CONSTANT Function
Returns the value of various mathematical and physical constants.
Usage
result = CONSTANT(name[, units])
Input Parameters
name—Scalar string specifying the name of the desired constant. The case of the characters is not relevant when specifying name, i.e., character strings “PI”, “Pi”, “pI”, and “pi” are equivalent. Spaces and underscores are allowed and ignored.
units—Scalar string specifying the units of the desired constant. If empty, then Systeme International d’Unites (SI) units are assumed. The case of the characters is not relevant when specifying units, i.e., character strings “METER”, “Meter”, and “meter” are equivalent. Parameter units has the form “U1*U2*...*Um/V1/.../Vn,” where Ui and Vi are the names of basic units or the names of basic units raised to a power. Basic units must be separated by * or /. Powers are indicated by ^, as in “m^2” for m2. Examples are “METER*KILOGRAM/SECOND”, “M*KG/S”, “METER”, or “M/KG^2”.
Returned Value
result—By default, returns the desired constant. If no value can be computed, NaN (Not a Number) is returned.
Input Keywords
Double—If present and nonzero, double precision is used.
Discussion
The names allowed are listed in Constant Names. Values marked with (mp) are exact (to machine precision). The references in the right-hand column are indicated by code numbers: (1) for Cohen and Taylor (1986), (2) for Liepman (1964), and (3) for precomputed mathematical constants. The supported units are listed in Supported Units.
|
Name |
Description |
Value |
Ref. |
|
amu |
1.6605655 × 10–27 kg |
1 |
|
|
ATM |
1.01325 × 105 N/m2 (mp) |
2 |
|
|
AU |
1.496 × 1011 m |
|
|
|
Avogadro |
6.022045 × 1023 1/mole |
1 |
|
|
Boltzman |
1.380662 × 10–23 J / K |
1 |
|
|
C |
2.997924580 × 108 m/s |
1 |
|
|
Catalan |
0.915965... (mp) |
3 |
|
|
E |
2.718... (mp) |
3 |
|
|
ElectronCharge |
1.6021892 × 10–19 C |
1 |
|
|
ElectronMass |
9.109534 × 10–31 kg |
1 |
|
|
ElectronVolt |
1.6021892 × 10–19 J |
1 |
|
|
Euler |
0.577... (mp) |
3 |
|
|
Faraday |
9.648456 × 104 C/mole |
1 |
|
|
FineStructure |
7.2973506 × 10–3 |
1 |
|
|
Gamma |
Euler’s constant, g |
3 |
|
|
Gas |
8.31441 J/mole/K |
1 |
|
|
Gravity |
6.6720 × 10–11 N m2 / kg2 |
1 |
|
|
Hbar |
1.0545887 × 10–34 J s |
1 |
|
|
PerfectGasVolume |
2.241383 × 10–2 m3/mole |
1 |
|
|
Pi |
3 |
||
|
Planck |
Planck’s constant, h |
6.626176 × 10–34 J s |
1 |
|
ProtonMass |
1.6726485 × 10–27 kg |
1 |
|
|
Rydberg |
1.097373177 × 107 /m |
1 |
|
|
Speedlight |
speed of light, c |
2.997924580 × 108 m/s |
1 |
|
StandardGravity |
9.80665 m/s2 (mp) |
2 |
|
|
StandardPressure |
standard atm. pressure |
1.01325 × 105 N/m2 (mp) |
2 |
|
StefanBoltzman |
5.67032 × 10–8 W/K4 /m2 |
1 |
|
|
WaterTriple |
2.7316 × 102 K |
2 |
The units allowed are as follows:
|
Unit |
Description |
|
day, hour = hr, min = minute, s = sec = second, year |
|
|
Angstrom, AU, feet = foot, in = inch, |
|
|
l = liter = litre |
|
|
other units |
The metric prefixes listed in Supported Prefixes can be used with the previous units. The one- or two-letter prefixes can only be used with one-letter unit abbreviations.
|
Prefix |
Definition |
Value |
|
a |
10–18 |
|
|
f |
10–15 |
|
|
p |
10–12 |
|
|
n |
10–9 |
|
|
u |
10–6 |
|
|
m |
10–3 |
|
|
c |
10–2 |
|
|
d |
10–1 |
|
|
dk |
102 |
|
|
k |
103 |
|
|
|
104 |
|
|
|
106 |
|
|
g |
109 |
|
|
t |
1012 |
There is no one-letter unit abbreviation for myria or mega since m means milli.
Example 1
In this example, Euler’s constant g is obtained and printed. Euler’s constant is defined to be as follows:
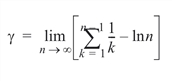
PM, CONSTANT('gamma'); PV-WAVE prints: 0.577216
Example 2
In this example, the speed of light is obtained using several different units.
c1 = CONSTANT('SpeedLight', 'meter/second')c2 = CONSTANT('SpeedLight', 'mile/second')c3 = CONSTANT('SpeedLight', 'cm/ns')PM, 'speed of light = ', c1, c2, c3, $
Title =' meters/second ' + $
'miles/second cm/ns'
Warning Errors
MATH_MASS_TO_FORCE—Conversion of units-of-mass to units-of-force required for consistency.





