by the server. Those messages are processed later in the Swing thread dedicated to graphical updates. See Java Data Source Adapters for additional information.