
The Functor package consists of a sizable family of template classes designed to accommodate global, static, and member function calls with varying numbers of arguments, as shown in Figure 50 and Figure . Like many other Threads.h++ packages, the Functor package uses the handle-body idiom. In the hierarchies, the handle classes are on the left and the matching sets of body classes are on the right.
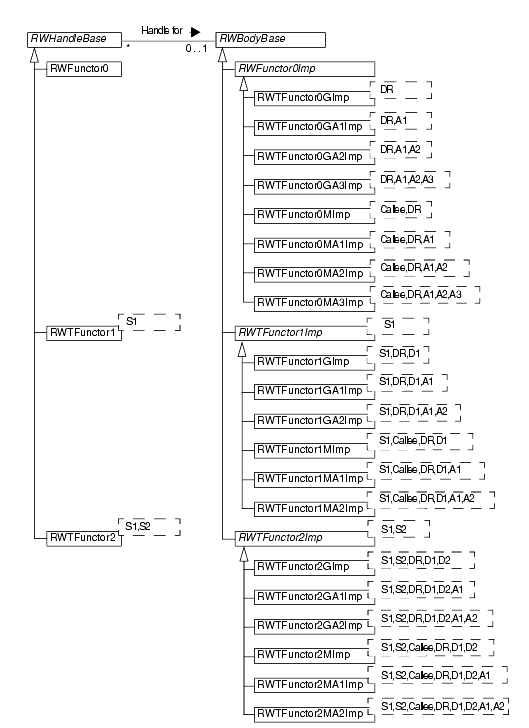
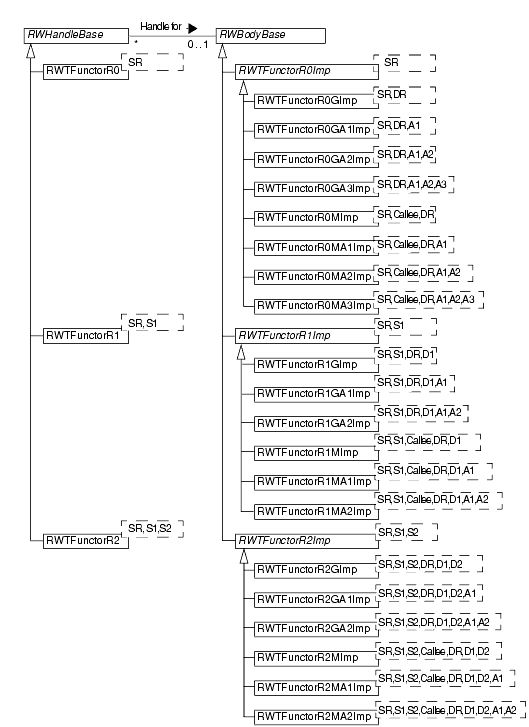
The base name for functor classes is RWTFunctor, for templatized classes, or RWFunctor, for the few non-templatized classes. Body class names end in Imp. Both handle and body class names are constructed by adding characters that encode information about the functor to the base name. These codes will make more sense as you go through the rest of the chapter.
An optional character R that indicates whether or not the functor returns a value.
A digit indicating the number of caller arguments the functor accepts: 1 or 2.
Body class names also include additional characters that encode and identify the function type and number of additional arguments accepted by the function. This sequence consists of the following elements:
A single letter indicating the function type:
G - The function is a global function or a static member function, which has no callee object.
M - The function is a non-static member function.
An optional two-letter code describing the number of callee arguments that the functor will store and automatically pass to the function (in addition to the caller arguments):
A1 - One callee argument.
A2 - Two callee arguments.
A3 - Three callee arguments. Only functors with no caller arguments can take three callee arguments.
The classes in the hierarchies include formal template parameters that represent argument types and return types. These parameters include:
DR - The declared return type of the encapsulated function.
D1 - The declared type of the encapsulated function's first argument.
D2 - The declared type of the encapsulated function's second argument.
SR - The return type of the functor.
S1 - The type of the functor's first argument.
S2 - The type of the functor's second argument.
Callee - The type of object on which the encapsulated function is invoked, if it is a member function.
A1 - The type of the first callee argument added to the function invocation by the functor.
A2 - The type of the second callee argument added to the function invocation by the functor.
A3 - The type of the third callee argument added to the function invocation by the functor, only available for functors with no caller arguments.
©Copyright 2000, Rogue Wave Software, Inc.
Contact Rogue Wave about documentation or support issues.