About SOAP
SOAP is an Extensible Markup Language (XML)-based protocol used to exchange information over a network infrastructure. SOAP uses application layer protocols, such as Remote Procedure Call (RPC) or the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), for message negotiation and transmission. SOAP can be used with a variety of different programming languages, such as C# (Visual Studio .NET), Perl, and Java.
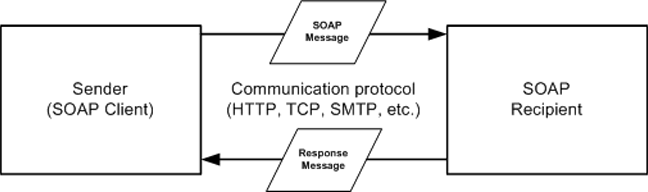
When a client sends a SOAP message, it travels over a communications protocol to the recipient. When the message is received, the recipient system processes it. If the message requires a response, the recipient sends the response to the sender.
A SOAP message has the following parts:
- Envelope—Identifies the message to the recipient.
- Header (optional)—Contains additional information about the message, such as security credentials.
- Body—Contains information for the message recipient.
- Fault—Contains error handling and status information for the message. Commonly used if a message response is required.
Message example
The following example is a SOAP message that returns the name of a new customer from the WysiCorp web site.
POST /NewCustomers HTTP/1.1
Host: www.wysicorp.com
Content-Type: application/soap+xml; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 299
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope">
<soap:Header>
<!-- security credentials -->
<s:credentials xmlns:s="http://www.wysicorp.com/security">
<username>SOAPUser</username>
<password>SoAp123</password>
</s:credentials>
</soap:Header>
</soap:Body>
<m:GetNewCustomer xmlns:m="http://www.wysicorp/newcustomer">
<m:CustomerName>BigCorporation</m:CustomerName>
</m:GetNewCustomer>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>