Using layout algorithms through the graph layout API
Explains how to use layout algorithms through the graph layout API.
Explains how to use a layout algorithm on a grapher.
Illustrates an application that uses a graph layout on a grapher.
Using layout algorithms on graphers
Graphers (class IlvGrapher).store nodes and links and provide the minimal infrastructure that is necessary to perform a graph layout.
To use the layout algorithms provided by the graph layout package:
-
Create a grapher object ( IlvGrapher ) and fill it with nodes and links.
-
Create an instance of the layout algorithm (any subclass of IlvGraphLayout).
-
Declare a handle for the corresponding layout report. The layout report is an object in which the layout algorithm stores information about its behavior. For details, see Performing a layout.
-
Attach the grapher to the layout instance.
-
Modify the default settings for the layout parameters, if necessary.
-
Call the performLayout method inside a try block.
-
Read and display information from the layout report.
-
Catch the exceptions.
-
When the layout instance is no longer needed, detach the grapher from it.
Running the sample application that uses the graph layout API
You can use this application as an example to get started with the layout algorithms of the graph layout package.
The example uses the Tree layout, but most of the principles apply to any of the other layouts. The source code of the application is named Sample4.java and it is located at <installdir>/jviews-diagrammer/codefragments/graphlayout/sample4/src/Sample4.java.
To compile and run sample 4:
-
Go to the sample4 directory. On Microsoft® Windows® systems, you must open a Command Prompt window.
-
Set the CLASSPATH variable to the JViews Diagrammer library and the current directory.
On Microsoft Windows systems
.;<installdir>\jviews-diagrammer\lib\jviews-diagrammer-all.jar;<installdir>\jviews-framework\lib\jviews-framework-all.jar
On UNIX® systems
.:<installdir>/jviews-diagrammer/lib/jviews-diagrammer-all.jar:<installdir>/jviews-framework/lib/jviews-framework-all.jar
-
Compile the application:
javac -d . src/Sample4.java
-
Run the application:
java Sample4
The Sample4.java file contains the following code:
// the JViews Graphic Framework
import ilog.views.*;
// the JViews Graph Layout Framework
import ilog.views.graphlayout.*;
// the JViews Tree Layout
import ilog.views.graphlayout.tree.*;
// the Java AWT package
import java.awt.*;
// the Java Swing package
import javax.swing.*;
public class Sample4
{
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// Declare a handle for the layout instance
IlvTreeLayout layout = new IlvTreeLayout();
// Create the grapher instance
IlvGrapher grapher = new IlvGrapher();
// Create the manager view instance
IlvManagerView view = new IlvManagerView(grapher);
// Change view parameters.
view.setBackground(Color.white);
view.setKeepingAspectRatio(true);
// The name of the IVL file containing the graph data
String fileName = "data/Sample.ivl";
// Fill the grapher with nodes and links from a JViews IVL file.
// Alternatively, the nodes and links could be created
// programmatically.
try {
grapher.read(fileName);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("could not read " + fileName);
return;
}
// A Swing Frame to display
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Layout Sample");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// Put the manager view inside the Swing Frame and show it.
frame.getContentPane().add(view);
frame.setSize(600, 600);
frame.setVisible(true);
// perform the layout in the AWT thread
performLayout(grapher, view, layout);
}
});
}
/**
* Perform the layout.
*/
private static void performLayout(IlvGrapher grapher, IlvManagerView view,
IlvTreeLayout layout)
{
// Attach the grapher to the layout instance
layout.attach(grapher);
// Change some layout parameters
layout.setFlowDirection(IlvDirection.Bottom);
layout.setGlobalLinkStyle(IlvTreeLayout.ORTHOGONAL_STYLE);
try {
// Perform the layout and get the layout report
IlvGraphLayoutReport layoutReport = layout.performLayout();
int code = layoutReport.getCode();
// Print information from the layout report (optional)
System.out.println("Done in " +
layoutReport.getLayoutTime() +
" millisec., return code = " +
code + " (" +
layoutReport.codeToString(code) + ")");
}
// Catch the exceptions
catch (IlvGraphLayoutException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
finally {
// Fit the view to show the entire graph
view.fitTransformerToContent();
// Redraw the grapher
grapher.reDraw();
}
// Detach the grapher from the layout instance
layout.detach();
}
}
The sample Java™ application sample 4 produces the following graph.
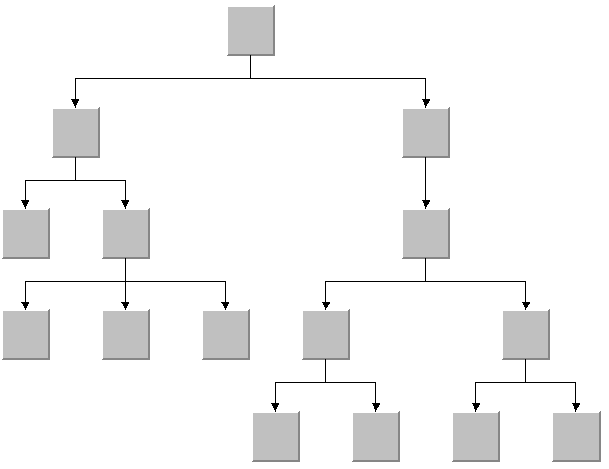
Output from sample 4