BILINTRANS Function
Computes the bilinear transform of an analog transfer function.
Usage
result = BILINTRANS(h [, k])
Input Parameters
h—A valid analog filter structure defined as the ratio of two polynomials in positive powers of s.
k—(optional) A multiplier constant. (Default: k = 1)
Returned Value
result—A digital filter structure containing the transfer function made of a ratio of polynomials in negative powers of z.
Keywords
Newname—A scalar string specifying a name for the new filter structure. If not used, the new filter structure has the same name as the old one.
Discussion
For a given analog transfer function of the form:
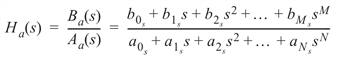
where Ba and Aa are polynomials in positive powers of s, BILINTRANS performs a bilinear transformation:
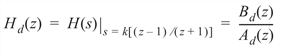
to obtain a digital rational transfer function Hd(z) in negative powers of z.
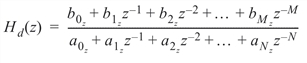
Example
In this example we call BILINTRANS with a simple lowpass filter and plot the frequency response of both the analog and digital form of the filter.
b = [0.1]
a = [–0.1, 1.0]
; Define a simple analog lowpass filter H(s) = 0.1/(s – 0.1).
h= FILTSTR(b, a)
omega = FINDGEN(100)/50.0
; Plot the frequency response of the analog transfer function.
; See Frequency Response of Analog and Digital Filter (a).PLOT, omega, ABS(FREQRESP_S(h, COMPLEX(FLTARR(100), omega))), $
Title = 'Analog'
; Transform the analog transfer function to digital.
hd = BILINTRANS(h)
hdresp = FREQRESP_Z(hd, Outfreq = f)
; Plot result.
PLOT, f, ABS(hdresp), Title = 'Digital'
; See Frequency Response of Analog and Digital Filter (b).
See Also
For Additional Information
Oppenheim and Schafer, 1989.
Parks and Burrus, 1987.
Proakis and Manolakis, 1988.
Roberts and Mullis, 1987.





