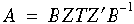

#include <rw/dschur.h> // DoubleSchurDecomp #include <rw/cschur.h> // DComplexSchurDecomp DoubleSchurDecomp schur(A); // A is an RWGenMat<double>
A Schur decomposition uses orthogonal transformations to reduce a matrix A to a matrix T that is upper quasitriangular. For a complex matrix, T is actually triangular. For a real matrix, T is triangular, except the diagonal can contain 2 x 2 blocks, allowing nonzero entries on the subdiagonal. The columns of the orthogonal transformation matrix, Z, are called Schur vectors.
The classes {TYPE}SchurDecomp encapsulate a Schur decomposition as well as an optional balance transformation. The decomposition of a matrix A is:
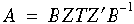
where Z is orthogonal, T is quasi-upper triangular, and B is a balance transformation (see {TYPE}BalanceTransform). The Schur decomposition yields eigenvalues immediately. Since the eigenvalues of A and T are the same, and since T is quasi-upper triangular, the eigenvalues are simply either the diagonal elements of T, or the complex conjugate pair corresponding to the eigenvalues of a 2 x 2 block on the diagonal. The invariant subspace corresponding to the first k eigenvalues of A is spanned by the first k Schur vectors; since the matrix of Schur vectors, Z, is orthogonal, this basis is orthonormal. Often, the Schur vectors are preferable to the eigenvectors themselves because of this orthogonality.
#include <iostream.h>
#include <rw/dhess.h>
main()
{
RWGenMat<double> A;
cin >> A;
DoubleSchurDecomp schur(A,FALSE,FALSE); // FALSE for
// no balancing
cout << "Input matrix: " << A << endl;
cout << "eigenvalues: " << schur.eigenvalues() << endl;
cout << "Schur vectors: " << schur.Z() << endl;
}
DoubleSchurDecomp(); DComplexSchurDecomp();
Default constructor. Builds a decomposition of size 0 x 0.
DoubleSchurDecomp(const RWGenMat<double>& A,
RWBoolean permute=TRUE, RWBoolean scale=TRUE);
DComplexSchurDecomp(const RWGenMat<DComplex>& A,
RWBoolean permute=TRUE, RWBoolean scale=TRUE);
Constructs the Schur decomposition of the matrix A. The boolean parameters determine whether or not the permutation or scaling parts of the balance transformation are applied prior to forming the Schur decomposition.
DoubleSchurDecomp(const DoubleBalanceDecomp& A); DComplexSchurDecomp(const DComplexBalanceDecomp& A);
Builds a Schur decomposition of the matrix represented by the balance decomposition.
DoubleSchurDecomp(const DoubleHessenbergDecomp& A); DComplexSchurDecomp(const DComplexHessenbergDecomp& A);
Builds a Schur decomposition of the matrix represented by the Hessenberg decomposition.
RWGenMat<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::B() const; RWGenMat<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::B() const;
Computes an explicit representation of the balance transformation.
RWMathVec<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::Bx(const RWMathVec<double>& x); RWMathVec<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::BInvTx(const RWMathVec<double>& x); RWGenMat<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::BX(const RWGenMat<double>& X); RWGenMat<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::BInvTX(const RWGenMat<double>& X); RWMathVec<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::Bx(const RWMathVec<DComplex>& x); RWMathVec<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::BInvTx(const RWMathVec<DComplex>& x); RWGenMat<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::BX(const RWGenMat<DComplex>& X); RWGenMat<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::BInvTX(const RWGenMat<DComplex>& X);
Computes the inner product of the balance transformation B, or its (conjugate) transpose inverse, and the vector x or the matrix X.
unsigned DoubleSchurDecomp::cols(); unsigned DComplexSchurDecomp::cols();
Returns the number of columns in the matrix that the decomposition represents.
DComplex DoubleSchurDecomp::eigenValue(int i) const; DComplex DComplexSchurDecomp::eigenValue(int i) const;
Returns the ith eigenvalue.
RWMathVec<DComplex> DoubleSchurDecomp::eigenValues() const; RWMathVec<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::eigenValues() const;
Returns a vector of all computed eigenvalues.
void DoubleSchurDecomp::factor(const RWGenMat<double>& A,
RWBoolean permute=TRUE, RWBoolean scale=TRUE); void DComplexSchurDecomp::factor(const RWGenMat<DComplex>& A,
RWBoolean permute=TRUE, RWBoolean scale=TRUE);
Replaces the current decomposition with the Schur decomposition of the matrix A. The boolean parameters determine whether or not the permutation or scaling parts of the balance transformation are applied prior to forming the Schur decomposition.
void DoubleSchurDecomp::factor(const DoubleHessenbergDecomp& A); void DComplexSchurDecomp::factor(const DComplexHessenbergDecomp& A);
Replaces the current decomposition with the Schur decomposition of the matrix represented by the Hessenberg decomposition.
void DoubleSchurDecomp::factor(const DoubleBalanceDecomp& A); void DComplexSchurDecomp::factor(const DComplexBalanceDecomp& A);
Replaces the current decomposition with the Schur decomposition of the matrix represented by the balance decomposition.
RWBoolean DoubleSchurDecomp::good(); RWBoolean DComplexSchurDecomp::good();
Returns TRUE if the decomposition was successfully computed, FALSE if not.
int DoubleSchurDecomp::move(int i, int j); int DComplexSchurDecomp::move(int i, int j);
Reorders the decomposition so that the ith eigenvalue is moved to the jth position. In the real case, if i corresponds to a 2 x 2 block (a complex eigenvalue) , the entire block is moved. The function returns where the eigenvalue was actually moved to; this may differ from j for two reasons: it may have been impossible to move the eigenvalue to position j due to the presense of 2 x 2 blocks, or the matrix may be extremely ill-conditioned.
RWBoolean DoubleSchurDecomp::moveToFront(const RWMathVec<int>&); RWBoolean DComplexSchurDecomp::moveToFront(const RWMathVec<int>&);
Reorders the decomposition so that the eigenvalues whose indices are passed in the vector are moved to the front. In the real case, if an index corresponds to a 2 x 2 block (a complex eigenvalue), the entire block is moved. The function returns TRUE if the reordering is successful.
unsigned DoubleSchurDecomp::rows(); unsigned DComplexSchurDecomp::rows();
Returns the number of rows in the matrix that the decomposition represents.
RWGenMat<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::Z() const; RWGenMat<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::Z() const;
Computes an explicit representation of the orthogonal matrix Z.
RWMathVec<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::Zx(const RWMathVec<double>& x); RWMathVec<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::ZTx(const RWMathVec<double>& x); RWGenMat<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::ZX(const RWGenMat<double>& X); RWGenMat<double> DoubleSchurDecomp::ZTX(const RWGenMat<double>& X); RWMathVec<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::Zx(const RWMathVec<DComplex>& x); RWMathVec<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::ZTx(const RWMathVec<DComplex>& x); RWGenMat<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::ZX(const RWGenMat<DComplex>& X); RWGenMat<DComplex> DComplexSchurDecomp::ZTX (const RWGenMat<DComplex>& X);
Computes the inner product of the orthogonal matrix Z, or its (conjugate) transpose, and the vector x or the matrix X.
©Copyright 1999, Rogue Wave Software, Inc.
Send mail to report errors or comment on the documentation.