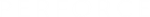The Palette toolbars
Describes the palettes of objects provided by JViews BPMN Modeler in the form of toolbars.
Describes the Activity toolbar of the JViews BPMN Modeler GUI.
Describes the Events toolbar of the JViews BPMN Modeler GUI.
Describes the Gateway toolbar of the JViews BPMN Modeler GUI.
Describes the Links toolbar of the JViews BPMN Modeler GUI.
Describes the Artifacts and Association toolbar of the JViews BPMN Modeler GUI.
Describes the Lanes toolbar of the JViews BPMN Modeler GUI.
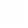
The Activity toolbar

The Activity toolbar
The Activity toolbar includes the various types of task offered in BPMN:
-
Task
-
Subprocess
-
Loop
-
Loop subprocess
-
Parallel
-
Parallel subprocess
-
Compensation
-
Compensation subprocess
-
Ad-hoc subprocess
To add a new activity, select the type of activity in the palette, and position the activity within the diagram.
Subprocesses
The main characteristics of subprocesses are as follows:
-
They are diagrams encapsulated in a subprocess element.
-
They can be inserted into subprocesses.
-
Diagram elements can be added into a subprocess by simply dropping them inside the subprocess.
-
The extent (the size) of a subprocess is determined by the position of its elements.
-
They can be expanded or collapsed by clicking on the

-
button.
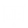
The Events toolbar
The Events toolbar gives access to several types of event that can occur within a BPMN process:
-
Message
-
Timer
-
Exception
-
Cancel
-
Compensation
-
Rule
-
Link
-
Multiple
-
Signal
-
Terminate
These events can start or terminate a process, or they can occur during the process. There are three distinct representations for each case.
Start events

The Start events toolbar
These events trigger the start of a process. They should be placed directly onto the diagram, and linked to the activities representing the tasks to be performed when the event occurs.
End events

The End events toolbar
These events terminate a process. They should be placed directly onto the diagram.
Intermediate events

The Intermediate events toolbar
Intermediate events can be either placed onto the diagram or directly onto an activity. For example:
-
When placed within the diagram, a message event specifies that the process is waiting for a message in order to resume its activity. There are usually flow links before and/or after this event.
A Message event
-
When placed onto an activity, the event represents something that can occur during the execution of an activity. There is usually a link (flow, message) going out of the event to specify the action to perform if such an event occurs. To create these types of event, click the event command you require on the toolbar. In the diagram, select the task onto which you want to place the event. When you do this, the event sticks to the activity.

Timer event during activity execution
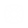
The Gateway toolbar
This toolbar lets you add gateways inside the diagram.

The Gateway toolbar
BPMN gateways are:
-
Data-XOR
-
Event-XOR
-
OR
-
Complex
-
AND
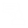
The Links toolbar

The Links toolbar
The Links toolbar gives access to several types of BPMN link:
-
Flow
-
Conditional Flow
-
Message
-
Compensation Association
To create a link, click one of the link creation commands. In the Diagram View, select the source element and then select the destination element.
There are restrictions on objects that can be linked together. For instance flow links cannot traverse subprocesses or pools.
The Artifacts and Association toolbar

The Artifacts and Association toolbar
These commands let you add Artifacts (Annotation, Data Object and Group objects) and Association elements to the diagram.
The Lanes toolbar

The Lanes toolbar
BPMN supports the notion of Pools for representing organizations, and Lanes for representing departments within an organization. JViews BPMN Modeler supports both concepts.
Lanes
To create Lanes in a diagram, click the Create Lane command, and place the lane onto the diagram. Then, drop your diagram objects into the lane. The property of the object (see Properties view), is then updated to indicate that it belongs to the lane.

Lanes
To remove an object from a Lane, select the object and remove its Lane property; see Properties view.
The size of the lane is determined by the position of the objects within the lane. In some cases, an object may appear to be inside a lane to which it does not belong. This can happen if a lane is enlarged when one of its elements is moved.
Pools
Pools are similar to lanes but they can include lanes within them.
To add a Lane into a Pool, just drop a Lane into the pool
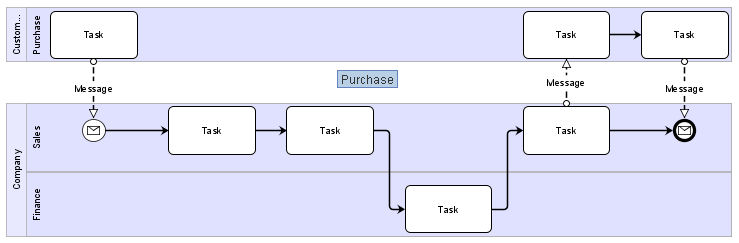
Pools