S
seed value
The value that is used for the initialization of a random number generator. Some layout algorithms use random numbers during the layout computation.
self-link
A link whose origin and destination nodes are the same node.
semiautomatic layout
A layout process where the user makes manual improvements to the result of the automatic layout process.
sibling node
Child nodes that have the same parent node are called sibling nodes.
simulated annealing
A mathematical technique assisted by a temperature scheme to find a good approximation of the optimum with respect to a certain goal. Simulated annealing was originally inspired by the physical effect of steel annealing when steel is heated and cooled down slowly. In graph layout, simulated annealing is used to place labels in such a way that they do not overlap with one another or with nodes and links.
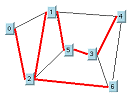
spanning tree
A minimal subgraph, defined as follows: A spanning tree S of a flat graph G is a subgraph of G containing all the nodes of the graph and whose links are a subset of the links of the graph. The number of links of G that are not present in S must be the minimum number for which there are no cycles in S. The spanning tree is shown by the red links in the following illustration.
spline
One possible appearance of a link connecting nodes: it is a smooth curve governed by control points.
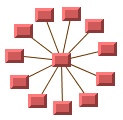
star
A type of network topology where the nodes are arranged on a circle with each node being connected to a center node.
straight-line
Denotes a drawing where each link is drawn as a straight line segment.
subgraph
A graph that is contained in another graph. In flat graphs, G' is a subgraph of G if its node and link sets are included in the node and link sets of G.
In nested graphs, a node that is a graph is called a subgraph of the nested graph.
Copyright © 2018, Rogue Wave Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.