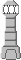Representation of network elements in a network
Describes the different aspects of the graphical representation of a network element in a network.
Shows the graphical representations used for the different types of network element.
Shows the graphical representations used for the different network element functions.
Shows the graphical representations used for the different network element families.
Explains how to create a partial network element and shows its graphic representation.
Explains how to create a shortcut network element and shows its graphic representation.
Shows which type of information is represented depending on the size of the network element.
Network element types
The network element type defines how a given network element will be displayed. The network element type is specified by setting the value of the attribute type in the business object. This attribute can be set programmatically using IltNetworkElement.TypeAttribute or through XML.
How to set the network element type using the API
IltNetworkElement ne = new IltNetworkElement("NE1");
ne.setType (IltNetworkElement.Type.NMW);
or
IlpObject ne = ...;
ne.setAttributeValue(IltNetworkElement.TypeAttribute,
IltNetworkElement.Type.NMW);
How to set the network element type using XML
<addObject id="NE1">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltNetworkElement</class>
<attribute name="name">NE1</attribute>
<attribute name="type">NMW</attribute>
</addObject>
Depending on the nature of the application, a network element can be represented by a bitmap image, a symbol, or a shape.
Pictorial representation
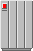
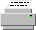
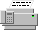
In its pictorial representation, the network element base is a bitmap drawing, which is composed of individual graphic objects. This drawing is meant to be realistic, as you can see in the following figure:
Pictorial representations of a terminal
Several predefined bases are available for shelf-based equipment, terminals, and mobile phone access network elements. JViews TGO includes a number of predefined network element images. The following tables show these drawings and the corresponding network element type name.
|
Network Element Type |
Representation |
|
IP_ComputerFlat |
|
|
IP_ComputerTower |
|
|
IP_Database |
|
|
IP_Desktop |
|
|
IP_Equipment |
|
|
IP_Firewall |
|
|
IP_Firewall2 |
|
|
IP_InkjetPrinter |
|
|
IP_Laptop |
|
|
IP_Laptop2 |
|
|
IP_LaserPrinter |
|
|
IP_Mainframe |
|
|
IP_Mainframe2 |
|
|
IP_Mainframe3 |
|
|
IP_Modem |
|
|
IP_Modem2 |
|
|
IP_Network |
|
|
IP_Network2 |
|
|
IP_Network3 |
|
|
IP_PDA |
|
|
IP_Printer |
|
|
IP_Printer2 |
|
|
IP_Router |
|
|
IP_Router2 |
|
|
IP_Router3 |
|
|
IP_SatelliteAntenna |
|
|
IP_Server |
|
|
IP_Server2 |
|
|
IP_Terminal |
|
|
IP_Terminal2 |
|
|
Network Element Type |
Representation |
|
Office_ComputerFlat |
|
|
Office_ComputerTower |
|
|
Office_Desktop |
|
|
Office_Fax |
|
|
Office_Fax2 |
|
|
Office_InkjetPrinter |
|
|
Office_Laptop |
|
|
Office_Laptop2 |
|
|
Office_LaserPrinter |
|
|
Office_Modem |
|
|
Office_Modem2 |
|
|
Office_PDA |
|
|
Office_Phone |
|
|
Office_Phone2 |
|
|
Office_Printer |
|
|
Office_Printer2 |
|
|
Office_Server |
|
|
Office_Server2 |
|
|
Office_Terminal |
|
|
Office_Terminal2 |
|
|
Network Element Type |
Representation |
|
SAN_CartridgeSystem |
|
|
SAN_Database |
|
|
SAN_Disk |
|
|
SAN_DoubleDatabase |
|
|
SAN_FiberChannelSwitch |
|
|
SAN_FiberChannelSwitch2 |
|
|
SAN_Modem |
|
|
SAN_Modem2 |
|
|
SAN_Router |
|
|
SAN_Router2 |
|
|
SAN_Router3 |
|
|
SAN_ServerExternalDisk |
|
|
SAN_ServerInternalDisk |
|
|
SAN_SingleDatabase |
|
|
SAN_TapeDrive |
|
|
SAN_TripleDatabase |
|
|
Network Element Type |
Representation |
|
Telecom_Database |
|
|
Telecom_Lighthouse |
|
|
Telecom_Mainframe |
|
|
Telecom_Mainframe2 |
|
|
Telecom_Mainframe3 |
|
|
Telecom_MD |
|
|
Telecom_MD2 |
|
|
Telecom_NMW |
|
|
Telecom_Server |
|
|
Telecom_Server2 |
|
|
Telecom_Terminal |
|
|
Telecom_Terminal2 |
|
|
Network Element Type |
Representation |
|
Wireless network elements |
|
|
Wireless_Antenna |
|
|
Wireless_Antenna2 |
|
|
Wireless_BSC |
|
|
Wireless_BSC2 |
|
|
Wireless_BTS |
|
|
Wireless_BTS2 |
|
|
Wireless_HLR |
|
|
Wireless_MobilePhone |
|
|
Wireless_MSC |
|
|
Wireless_MSC2 |
|
|
Wireless_Satellite |
|
|
Wireless_SatelliteAntenna |
|
JViews TGO also provides a pictorial representation for clusters. A cluster network element is an abstraction of a network element that is made up of two or more distinct subcomponents such as other network elements that can be (and often are) managed as standalone telecom objects. Clusters can be co-located or distributed, depending on how their subcomponents are organized (either within a managed area or spread across different areas). As with the new partial network elements concept, it is possible to represent wholly owned clusters (that is, all the subcomponents are managed by the user), or partially-owned clusters (only some of the subcomponents are managed by the user).
|
Network Element Type |
Representation |
|
|
|
|
Cluster_Colocated |
|
|
Cluster_Distributed |
|
You can create custom network element types by providing a bitmap image or a vector drawing. This process is detailed in Customizing network element types in the Styling documentation.
Symbolic representation
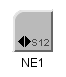
In the symbolic representation, network elements can be used for components, nodes or clusters. These objects are represented differently depending on which aspect of the OSS application you consider, for example, the data plane of physical managed telecom objects, the control and management planes or the logical managed telecom objects. The default type corresponding to the default symbolic network element representation is simply called NE (for Network Element). The following figure illustrates an NE type network element: here, an add-drop multiplexer with a capacity of OC192.

Symbolic representation of NE type network element
Symbolic information for NE type network elements consists of an icon representing the function of the equipment corresponding to the network element and a string representing the family of the equipment.
|
Network Element Type |
Representation |
Description |
|
Node |
||
|
NE |
|
A network element is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object unit on the data plane, such as a router or a computer. |
|
Control_Element |
|
A control element is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object unit on the control plane. |
|
Management_Element |
|
A management element is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object unit on the management plane. |
|
NE_Logical |
|
A logical network element is an abstraction of a non-physical managed telecom object such as a service or a software component. |
|
Component |
||
|
NE_Component |
|
An NE component is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object that is part of a network element, such as a network card attached to a router. |
|
Control_Component |
|
A control component is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object that is part of a network element, on the control plane. |
|
Management_Component |
|
A management component is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object that is part of a network element, on the management plane. |
|
NEComponent_Logical |
|
A logical NE component is an abstraction of a non-physical managed telecom object that is part of a logical network element, such as a software element or a logical processor. |
|
Cluster |
||
|
NE_Cluster |
|
An NE cluster is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object that is made up of two or more distinct subcomponents such as other network elements that can be (and often are) managed as standalone telecom objects. |
|
Control_Cluster |
|
A control cluster is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object that is made up of two or more distinct subcomponents, on the control plane. |
|
Management_Cluster |
|
A management cluster is an abstraction of a physical managed telecom object that is made up of two or more distinct subcomponents, on the management plane. |
|
NECluster_Logical |
|
A logical NE cluster is an abstraction of a non-physical managed telecom object made up of two or more subcomponents such as other services or software components that can be (and ofter are) managed as standalone telecom objects |
Shape representation
In this representation, the network element base is depicted by a geometric shape that symbolizes the network element type (or function class). The center of the base can contain an icon that further defines the representation of the network element function. Several predefined shapes are provided as types of the network element.
JViews TGO includes a limited number of network element shapes that can be used to build iconic network elements. The following table gives the available shapes and the corresponding network element type name.
|
Network Element Type |
Shape |
|
Shape_CellShape |
|
|
Shape_Circle |
|
|
Shape_CircleSmall |
|
|
Shape_Diamond |
|
|
Shape_Hexagon |
|
|
Shape_HexagonFlat |
|
|
Shape_HexagonSmall |
|
|
Shape_Octogon |
|
|
Shape_Oval |
|
|
Shape_OvalSmall |
|
|
Shape_Pentagon |
|
|
Shape_PentagonBottom |
|
|
Shape_PentagonLeft |
|
|
Shape_PentagonRight |
|
|
Shape_PentagonTop |
|
|
Shape_Rectangle |
|
|
Shape_RectangleSmall |
|
|
Shape_RoundSquare |
|
|
Shape_Square |
|
|
Shape_Transceiver |
|
|
Shape_TransceiverBottom |
|
|
Shape_TransceiverLeft |
|
|
Shape_TransceiverRight |
|
|
Shape_TransceiverTop |
|
|
Shape_Trapezoid |
|
|
Shape_TrapezoidBottom |
|
|
Shape_TrapezoidLeft |
|
|
Shape_TrapezoidRight |
|
|
Shape_TrapezoidTop |
|
|
Shape_Triangle |
|
|
Shape_TriangleBottom |
|
|
Shape_TriangleLeft |
|
|
Shape_TriangleRight |
|
|
Shape_TriangleTop |
|
The API that enables developers to include new network element shapes corresponding to new types of network element is detailed in Customizing network element types in the Stylingdocumentation.
How to retrieve a network type image through the API
You can retrieve the URL path of the image used by a network element type by calling IltSettings.GetValue (Object), where the Object argument is the access key to the icon renderer factory for the network element type. When the network element is rendered using an image, its default renderer factory is an IltNEImageBaseRendererFactory object. The getSourceImageName method on this object points to the image location inside the image repository service (the IltDefaultImageRepository object, accessible from IlpContext).
The following code retrieves the URL path in the distribution package for the image used by the IP_ComputerFlat network element type:
IltNEImageBaseRendererFactory rf = (IltNEImageBaseRendererFactory)IltSettings.GetValue("NetworkElement.Type.IP_ComputerFlat.Renderer");
Replace the IP_ComputerFlat type name with the name of any network element type to retrieve the image associated with that network element type.
Network element functions
JViews TGO includes a certain number of icons representing functions. The design of the icons included in the library stem from recommendations of Standards organizations specialized in this domain (ITU/ANSI).
ANSI T1.232-1996: Operations, Administration, Maintenance and Provisioning (OAM&P) - G Interface Specification for Use with Telecommunications Management Network (TMN).
The following table illustrates the icons that are available in the library.
|
Function Name |
Icon |
Equipment Function |
|
Edge equipment functions |
||
|
EdgeCellRegenerator |
|
Cell Regenerator |
|
EdgeCrossConnect |
|
X-Connect |
|
EdgeEndOffice |
|
End Office |
|
EdgeGateway |
|
Gateway |
|
EdgeHub |
|
Hub |
|
EdgeLineTerminatingEquipment |
|
Line Terminating Equipment |
|
EdgeMediationDevice |
|
Edge Mediation Device |
|
EdgeMux |
|
Multiplexer |
|
EdgeNonTechnologySpecificMediationDevice |
|
Mediation Device |
|
EdgeRadioCellSiteEquipment |
|
Radio Cell Site Equipment |
|
EdgeWirelessEdge |
|
Wireless Edge |
|
IP equipment functions |
||
|
IP |
|
IP |
|
IPAccess |
|
Access |
|
IPAlarmCollector |
|
Alarm Collector |
|
IPBridge |
|
Bridge |
|
IPHub |
|
Hub |
|
IPLANRegenerator |
|
LAN Regenerator |
|
IPLineTerminatingEquipment |
|
Line Terminating Equipment |
|
IPMediationDevice |
|
IP Mediation Device |
|
IPMUX |
|
Multiplexer |
|
IPRouter |
|
Router |
|
IPSignalingGateway |
|
Signaling Gateway |
|
IPSTP |
|
STP |
|
IPSwitch |
|
Switch |
|
IPSwitchRouter |
|
Switch Router |
|
IPTrafficGateway |
|
Traffic Gateway |
|
Multilayer equipment functions |
||
|
MultiLayer |
|
Multilayer |
|
MultiLayerAccess |
|
Multilayer Access |
|
Switch equipment functions |
||
|
Switch |
|
Switch |
|
SwitchingMediationDevice2 |
|
Switching Mediation Device |
|
SwitchingMediationDevice1 |
|
Switching Mediation Device |
|
SwitchCrossConnect |
|
X-Connect |
|
SwitchingATM |
|
ATM |
|
SwitchingDatabase |
|
Database |
|
SwitchingDMS |
|
DMS |
|
SwitchingEndOffice1 |
|
End Office |
|
SwitchingEndOffice2 |
|
End Office |
|
SwitchingHub1 |
|
Hub |
|
SwitchingHub2 |
|
Hub |
|
SwitchingLineTerminatingEquipment1 |
|
Line Terminating Equipment |
|
SwitchingLineTerminatingEquipment2 |
|
Line Terminating Equipment |
|
SwitchingMUX1 |
|
Multiplexer |
|
SwitchingMUX2 |
|
Multiplexer |
|
SwitchingSTP1 |
|
STP |
|
SwitchingSTP2 |
|
STP |
|
SwitchingTollGateway1 |
|
Toll Gateway |
|
SwitchingTollGateway2 |
|
Toll Gateway |
|
SwitchingTollTandem1 |
|
Toll Tandem |
|
SwitchingTollTandem2 |
|
Toll Tandem |
|
Transport equipment functions |
||
|
Transport |
|
Transport |
|
TransportAccess1 |
|
Access |
|
TransportAccess2 |
|
Access |
|
TransportAddDropMux1 |
|
Add/Drop Multiplexer |
|
TransportAddDropMux2 |
|
Add/Drop Multiplexer |
|
TransportAmplifier |
|
Amplifier |
|
TransportCirculator |
|
Circulator |
|
TransportCombiner |
|
Combiner |
|
TransportCrossConnect |
|
X-Connect |
|
TransportCrossConnect1 |
|
X-Connect |
|
TransportCrossConnect2 |
|
X-Connect |
|
TransportDigitalVideo |
|
Digital Video |
|
TransportDispersionComponentModule |
|
Dispersion Component Module |
|
TransportDWDMOptical |
|
DWDM Optical |
|
TransportFixedAttenuator |
|
Fixed Attenuator |
|
TransportHub1 |
|
Hub |
|
TransportHub2 |
|
Hub |
|
TransportInterleaveFilter |
|
Interleave Filter |
|
TransportLineTerminatingEquipment1 |
|
Line Terminating Equipment |
|
TransportLineTerminatingEquipment2 |
|
Line Terminating Equipment |
|
TransportMediationDevice1 |
|
Transport Mediation Device |
|
TransportMediationDevice2 |
|
Transport Mediation Device |
|
TransportOpticalSwitchingModule |
|
Optical Switching Module |
|
TransportRegenerator2 |
|
Regenerator |
|
TransportSONET_SDH |
|
SONET SDH |
|
TransportTrafficGateway1 |
|
Traffic Gateway |
|
TransportTrafficGateway2 |
|
Traffic Gateway |
|
TransportVariableAttenuator |
|
Variable Attenuator |
|
TransportWaveLengthTranslator |
|
Wave Length Translator |
|
Other equipment functions |
||
|
Access |
|
Access |
|
ADM |
|
ADM |
|
LTE |
|
Line Termination Equipment |
|
Other |
|
Other |
|
Regenerator |
|
Regenerator |
|
Unknown |
|
Unknown |
New functions can be added, as detailed in Customizing network element types in the Stylingdocumentation.
Network element families
For a given function, several families of network elements can exist. Usually the family represents the capacity of the network element. Values of the network element families are listed in the following table along with their corresponding numbers as shown on the symbolic network element.
|
Network Element Family |
Label on symbolic NE |
|
OC1 |
1 |
|
OC3 |
3 |
|
OC9 |
9 |
|
OC12 |
12 |
|
OC18 |
18 |
|
OC24 |
24 |
|
OC36 |
36 |
|
OC48 |
48 |
|
OC96 |
96 |
|
OC192 |
192 |
|
STM1 |
S1 |
|
STM3 |
S3 |
|
STM4 |
S4 |
|
STM6 |
S6 |
|
STM8 |
S8 |
|
STM12 |
S12 |
|
STM16 |
S16 |
|
STM32 |
S32 |
|
STM64 |
S64 |
Partial network elements
A partial network element is an abstraction which denotes a network element that is only part of the real-world network element. Partial network elements can be used in several situations, for example:
-
To represent distributed clusters where parts of a cluster need to be divided across different subnetworks.
-
To allow one network element to be used by different service providers. In this case, the network element needs to be divided in several parts. Each part is represented as a partial network element and its state reflects only the elements that are interesting for the service provider that is using it.
A network element can be defined as partial by setting the value of the attribute partial in the business object. This attribute can be set programmatically using PartialAttribute.
How to create a partial network element
The following example illustrates how a network element is created using the attribute partial via XML
<addObject id="NE1">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltNetworkElement</class>
<attribute name="name">NE1</attribute>
<attribute name="partial">true</attribute>
<attribute name="type">NE</attribute>
</addObject>
Partial network elements are graphically represented by an icon located at the bottom left of the network element base.

Partial network elements expanded and collapsed
Shortcut network elements
A shortcut network element is an abstraction denoting an object that is only a reference to an existing network element. IltNetworkElement provides a new attribute, ShortcutAttribute, whose value can be:
-
IltShortcutAttributeType. STANDARD: The network element is a regular shortcut.
-
IltShortcutAttributeType. DANGLING: The network element is a shortcut to an object that is no longer available.
-
null : The network element is not a shortcut
A network element can be defined as shortcut by setting the value of attribute shortcut in the business object. This attribute can be set programmatically using IltNetworkElement. ShortcutAttribute.
How to create a shortcut
The following example illustrates how a network element is created using the attribute shortcut via XML.
<addObject id="NE1">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltNetworkElement</class>
<attribute name="name">NE1</attribute>
<attribute name="shortcut">STANDARD</attribute>
<attribute name="type">NE</attribute>
</addObject>
Shortcut network elements are graphically represented by an icon located at the bottom left of the network element base.

Standard shortcuts

Dangling shortcuts
Network element sizes
Network elements can be represented at various scales. The amount of information attached to the network element is proportional to the size of the network element. Two sizes are provided by default:
-
The standard size, which displays the network element function, family, and label (in the case of a symbolic representation) and which also supports icons reflecting changes in states and alarms.

Standard size network element
-
The small size, which displays only the network element type and label.

Small size network elements
Using the network element sizes in custom programming is shown in Customizing network element types in the Stylingdocumentation.