BESELI Function
Calculates the Bessel I function for the input parameter.
Usage
result = BESELI(x [, n])
Input Parameters
x—The expression that is evaluated.
n—(optional) An integer ≥ 0. (Default: 0)
Returned Value
result—The Bessel I function for x, having the same dimensions as x.
Keywords
None.
Discussion
The Bessel I function is one of a mathematical series that arise in solving differential equations for systems with cylindrical symmetry. The Bessel series can be useful in communications and signal processing, since they give the relative amplitude of the spectral components of a frequency-modulated carrier wave.
The Bessel I function is similar to the Bessel J function, except that it is evaluated for imaginary parameters.
BESELI is a numerical approximation to the solution of the differential equation for an imaginary x:
x2 * y'' + x * y' – (x2 + n2) * y = 0 n ≥ 0
The BESELI function is a solution of the first kind of (modified) Bessel functions of order n. The general solution of the above differential equation using the BESELI function can be shown in the following ways for arbitrary constants A and B:
; Solution for n ≠ 0, 1, 2, . . . y = A * BESELI(x, n) + B * BESELI(x, –n) ; Solution for all n. y = A * BESELI(x, n) + B * BESELK(x, n)
or:
; Solution for all n.
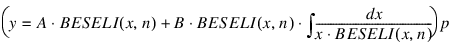
Note that BESELK may be generated from the BESELI function.
See Also
For a synopsis of all the Bessel functions, see Mathematical Handbook of Formulas and Tables, by Murray R. Spiegel, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1968.
For sample usage of the Bessel functions in physics, see Boundary Value Problems, Second Edition, edited by David L. Powers, Academic Press, New York, 1979, pp. 213-216.





