TIE_STATS Function
Computes tie statistics for a sample of observations.
Usage
result = TIE_STATS(x)
Input Parameters
x—One-dimensional array containing the observations. x must be ordered monotonically increasing with all missing values removed.
Returned Value
result—One-dimensional array of length 4 containing the tie statistics.
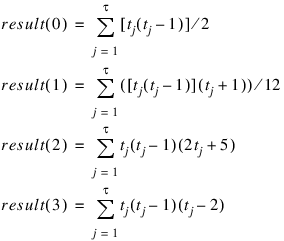
where tj is the number of ties in the jth group (rank) of ties, and τ is the number of tie groups in the sample.
Input Keywords
Double—If present and nonzero, double precision is used.
Fuzz—Nonnegative constant used to determine ties. Observations i and j are tied if the successive differences x(k + 1) – x(k) between observations i and j, inclusive, are all less than Fuzz. Default: Fuzz = 0.0
Discussion
Function TIE_STATS computes tie statistics for a monotonically increasing sample of observations. “Tie statistics” are statistics that may be used to correct a continuous distribution theory nonparametric test for tied observations in the data. Observations i and j are tied if the successive differences x(k + 1) – x(k), inclusive, are all less than Fuzz. Note that if each of the monotonically increasing observations is equal to its predecessor plus a constant, if that constant is less than Fuzz, then all observations are contained in one tie group. For example, if Fuzz = 0.11, then the following observations are all in one tie group.
0.0, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, 0.40, 0.50, 0.60, 0.70, 0.80, 0.90, 1.00
Example
We want to compute tie statistics for a sample of length 7.
fuzz = 0.001
x = [1.0, 1.0001, 1.0002, 2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 4.0]
tstat = TIE_STATS(x, Fuzz = fuzz)
PRINT, tstat
; PV-WAVE prints: 4.00000 2.50000 84.0000 6.00000