Secure Sockets (SSL)
The Secure Sockets (SSL) network stack supports the Secure Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security protocols.
See Open SSL License.
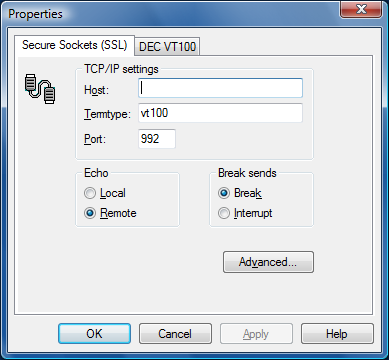
Set the options as follows:
-
Fill in your Host Telnet address. This can be an IP address or a name if defined in the hosts database. This is usually found in your Windows directory.
-
Termtype is a Telnet variable. This should normally not be changed.
-
Define your Port number, for Secure Sockets, this is usually 992.
-
Use Echo to specify whether data keyed in is echoed locally, (Local) or by the host (Remote). The default is Remote.
-
Break sends defines the effect of sending a break to the host. Select Break for a break or Interrupt for a program interrupt.
Secure Sockets (SSL) Advanced Settings
To configure the advanced settings for a Secure Sockets (SSL) connection, select Advanced in the Secure Sockets (SSL) Properties dialog box.
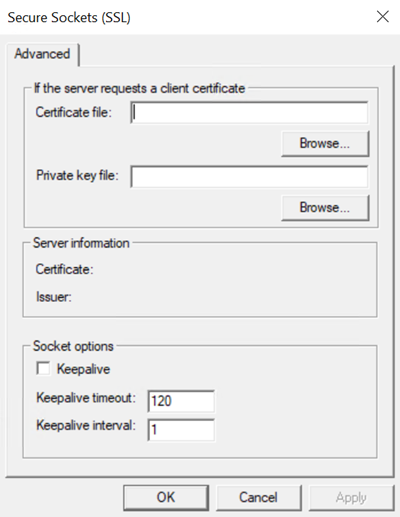
Set the options as follows:
-
Browse for a client certificate file. This certificate will be sent to the Secure Sockets (SSL) host if the host requires client certificates.
-
Browse for a client private key file. This must correspond to the client certificate file and will be used to decrypt data encrypted using the client certificate.
-
Select the Keepalive check box to enable the keepalive packets transmission.
-
In the Keepalive timeout field, enter the packet timeout in seconds.
-
In the Keepalive interval field, enter the packet interval in seconds.