Card items
Describes the following card items: LEDs and ports.
Provides details about the positioning of card items.
Describes the attributes of the IltCardItem class.
Describes the facilities available for LEDs.
Describes the facilities available for ports.
Overview of card items
Card items are placed inside a card item container ( IltCard). Their positioning is relative to the top left corner of the container. Regardless of the orientation of the container, the top left corner constitutes the origin for positioning the card items; the X coordinate of card items increases from left to right and the Y coordinate increases from top to bottom, with regard to this origin.
The positioning point of a card item is its center point and is relative to the origin of the card item container (top left corner).
When planning the size of shelves and slots, remember to take into account the child objects, particularly the card and its card items.
JViews TGO defines two types of card items: LEDs and ports.
Card item class
The abstract class IltCardItem defines all the common characteristics of a business object that can be associated with a card or any implementation of IltCard.
The IltCardItem class defines the following attributes:
-
Type — Specifies the category of a card item. There are different predefined types of card items in JViews TGO; all of them are described in this section.
Name: type
Value class: IltCardItem.Type
Attribute: IltCardItem.TypeAttribute
-
Direction —Specifies the direction of the card item.
Name: direction
Value class: IlpDirection
Attribute: IltCardItem.DirectionAttribute
LEDs
Describes the facilities available for LEDs.
Provides details about the use of LEDs.
Describes the attributes of the IltLed class.
Shows how to load an LED from an XML file in a data source.
Shows how to create an LED using the API and how to add it to the data source.
Lists the different types of LED and their graphic representation.
Overview of LEDs
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is an object used to represent a state through a color. Most types of equipment use LEDs as interfaces that give the user information on hardware and software conditions. JViews TGO provides an LED business object to help you create real world items of equipment.
Although a state object can be associated with LEDs, it does not affect their graphic representation. LEDs are not managed objects themselves; they help represent the state of managed objects such as ports or cards.
Depending on the nature of the application, LEDs can be represented by a bitmap image or by a vector graphic. Like a network element, the LED representation is set through the TypeAttribute attribute assigned to the object represented by the LED.
To find all necessary information on the styling properties of LEDs, refer to Customizing shelves and cards.
LED class
LEDs are predefined business objects of the class IltLed, which defines a card item by extending the IltCardItem abstract class.
The parent class IltCardItem defines the TypeAttribute, which is used to create several different graphic representations for different instances of the same IltLed class.
The IltLed class defines the following attributes:
-
Width —Specifies the width of the LED in its vector graphic representation
Name: width
Value class: java.lang.Float
Attribute: IltLed.WidthAttribute
-
Height —Specifies the height of the LED in its vector graphic representation
Name: height
Value class: java.lang.Float
Attribute: IltLed.HeightAttribute
Loading an LED defined in XML
For detailed information about data sources, see Data sources.
How to add an LED to a card defined in XML
The following example extends the example in Loading a shelf defined in XML and adds an LED to a card. For details about the XML elements used in this example, see Elements in an XML data file .
<cplData>
<addObject id="Shelf">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltShelf</class>
<attribute name="name">Shelf</attribute>
<attribute name="slotSizes" javaClass="ilog.cpl.equipment.IlpSlotSizes">
<width>
<value>30</value>
<value>20</value>
<value>40</value>
</width>
<height>
<value>90</value>
<value>20</value>
</height>
</attribute>
<attribute name="position" javaClass="ilog.cpl.graphic.IlpPoint">
<x>100</x> <y>50</y>
</attribute>
</addObject>
<addObject id="Card">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltCard</class>
<parent>Shelf</parent>
<attribute name="name"></attribute>
<attribute name="position"
javaClass="ilog.cpl.graphic.views.IlpShelfItemPosition">
<x>0</x> <y>0</y> <width>3</width> <height>1</height>
</attribute>
</addObject>
<addObject id="Led">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltLed</class>
<parent>Card</parent>
<attribute name="name">Led</attribute>
<attribute name="type">Circular</attribute>
<attribute name="position" javaClass="ilog.cpl.graphic.IlpRelativePoint">
<x>70</x> <y>65</y>
</attribute>
</addObject>
</cplData>
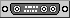
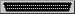
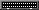
The result looks like this:
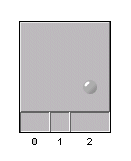
An array shelf with a card and an LED
When you create an LED with the API, you must provide its type, which can be set through the constructor or through the setAttributeValue method.
How to create an LED with the API
The following sample shows how to create an LED of type Circular.
List objects = new ArrayList();
// create shelf identified as myShelf
IltShelf s1 = new IltShelf("myShelf");
s1.setSlotSizes(2,50,1,100);
objects.add(s1);
// create card
IltCard c1 = new IltCard(new IltOSIObjectState(), "card 1");
c1.setPosition(new IlpShelfItemPosition(0, 0, 1, 1));
objects.add(c1);
// create card item
IltLed l1 = new IltLed("myLed");
l1.setType(IltLed.Type.Circular);
l1.setPosition(new IlpRelativePoint(25,85));
objects.add(l1);
// add all objects to data source
datasource.addObjects(objects);
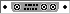
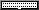
The result looks like this:

A shelf containing a card with an LED
There are several predefined LED types, using both bitmap and vector representations. You can extend the predefined types and define new representations using either images or drawers capable of creating vector images. For information on how to create new LED types, see Customizing LED types.
|
LED Type |
Graphic Representation |
|
|
Circular |
|
|
|
CircularShape |
|
|
|
CircularFlat |
|
|
|
Rectangular |
|
|
|
RectangularShape |
|
|
|
HardDisk A |
|
|
|
HardDisk B |
|
|
|
HardDiskPwr A |
|
|
|
HardDiskPwr B |
|
|
|
Power A |
|
|
|
Power B |
|
|
Among the LEDs listed in this table, IltLed.Type.Circular, IltLed.Type.CircularShape, IltLed.Type.CircularFlat, IltLed.Type.Rectangular, and IltLed.Type.RectangularShape are vector graphic representations; all the others are bitmap images.
Ports
Describes the facilities available for ports.
Provides details about the use of ports.
Describes the attributes of the IltPort class.
Shows how to load a port from an XML file in a data source.
Shows how to create a port using the API and how to add it to the data source.
Lists the different types of port and their graphic representation.
Most real world cards have a physical interface to connect them to other sets of equipment or to a network. The connections are usually achieved through connectors or ports. JViews TGO provides port objects to represent connections between a card ( IltCard) and the external world.
Ports allow you to represent alarms and states graphically in the same way as network elements do, with alarm balloons and colors depending on the alarm severity.
Depending on the nature of the application, ports can be represented by a bitmap image or by a vector graphic. Like a network element, the port representation is set through the TypeAttribute attribute assigned to the object represented by the port.
To find all necessary information on the styling properties of ports, refer to Customizing shelves and cards.
Port class
Ports are predefined business objects of the class IltPort, which defines a card item by extending the IltCardItem abstract class to fit inside card objects.
The parent class IltCardItem defines the TypeAttribute, which is used to create different graphic representations for different instances of the same IltLed class.
The IltPort class does not define any specific attribute:
Loading a port defined in XML
For detailed information about data sources, see Data sources.
How to add a port to a card defined in XML
The following example extends the example in Loading a shelf defined in XML and adds a port to a card. For details about the XML elements used in this example, see Elements in an XML data file .
<cplData>
<addObject id="Shelf">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltShelf</class>
<attribute name="name">Shelf</attribute>
<attribute name="slotSizes" javaClass="ilog.cpl.equipment.IlpSlotSizes">
<width>
<value>30</value>
<value>20</value>
<value>40</value>
</width>
<height>
<value>90</value>
<value>20</value>
</height>
</attribute>
<attribute name="position" javaClass="ilog.cpl.graphic.IlpPoint">
<x>100</x> <y>50</y>
</attribute>
</addObject>
<addObject id="Card">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltCard</class>
<parent>Shelf</parent>
<attribute name="name"></attribute>
<attribute name="position"
javaClass="ilog.cpl.graphic.views.IlpShelfItemPosition">
<x>0</x> <y>0</y> <width>3</width> <height>1</height>
</attribute>
</addObject>
<addObject id="Port">
<class>ilog.tgo.model.IltPort</class>
<parent>Card</parent>
<attribute name="name">Port</attribute>
<attribute name="type">DB15_f</attribute>
<attribute name="position" javaClass="ilog.cpl.graphic.IlpRelativePoint">
<x>30</x> <y>65</y>
</attribute>
</addObject>
</cplData>
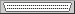
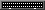
The result looks like this:
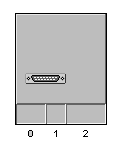
An array shelf with a card and a port
Creating a port with the API
When you create a port with the API, you must provide its type, which can be set through the constructor or through the setAttributeValue method.
How to create a port with the API
The following sample shows how to create a port of type Centronics_36f.
// Create a shelf, set its position and add to data source
IltShelf s1 = new IltShelf(2, 65, 3, 20, 0);
s1.setAttributeValue(IltShelf.PositionAttribute, new IlpPoint(20, 50));
dataSource.addObject(s1);
// create a card, set its position (relative to s1) and
// add to data source
IltCard c1 = new IltCard();
c1.setAttributeValue(IltCard.PositionAttribute,
new IlpShelfItemPosition(0, 1, 1, 1));
dataSource.addObject(c1);
// create shelf item, set its position (relative to c1) and
// add it to data source
IltPort port = new IltPort("port", IltPort.Type.Centronics_36f, null);
port.setAttributeValue(IltPort.PositionAttribute,
new IlpRelativePoint(33, 10));
dataSource.addObject(port);
// set relationship
dataSource.setParent(port.getIdentifier(), c1.getIdentifier());
dataSource.setParent(c1.getIdentifier(), s1.getIdentifier());
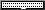
The result looks like this:

A shelf containing a card with a port
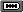
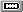
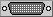
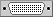
Predefined port types
There are several predefined port types using both vector and bitmap representations. You can also define new types using either images or drawers capable of creating vector images.
For information on how to create new port types, see Customizing port types.
All port types in the following table are image ports.
|
Port Type |
Graphic Representation |
|
BNC_f |
|
|
BNC_m |
|
|
CardEdge_34f |
|
|
Centronics_36f |
|
|
Centronics_36m |
|
|
Centronics_50f |
|
|
Centronics_50m |
|
|
Centronics_HP_36f |
|
|
Centronics_HP_36m |
|
|
Centronics_HP_50f |
|
|
Centronics_HP_50m |
|
|
Centronics_VHD_68f |
|
|
Centronics_VHD_68m |
|
|
Composed_13W3_f |
|
|
Composed_13W3_m |
|
|
DB_15f |
|
|
DB_15m |
|
|
DB_25f |
|
|
DB_25m |
|
|
DB_37f |
|
|
DB_37m |
|
|
DB_50f |
|
|
DB_50m |
|
|
DB_9f |
|
|
DB_9m |
|
|
DB_HD_15f |
|
|
DB_HD_15m |
|
|
DB_HP_50f |
|
|
DB_HP_50m |
|
|
DB_HP_68f |
|
|
DB_HP_68m |
|
|
DIN_4f |
|
|
DIN_4m |
|
|
DIN_5f |
|
|
DIN_5m |
|
|
DIN_6f |
|
|
DIN_6m |
|
|
DIN_8f |
|
|
DIN_8m |
|
|
ExternalPower_f |
|
|
ExternalPower_m |
|
|
FDD_Power_f |
|
|
FDD_Power_m |
|
|
HDD_Power_f |
|
|
HDD_Power_m |
|
|
HoodedPower_f |
|
|
HoodedPower_m |
|
|
IDC_34f |
|
|
IDC_34m |
|
|
IDC_40f |
|
|
IDC_40m |
|
|
IDC_50f |
|
|
IDC_50m |
|
|
IDC_68 |
|
|
IEEE_1394_4f |
|
|
IEEE_1394_4m |
|
|
IEEE_1394_6f |
|
|
IEEE_1394_6m |
|
|
LFH_60f |
|
|
LFH_60m |
|
|
RJ45_f |
|
|
RJ45_m |
|
|
SC_Fiber_f |
|
|
SC_Fiber_m |
|
|
SCA_80f |
|
|
SCA_80m |
|
|
ST_Fiber_f |
|
|
ST_Fiber_m |
|
|
TwoProngPower_f |
|
|
TwoProngPower_m |
|
|
USB_A_f |
|
|
USB_A_m |
|
|
USB_B_f |
|
|
USB_B_m |
|
|
V35_f |
|
|
V35_m |
|