Perforce TeamHub license
The type of licenses and number of seats depend on your installation. See License plan types and number of seats required. Contact Perforce Sales for license information.
Unless you are using P4 authentication, every Perforce TeamHub instance requires a license.
Viewing license information
-
In a browser, go to the
/adminURL for the TeamHub installation and log in with an administrator account.The TeamHub admin UI opens.
-
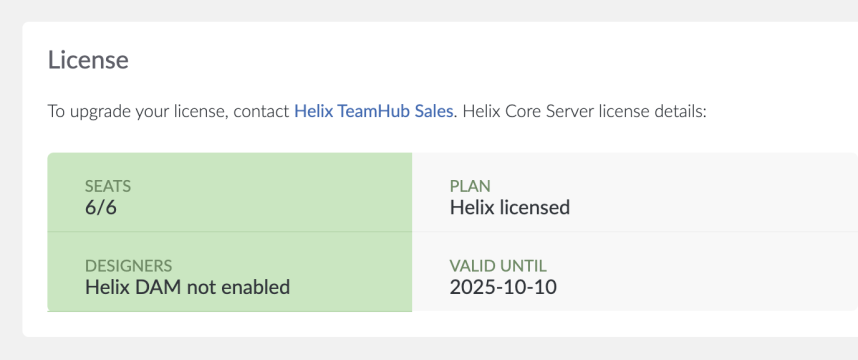
Click Dashboard.
The license information is displayed.
Adding or updating the license
On-premises installations that do not use P4 authentication
-
In a browser, go to the
/adminURL for the TeamHub installation and log in with an administrator account.The TeamHub admin UI opens.
- Click Dashboard.
- Click Update license, paste the license contents, and click Apply.
Installations that use P4 authentication
For instructions on how to add or update your P4 Server license, see Adding or updating the license file in the P4 Server Administration Documentation.
After updating the license on P4 Server, for Perforce TeamHub, you must restart the unicorn_backend service on the Standard node and all web nodes using the following hth-ctl command:
sudo hth-ctl restart unicorn_backend
License plan types and number of seats required
Use the following information to help decide what licenses you need and how many seats you need on each license. To buy or renew licenses, contact Sales.
If you use P4 authentication, you make license updates on P4 Server. See Adding or updating the license file in the P4 Server Administration Documentation. After you update the license, for Perforce TeamHub, you must restart the unicorn_backend service on the Standard node and all web nodes using the following hth-ctl command:
sudo hth-ctl restart unicorn_backend
| Product | Authentication type | Repository type supported | License plan required | Number of licensed seats required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Perforce TeamHub Cloud |
Standard authentication |
Git, SVN, Mercurial, Maven, Ivy, Docker, and WebDav |
Perforce TeamHub Cloud |
Various seat and storage options are available. See Pricing for Perforce TeamHub on the Perforce website. You cannot use P4 authentication for Git repositories with TeamHub Cloud plans. Perforce TeamHub Cloud plans only support native Git repositories. Git LFS (Large File Storage) is only supported by P4 Git with TeamHub on-premise plans. |
|
Perforce TeamHub on-premise |
Standard authentication |
Git, SVN, Mercurial, Maven, Ivy, Docker, and WebDav |
Perforce TeamHub |
You must purchase enough seats on the TeamHub Cloud license plan to cover all of your active TeamHub accounts. A seat is any individual account that logs in to TeamHub (user and collaborator accounts). For instructions on how to add or update your TeamHub on-premise license plan, see Adding or updating the license. |
|
P4 authentication |
P4 Git |
P4 Server |
You must purchase enough seats on the P4 Server license plan to cover all of your active TeamHub accounts. Total number of seats on the P4 Server license =
The Git Connector (gconn) user does not count against your P4 Server license plan seats but it does require a background license. Request a background license for the Gconn user using the Background user request form on the Perforce website. |
Reducing storage
If required, you can reduce your active storage by deleting repositories. See Maintenance settings.
When you delete content from your repositories:
- P4 streams and stream depots are versioned by the P4 Server. Underlying files, revision history, and other data are not deleted. Only protection entries and groups created by TeamHub are removed from the server.
- P4 Git repositories are versioned and track change history, repository data is not deleted from the P4 Server.
- Git, Mercurial, and Subversion repositories are versioned and track change history. Files committed to the remote repository stay in the history even if you remove them. Those files continue to consume storage.
- Ivy, Maven, and WebDAV repositories are unversioned and do not track history. Removing files frees up storage.
- Docker repositories are unversioned and do not track history. Removing tags frees up storage.