BINORMALCDF Function
Evaluates the bivariate normal distribution function.
Usage
result = BINORMALCDF(x, y, rho)
Input Parameters
x—The x-coordinate of the point for which the bivariate normal distribution function is to be evaluated.
y—The y-coordinate of the point for which the bivariate normal distribution function is to be evaluated.
rho—Correlation coefficient.
Returned Value
result—The probability that a bivariate normal random variable with correlation rho takes a value less than or equal to x and less than or equal to y.
Input Keywords
Double—If present and nonzero, double precision is used.
Discussion
Function BINORMALCDF evaluates the distribution function F of a bivariate normal distribution with means of zero, variances of 1, and correlation of rho; that is, r = rho and |r| < 1.
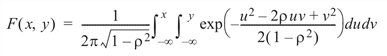
To determine the probability that U £ u0 and V £ v0, where (U, V) is a bivariate normal random variable with mean m = (mU, mV) and the following variance-covariance matrix:

transform (U, V)T to a vector with zero means and unit variances. The input to BINORMALCDF would be as follows:
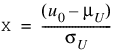 ,
,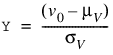 , and
, and 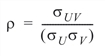
The BINORMALCDF function uses the method of Owen (1962, 1965). For |r| = 1, the distribution function is computed based on the univariate statistic Z = min(x, y) and on the normal distribution NORMALCDF.
Example
Suppose (x, y) is a bivariate normal random variable with mean (0, 0) and the following variance-covariance matrix:

This example finds the probability that x is less than –2.0 and y is less than 0.0.
; Define x, y, and rho.
x = -2
y = 0
rho = .9
; Call BINORMALCDF and output the results.
p = BINORMALCDF(x, y, rho)
PM, 'P((x < -2.0) and (y < 0.0)) = ', p, Format = '(a29, f8.4)'
; PV-WAVE prints: P((x < -2.0) and (y < 0.0)) = 0.0228





