HYPERGEOCDF Function
Evaluates the hypergeometric distribution function.
Usage
result = HYPERGEOCDF(k, n, m, l)
Input Parameters
k—Parameter for which the hypergeometric distribution function is to be evaluated.
n—Sample size. Argument n must be greater than or equal to k.
m—Number of defectives in the lot.
l—Lot size. Parameter l must be greater than or equal to n and m.
Returned Value
result—The probability that k or fewer defectives occur in a sample of size n drawn from a lot of size l that contains m defectives.
Input Keywords
Double—If present and nonzero, double precision is used.
Discussion
Function HYPERGEOCDF evaluates the distribution function of a hypergeometric random variable with parameters n, l, and m. The hypergeometric random variable X can be thought of as the number of items of a given type in a random sample of size n that is drawn without replacement from a population of size l containing m items of this type.
The probability function is:
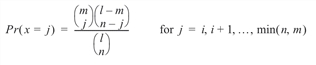
where:
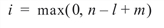
If k is greater than or equal to i and less than or equal to min(n, m), BINOMIALCDF sums the terms in this expression for j going from i up to k; otherwise, 0 or 1 is returned, as appropriate. To avoid rounding in the accumulation, BINOMIALCDF performs the summation differently, depending on whether or not k is greater than the mode of the distribution, which is the greatest integer in (m + 1) (n + 1) / (l + 2).
Example
Suppose X is a hypergeometric random variable with n = 100, l = 1000, and
m = 70. In this example, the distribution function is evaluated at 7.
p = HYPERGEOCDF(7, 100, 70, 1000)
PM, 'Pr(x <= 7) = ', p, Format = '(a13,f7.4)'
; PV-WAVE prints: Pr(x <= 7) = 0.5995
Informational Errors
STAT_LESS_THAN_ZERO—Input parameter, k, is less than zero.
STAT_K_GREATER_THAN_N—Input parameter, k, is greater than the sample size.
Fatal Errors
STAT_LOT_SIZE_TOO_SMALL—Lot size must be greater than or equal to n and m.





