P_DIV Procedure
Divides two polynomials and returns the quotient polynomial and the remainder polynomial.
Usage
P_DIV, b, a, q, r
Input Parameters
b—The array of real coefficients of the numerator polynomial.
a—The array of real coefficients of the denominator polynomial.
Output Parameters
q—The array of coefficients of the quotient polynomial.
r—The array of coefficients of the remainder polynomial.
Keywords
Epsilon—Specifies a value above which the procedure ignores all higher order coefficients of the polynomial. If Epsilon is not set, the default value is 0.0d.
Discussion
For two polynomials b(x) and a(x), such that:
b(x) = b0 + b1x + b2x2 + ... + bMxM and
a(x) = a0 + a1x + a2x2 + ... + aNxN
P_DIV computes q(z), called the quotient polynomial, and r(z), the remainder polynomial. P_DIV uses the following relationship:
b(x) = a(x)q(x) + r(x)
Example
In this example, P_DIV is used to compute the quotient of a polynomial with real coefficients b(x) = 2 + 7x + 6x2 + x3, divided by a(x) = 1 + x.
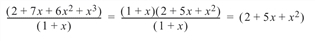
P_DIV, [2, 7, 6, 1], [1, 1], q, r
; The quotient polynomial is q(x) = 2 + 5x + x2.
PM, q
; No remainder.
PM, r
See Also
For Additional Information
Blahut, 1985.





