NORM Function
Computes various norms of a vector or the difference of two vectors.
Usage
result = NORM(x[, y])
Input Parameters
x—Vector for which the norm is to be computed.
y—If present, NORM computes the norm of (x – y).
Returned Value
result—The requested norm of the input vector. If the norm cannot be computed, NaN is returned.
Input Keywords
One—If present and nonzero, computes the 1-norm

Inf—If present and nonzero, computes the infinity norm max|xi|.
Output Keywords
Index_Max—Named variable into which the index of the element of x with the maximum modulus is stored. If Index_Max is used, then the keyword Inf also must be used. If the parameter y is specified, then the index of (x – y) with the maximum modulus is stored.
Discussion
By default, NORM computes the Euclidean norm as follows:
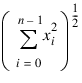
If the keyword One is set, then the 1-norm:
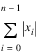
is returned. If the keyword Inf is set, the infinity norm max|xi| is returned. In the case of the infinity norm, the index of the element with maximum modulus also is returned. If the parameter y is specified, the computations of the norms described above are performed on (x – y).
Example 1
In this example, the Euclidean norm of an input vector is computed.
x = [ 1.0, 3.0, -2.0, 4.0 ]
n = NORM(x)
PM, n, Title = 'Euclidean norm of x:'
Example 2
This example computes max | xi – yi | and prints the norm and index.
x = [1.0, 3.0, -2.0, 4.0]
y = [4.0, 2.0, -1.0, -5.0]
n = NORM(x, y, /Inf, Index_Max = imax)
PM, n, Title = 'Infinity norm of (x-y):'
PM, imax, Title = 'Element of (x-y) with maximum modulus:'