ERFE Function
Evaluates a scaled function related to ERFC(z).
Usage
result = ERFE(z)
Input Parameters
z—A scalar or 1D array of floating point or complex values (single or double precision) for which the function value is desired.
Return Value
result—Scalar or 1D array. Containing the complex scaled function value related to ERFC(z).
Input Keywords
Double—If present and nonzero, double precision is used.
Description
Function ERFE is defined to be:
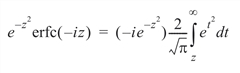
Let b be the largest representable floating-point number. To get this value, refer to the MACHINE Function in Utilities of the PV‑WAVE IMSL Mathematics Reference. The argument z must satisfy:
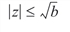
or else the value returned is zero. If the argument z does not satisfy:
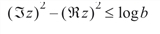
then b is returned. All other arguments are legal (Gautschi 1969, 1970).
Example
z = COMPLEX(2.5, 2.5)
value = ERFE(z)
PRINT, FLOAT(z(0)), IMAGINARY(z(0)), FLOAT(value(0)), $
IMAGINARY(value(0)), Format= "('erfe(', F5.3, ' + ', " + $"F5.3,'i) = ', F5.3, ' + ', F5.3, 'i')"
Output
erfe(2.500 + 2.500i) = 0.117 + 0.108i





